
月刊
ISSN 1000-7229
CN 11-2583/TM
- CSCD核心库收录期刊
- 中文核心期刊
- 中国科技核心期刊


月刊
ISSN 1000-7229
CN 11-2583/TM

电力建设 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 39-57.doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2024.03.004
• 综合能源系统能量品质理论与低碳高效应用·栏目主持 王丹副教授、陈奇成教授、胡枭副教授、喻洁副教授· • 上一篇 下一篇
高建伟1,2, 黄宁泊1,2( ), 高芳杰1,2, 吴浩宇1,2, 孟琪琛1,2, 刘江涛1,2
), 高芳杰1,2, 吴浩宇1,2, 孟琪琛1,2, 刘江涛1,2
收稿日期:2023-08-08
出版日期:2024-03-01
发布日期:2024-02-28
通讯作者:
黄宁泊(1995),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为综合能源系统、风险管理与决策理论等,E-mail:ncepu_hnb@163.com。作者简介:高建伟(1972),男,教授,博士生导师,主要研究方向为综合能源系统、风险管理与决策理论等;基金资助:
GAO Jianwei1,2, HUANG Ningbo1,2( ), GAO Fangjie1,2, WU Haoyu1,2, MENG Qichen1,2, LIU Jiangtao1,2
), GAO Fangjie1,2, WU Haoyu1,2, MENG Qichen1,2, LIU Jiangtao1,2
Received:2023-08-08
Published:2024-03-01
Online:2024-02-28
Supported by:摘要:
针对决策者风险态度(decision-makers’ risk attitudes, DMRA)和不确定性对社区综合能源系统调度策略的影响,提出了社区虚拟电厂(community virtual power plant, CVPP)的多目标调度模型。首先,建立了考虑DMRA的CVPP模型和经济-能源-环境多目标满意度模型。其次,考虑可再生能源、负荷和DMRA的不确定性,对信息间隙决策理论(information gap decision theory, IGDT)模型进行了改进。第三,在考虑DMRA的基础上,拓展自信双层语言术语下的改进VIKOR方法。最后,以某居民区为例,对该模型的有效性进行了验证。结果表明:1)基于DMRA的CVPP提供了切合实际的调度策略。2)实施需求响应后,居民成本和净碳排放分别降低了9%和91%,提高了能源供应商的利润和可再生能源的利用率,所构建的IGDT模型也改进了多个目标。3)改进后的IGDT模型的不确定性和偏差因素允许采用多种调度策略。同时,改进的VIKOR方法为决策者选择策略提供了一种新的方法。该模型为调度策略的选择提供了指导,同时也为鼓励可再生能源的使用提供了途径。
中图分类号:
高建伟, 黄宁泊, 高芳杰, 吴浩宇, 孟琪琛, 刘江涛. 基于改进信息间隙决策理论的考虑决策者风险态度的社区虚拟电厂经济-能源-环境调度策略选择[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45(3): 39-57.
GAO Jianwei, HUANG Ningbo, GAO Fangjie, WU Haoyu, MENG Qichen, LIU Jiangtao. Selection of Economics-Energy-Environment Scheduling Strategy for a Community Virtual Power Plant Considering Decision-makers’ Risk Attitudes Based on Improved Information Gap Decision Theory[J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(3): 39-57.
