Abstract
Background
Extramammary Paget’s disease (EMPD) is a rare intraepithelial malignancy with poorly described outcomes. EMPD in men is primarily found in the perianal and penoscrotal areas. We assessed incidence and time trends of EMPD in men as well as extent and predictors of survival using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program.
Methods
The data from 18 SEER registries were queried for men diagnosed with EMPD from 1973 to 2009. Cases were categorized by primary skin location: perianal, penoscrotal, and other truncal. Additional data included age, race, presence of another cancer, tumor stage, and treatment (surgery, radiation, combination). Kaplan–Meier, univariate, and multivariate Cox regression analyses were conducted.
Results
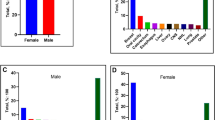
Incidence rates of EMPD in men have been increasing with an annual percent change of +3.2 % (p < .0002) since 1978. Incidence of EMPD in blacks was nearly four times lower (p = .0003) and in Asians/Pacific islanders four times higher (p < .0001), relative to whites. Overall survival among 495 patients was 60.2 % at 120 months postdiagnosis. On multivariate analysis, significant factors negatively impacting survival were primary site in the perianal region compared to penoscrotal and truncal lesions (both p < .001), age older than 75 years (p < .001), and presence of distant versus localized disease (p = .018). Survival did not differ by race or presence of additional cancer.
Conclusions
Survival in men with EMPD is lower among those with distant disease and primary tumors located in the perianal region. The reasons for increasing EMPD incidence over time and for the racial disparities in disease occurrence require further study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paget J. On disease of the mammary areola preceding cancer of the mammary gland. St. Bartholomew Hosp Rev. 1874;10:87–9.
Crocker H. Paget’s disease affecting the scrotum and penis. Trans Pathol Soc Lond. 1889;40:187–91.
Darier J, Couillaud P. Sur un cas de maladie de Paget de la region perinea-annale et scrotale. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr. 1893;4:25–31.
Wright JL, Morgan TM, Lin DW. Primary scrotal cancer: disease characteristics and increasing incidence. Urology. 2008;72:1139–43.
Wagner G, Sachse MM. Extramammary Paget disease—clinical appearance, pathogenesis, management. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:448–54.
Lam C, Funaro D. Extramammary Paget’s disease: summary of current knowledge. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:807–26.
Park S, Grossfeld GD, McAninch JW, Santucci R. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the penis and scrotum: excision, reconstruction and evaluation of occult malignancy. J Urol. 2001;166:2112–6; discussion 2117.
Yang WJ, Kim DS, Im YJ, Cho KS, Rha KH, Cho NH, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease of penis and scrotum. Urology. 2005;65:972–5.
Institute NC. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2012; http://seer.cancer.gov.
Johnson TV, Hsiao W, Delman KA, Jani AB, Brawley OW, Master VA. Extensive inguinal lymphadenectomy improves overall 5-year survival in penile cancer patients: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. Cancer. 2010;116:2960–6.
Tiwari RC, Clegg LX, Zou Z. Efficient interval estimation for age-adjusted cancer rates. Stat Methods Med Res. 2006;15:547–69.
Wang Z, Lu M, Dong GQ, Jiang YQ, Lin MS, Cai ZK, et al. Penile and scrotal Paget’s disease: 130 Chinese patients with long-term follow-up. BJU Int. 2008;102:485–8.
Lai YL, Yang WG, Tsay PK, Swei H, Chuang SS, Wen CJ. Penoscrotal extramammary Paget’s disease: a review of 33 cases in a 20-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112:1017–23.
Hegarty PK, Suh J, Fisher MB, Taylor J, Nguyen TH, Ivan D, et al. Penoscrotal extramammary Paget’s disease: the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center contemporary experience. J Urol. 2011;186:97–102.
Lian P, Gu WL, Zhang Z, Cai GX, Wang MH, Xu Y, et al. Retrospective analysis of perianal Paget’s disease with underlying anorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:2943–8.
Mengjun B, Zheng-Qiang W, Tasleem MM. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the perianal region: a review of the literature emphasizing management. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:69–75.
Chanda JJ. Extramammary Paget’s disease: prognosis and relationship to internal malignancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13:1009–14.
Disclosure
No financial disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrel, L.A., Weiss, A.D., Goodman, M. et al. Extramammary Paget’s Disease in Males: Survival Outcomes in 495 Patients. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 1625–1630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4139-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4139-y