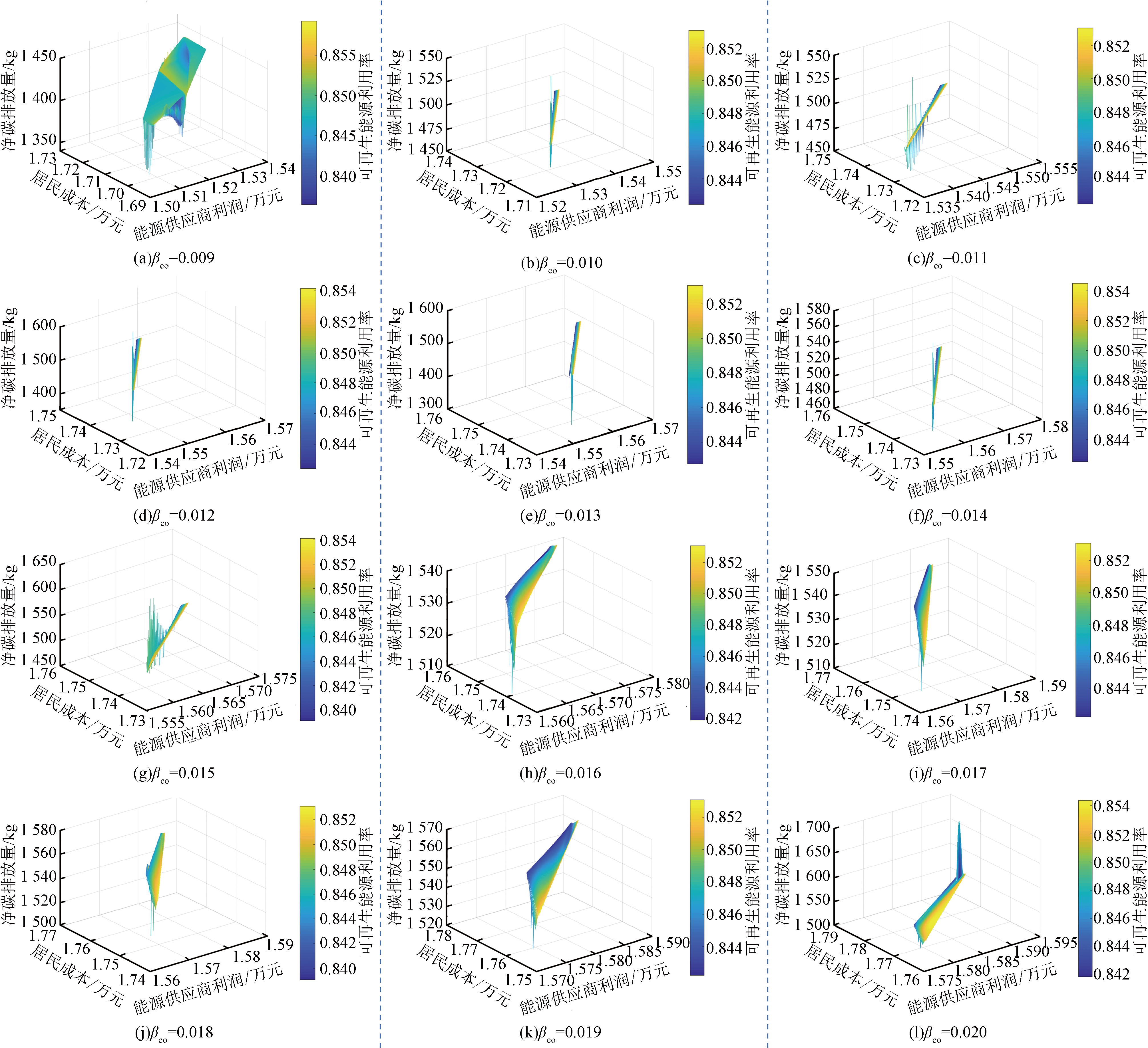
图4 考虑不确定因素的多目标优化后的保守型决策者Pareto前沿
Fig.4 Pareto Frontier for conservative decision makers after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors
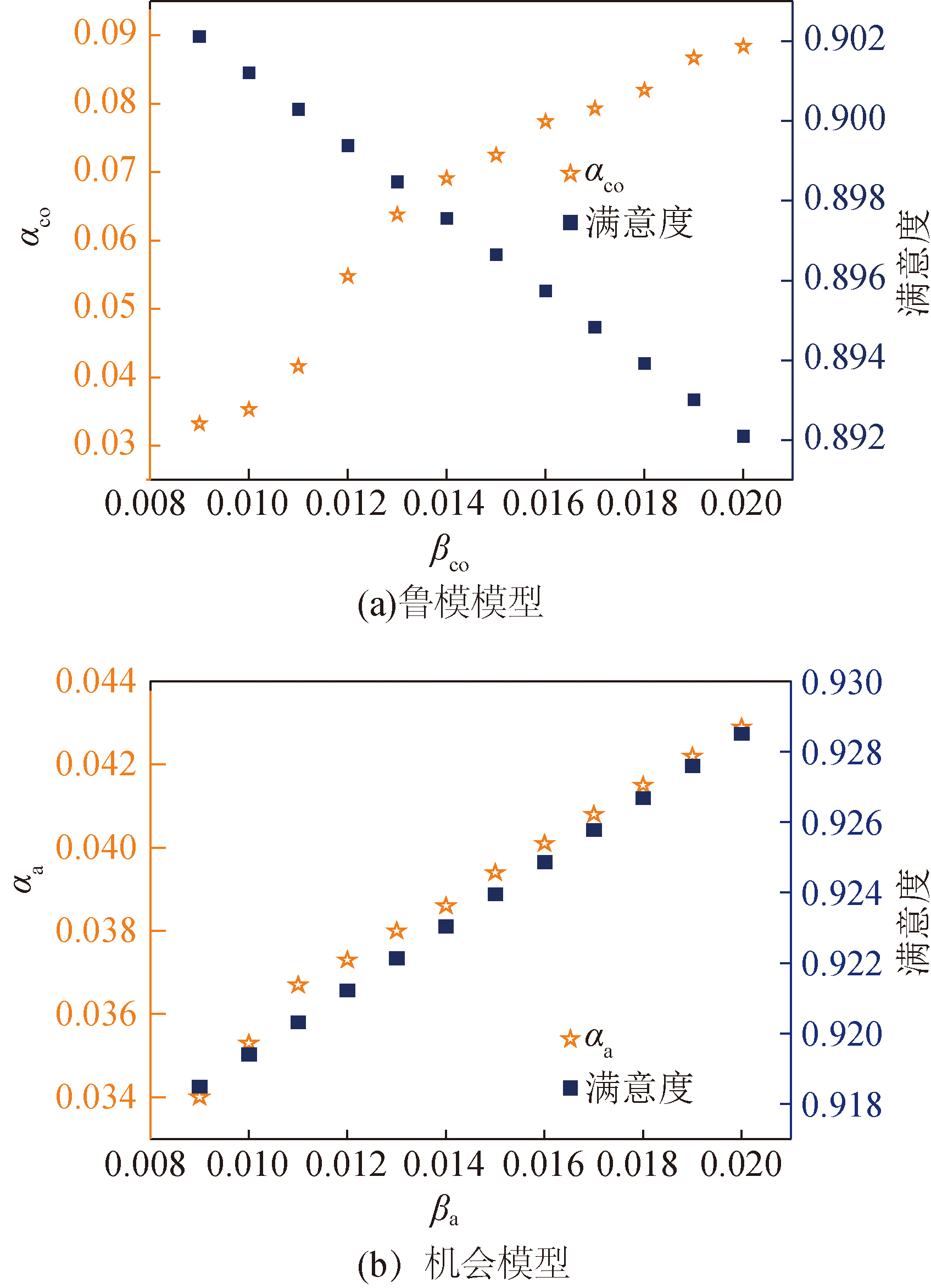
图5 考虑不确定因素的多目标优化策略下β与α的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between β and α under optimal strategy after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors
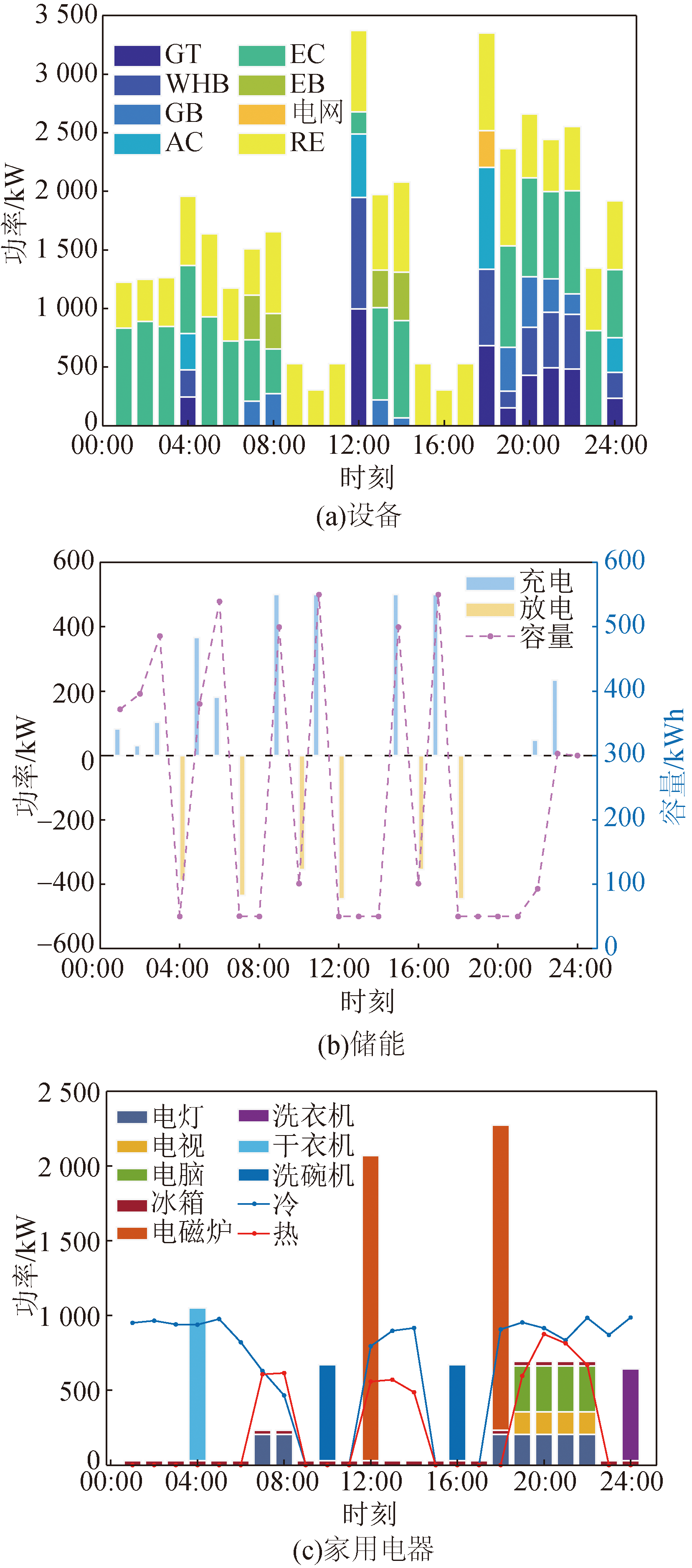
图6 考虑不确定因素的多目标优化后的设备输出和家用电器运行-保守决策者
Fig.6 Equipment output and household appliances operation after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors-conservative decision-makers

图7 考虑不确定因素的多目标优化后的设备产出和家用电器运行-冒险决策者
Fig.7 Equipment output and household appliances operation after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors-risk decision-makers
| [1] |
GAO J W, GAO F J, MA Z Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization of smart community integrated energy considering the utility of decision makers based on the Lévy flight improved chicken swarm algorithm[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 72: 103075.
doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103075 URL |
| [2] | 国家发展和改革委员会, 国家能源局. 关于促进智能电网发展的指导意见(发展改革行动[2015]1518)[EB/OL]. (2015-07-07)[2023-07-20]. http://www.nea.gov.cn/2015-07/07/c_134388049.htm. |
| [3] |
KIM I, JAMES J A, CRITTENDEN J. The case study of combined cooling heat and power and photovoltaic systems for building customers using HOMER software[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2017, 143: 490-502.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsr.2016.10.061 URL |
| [4] |
MATAMALA Y, FEIJOO F. A two-stage stochastic Stackelberg model for microgrid operation with chance constraints for renewable energy generation uncertainty[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 303: 117608.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117608 URL |
| [5] |
WANG Z K, CRAWLEY J, LI F G N, et al. Sizing of district heating systems based on smart meter data: quantifying the aggregated domestic energy demand and demand diversity in the UK[J]. Energy, 2020, 193: 116780.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.116780 URL |
| [6] | 刘蓉晖, 李阳, 杨秀, 等. 考虑需求响应的社区综合能源系统两阶段优化调度[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(9): 46-54. |
| LIU Ronghui, LI Yang, YANG Xiu, et al. Two-stage optimal dispatching of community comprehensive energy system considering demand response[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 46-54. | |
| [7] |
GAO F J, GAO J W, ZHANG Y, et al. Community decision-makers’ choice of multiple objectives scheduling strategy for integrated energy considering multiple uncertainties and demand response[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022, 83(8):103945.
doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103945 URL |
| [8] |
JU L W, ZHAO R, TAN Q L, et al. A multi-objective robust scheduling model and solution algorithm for a novel virtual power plant connected with power-to-gas and gas storage tank considering uncertainty and demand response[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250: 1336-1355.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.027 URL |
| [9] | 唐虎, 陈爱伦, 崔浩, 等. 社区型能源互联网下的虚拟电厂参与电力市场策略分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2019, 6(3): 40-47. |
| TANG Hu, CHEN Ailun, CUI Hao, et al. Strategy analysis of virtual power plants participation in electric power market with community energy internet[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2019, 6(3): 40-47. | |
| [10] |
MONIE S, NILSSON A M, WIDÉN J, et al. A residential community-level virtual power plant to balance variable renewable power generation in Sweden[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 228: 113597.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113597 URL |
| [11] |
GONG H J, JONES E S, ALDEN R E, et al. Virtual power plant control for large residential communities using HVAC systems for energy storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(1): 622-633.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2021.3120971 URL |
| [12] |
LIU C M, WANG C L, YIN Y J, et al. Bi-level dispatch and control strategy based on model predictive control for community integrated energy system considering dynamic response performance[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 310: 118641.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118641 URL |
| [13] | 缴傲, 胡臻, 向萌, 等. 考虑综合需求响应的社区综合能源系统主从博弈策略[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33(9): 94-102. |
| JIAO Ao, HU Zhen, XIANG Meng, et al. Master-slave game strategy for community integrated energy system considering integrated demand response[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33(9): 94-102. | |
| [14] | 陈华, 黄海晔. 考虑碳排放的社区级综合能源系统优化模型[J]. 上海电力大学学报, 2020, 36(6): 613-618. |
| CHEN Hua, HUANG Haiye. Optimal operation of community-level comprehensive energy systems considering carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2020, 36(6): 613-618. | |
| [15] |
FAYYAZ ROUHBAKHSH F, HASSANPOUR H, EFFATI S. Some new solution concepts in generalized fuzzy multiobjective optimization problems[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(10): 3261-3270.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2787-0 URL |
| [16] |
ZHOU Y Z, WEI Z N, SUN G Q, et al. A robust optimization approach for integrated community energy system in energy and ancillary service markets[J]. Energy, 2018, 148: 1-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.078 URL |
| [17] |
AIEN M, HAJEBRAHIMI A, FOTUHI-FIRUZABAD M. A comprehensive review on uncertainty modeling techniques in power system studies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 57: 1077-1089.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.070 URL |
| [18] |
TAJEDDINI M A, RAHIMI-KIAN A, SOROUDI A. Risk averse optimal operation of a virtual power plant using two stage stochastic programming[J]. Energy, 2014, 73: 958-967.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.06.110 URL |
| [19] |
TAN Z F, FAN W, LI H F, et al. Dispatching optimization model of gas-electricity virtual power plant considering uncertainty based on robust stochastic optimization theory[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 247: 119106.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119106 URL |
| [20] |
AGUILAR J, BORDONS C, ARCE A. Chance constraints and machine learning integration for uncertainty management in virtual power plants operating in simultaneous energy markets[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 133: 107304.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2021.107304 URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG Y, YUAN F M, ZHAI H P, et al. Optimizing the planning of distributed generation resources and storages in the virtual power plant, considering load uncertainty[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 387: 135868.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135868 URL |
| [22] |
VAHEDIPOUR-DAHRAIE M, RASHIDIZADEH-KERMANI H, ANVARI-MOGHADDAM A, et al. Risk-averse probabilistic framework for scheduling of virtual power plants considering demand response and uncertainties[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 121: 106126.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106126 URL |
| [23] | 于雪菲, 张帅, 刘琳琳, 等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的碳捕集电厂调度[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62(9): 1467-1473. |
| YU Xuefei, ZHANG Shuai, LIU Linlin, et al. Carbon capture power plant scheduling based on information gap decision theory[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(9): 1467-1473. | |
| [24] | BEN-HAIM Y. Info-gap decision theory: decisions under severe uncertainty[M]. Academic Press, 2006. |
| [25] | 秦绍基, 林靖淳, 张勇军, 等. 基于熵权自适应信息间隙决策的园区综合能源系统规划[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47(10): 4190-4203. |
| QIN Shaoji, LIN Jingchun, ZHANG Yongjun, et al. Comprehensive energy system planning of park based on entropy weight adaptive information gap decision[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47(10): 4190-4203. | |
| [26] |
FATHI R, TOUSI B, GALVANI S. A new approach for optimal allocation of photovoltaic and wind clean energy resources in distribution networks with reconfiguration considering uncertainty based on info-gap decision theory with risk aversion strategy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 295: 125984.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125984 URL |
| [27] |
KAHNEMAN D, TVERSKY A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[J]. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 263.
doi: 10.2307/1914185 URL |
| [28] |
LIN B Q, JIA Z J. Is emission trading scheme an opportunity for renewable energy in China? A perspective of ETS revenue redistributions[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 263: 114605.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114605 URL |
| [29] |
GOU X J, XU Z S, WANG X X, et al. Managing consensus reaching process with self-confident double hierarchy linguistic preference relations in group decision making[J]. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 2021, 20(1): 51-79.
doi: 10.1007/s10700-020-09331-y |
| [30] | 王铁旦, 李诗瑶, 彭定洪. 基于BB-VIKOR法的新型智慧城市建设质量评价研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2022, 22(3): 96-105. |
| WANG Tiedan, LI Shiyao, PENG Dinghong. Research on the quality evaluation of new smart city construction based on BB-VIKOR method[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Social Sciences), 2022, 22(3): 96-105. | |
| [31] | 缑迅杰, 邓富民, 徐泽水. 基于自信双层语言偏好关系的大规模群体共识决策方法及其应用研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2023, 31(9): 222-232. |
| GOU Xunjie, DENG Fumin, XU Zeshui. The application of the large-scale group consensus decision-making method based on self-confident double hierarchy linguistic preference relations[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2023, 31(9): 222-232. | |
| [32] |
OPRICOVIC S, TZENG G H. Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 178(2): 514-529.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.01.020 URL |
| [33] |
GOU X J, LIAO H C, XU Z S, et al. Group decision making with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations: consistency based measures, index and repairing algorithms and decision model[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 489: 93-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.03.037 URL |
| [34] |
MILLET I. The effectiveness of alternative preference elicitation methods in the analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, 1997, 6(1): 41-51.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1360(199701)6:1<41::AID-MCDA122>3.0.CO;2-D URL |
| [35] |
CHICLANA F, HERRERA-VIEDMA E, ALONSO S, et al. Cardinal consistency of reciprocal preference relations: a characterization of multiplicative transitivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(1): 14-23.
doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.2008028 URL |
| [36] |
尹儇鹏, 徐选华, 陈晓红. 风险视域下的大群体应急决策策略选择研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2021, 41(3): 678-690.
doi: 10.12011/SETP2019-0940 |
| YIN Xuanpeng, XU Xuanhua, CHEN Xiaohong. Study on the selection of large group emergency decision-making strategies under the perspective of risk[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2021, 41(3): 678-690. | |
| [37] | 梅文明, 李美成, 张宇威, 等. 基于前景理论和VIKOR法的多能源微电网效益评价[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37(3): 71-77. |
| MEI Wenming, LI Meicheng, ZHANG Yuwei, et al. Benefit evaluation of multi energy microgrid based on prospect theory and VIKOR method[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37(3): 71-77. |
| [1] | 张志一, 窦震海, 于润泽, 胡亚春, 陈佳佳, 尹文良. 考虑电-热等效虚拟储能的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45(3): 16-26. |
| [2] | 王利猛, 刘雪梦, 李扬, 常铎, 任星. 阶梯式碳交易机制下考虑需求响应的综合能源系统低碳优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45(2): 102-114. |
| [3] | 任洪波, 王楠, 吴琼, 时珊珊, 方陈, 万莎. 考虑阶梯型碳交易的多负荷聚合商协同优化调度与成本分配[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45(2): 171-182. |
| [4] | 杜维柱, 白恺, 李海波, 张蕾, 刘迪, 史新涛. 兼顾保供电/消纳的源荷储灵活性资源优化规划[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(9): 13-23. |
| [5] | 舒俊霖, 刘俊勇, 高红均, 何鑫, 胡人川. 考虑开关重构与需求响应的配电网分布鲁棒优化运行[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(6): 101-111. |
| [6] | 李玲, 曹锦业, Nikita Tomin, 杨德昌, 郑颖颖. 计及电动汽车接入的区域综合能源系统双层日前协调优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(5): 23-33. |
| [7] | 刘任, 刘洋, 许立雄, 李振伟, 李雪玲. 计及分布式需求响应的多微电网系统协同优化策略[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(5): 72-83. |
| [8] | 崔文倩, 魏军强, 赵云灏, 高炜, 陈康. 双碳目标下含重力储能的配电网多目标运行优化[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(4): 45-53. |
| [9] | 范馨予, 黄媛, 吴疆, 孙增杰, 宁静波. 考虑源网荷储协同优化的配电网韧性提升策略[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(4): 63-73. |
| [10] | 原希尧, 王关涛, 朱若源, 白星振, 葛磊蛟, 李顾辉. 碳—绿色证书交易机制下考虑回收P2G余热和需求响应的PIES优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(3): 25-35. |
| [11] | 姚寅, 朱烨冬, 李东东, 周波, 林顺富. 基于决策实验室算法-对抗解释结构模型的电动汽车多场景需求响应策略分析[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(3): 93-104. |
| [12] | 樊伟, 李旭东, 王尧, 李祥光, 王玉洁, 谭忠富, 鞠立伟. 新型电力系统灵活性资源聚合两阶段调度优化模型[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(2): 25-37. |
| [13] | 靳冰洁, 李家兴, 彭虹桥, 罗澍忻, 卢治霖, 冷媛, 董萍, 梁梓杨. 需求响应下计及电碳市场耦合的多元主体成本效益分析[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(2): 50-60. |
| [14] | 于昊正, 赵寒杰, 李科, 朱星旭, 皇甫霄文, 樊江川, 李翠萍, 李军徽. 计及需求响应的分布式光伏集群承载能力评估[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(2): 122-130. |
| [15] | 余彬, 翁利国, 练德强, 王思斌, 黄媛, 姚昊天. 计及价格引导机制的含分布式资源园区协调运行策略[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(2): 145-154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2020 《电力建设》编辑部
地址:北京市昌平区北七家未来科技城北区国家电网公司办公区 邮编:102209 电话:010-66602697
京ICP备18017181号-1 国网安备4511A3CPZ号
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发