Abstract
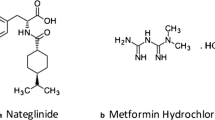
In the present work, co-amorphous mixture (COAM) of poorly soluble nateglinide (NT) and highly soluble Metformin hydrochloride (MT) was prepared by spray drying method to improve the dissolution rate of NT and the processability of COAM. Binary spray-dried COAM of NT and MT (120 mg: 500 mg) was prepared in its clinical dose ratio whereas 20% Neusilin®US2 (NS) was added to prepare non-sticky, free flowing ternary COAM. Solubility studies of binary and ternary COAM exhibited sevenfold and tenfold rise in the solubility of NT. Complete amorphization of NT was revealed in XRPD and DSC studies of both COAM and hydrogen-bonding interactions were reflected in FTIR-spectra. SEM microphotographs illustrated round-shaped microparticles in ternary COAM against the irregular particles in binary COAM. In vitro dissolution of NT was significantly improved in ternary COAM > binary COAM > NT irrespective of dissolution medium. On contrary, MT has partially transformed to the amorphous form in COAM without altering the solubility. In accelerated stability studies, NT and MT devitrification was not observed in XRPD of ternary COAM in contrast to binary COAM. Therefore, enhanced dissolution of NT, stabilization of spray-dried dispersion, and its improved processability can be achieved by preparing ternary COAM of NT:MT:NS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997 Jan 15;23(1–3):3–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00423-1.
Yu L. Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: preparation, characterization and stabilization. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;48(1):27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00098-9.
Laitinen R, Löbmann K, Strachan CJ, Grohganz H, Rades T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int J Pharm. 2013;453(1):65–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.04.066.
Janssens S, Van den Mooter G. Physical chemistry of solid dispersions. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61(12):1571–86. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.61.12.0001.
Khougaz K, Clas SD. Crystallization inhibition in solid dispersions of MK-0591 and poly (vinylpyrrolidone) polymers. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89(10):1325–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/1520-6017(200010)89:10<1325::AID-JPS10>3.0.CO;2-5.
Gao Y, Liao J, Qi X, Zhang J. Coamorphous repaglinide–saccharin with enhanced dissolution. Int J Pharm. 2013;450(1–2):290–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.04.032.
Jensen KT, Löbmann K, Rades T, Grohganz H. Improving co-amorphous drug formulations by the addition of the highly water soluble amino acid, proline. Pharmaceutics. 2014;6(3):416–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6030416.
Lenz E, Jensen KT, Blaabjerg LI, Knop K, Grohganz H, Löbmann K, et al. Solid-state properties and dissolution behaviour of tablets containing co-amorphous indomethacin–arginine. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;96:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.07.011.
Dengale SJ, Grohganz H, Rades T, Löbmann K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;100:116–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.12.009.
Löbmann K, Strachan C, Grohganz H, Rades T, Korhonen O, Laitinen R. Co-amorphous simvastatin and glipizide combinations show improved physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;81(1):159–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.02.004.
Chieng N, Aaltonen J, Saville D, Rades T. Physical characterization and stability of amorphous indomethacin and ranitidine hydrochloride binary systems prepared by mechanical activation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;71(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.06.022.
Maggi L, Bruni G, Maietta M, Canobbio A, Cardini A, Conte U. II. Technological approaches to improve the dissolution behavior of nateglinide, a lipophilic insoluble drug: co-milling. Int J Pharm. 2013;454(1):568–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.06.085.
Desai D, Wong B, Huang Y, Ye Q, Tang D, Guo H, et al. Surfactant-mediated dissolution of metformin hydrochloride tablets: wetting effects versus ion pairs diffusivity. J Pharm Sci. 2014;103(3):920–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23852.
Wairkar S, Gaud R. Co-amorphous combination of nateglinide-metformin hydrochloride for dissolution enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(3):673–81. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-015-0371-4.
Chauhan B, Shimpi S, Paradkar A. Preparation and evaluation of glibenclamide-polyglycolized glycerides solid dispersions with silicon dioxide by spray drying technique. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26(2):219–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2005.06.005.
Blenkinsopp A, Paxton P. Symptoms in the pharmacy: a guide to the management of common illness, 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998.
Rawlinson CF, Williams AC, Timmins P, Grimsey I. Polymer-mediated disruption of drug crystallinity. Int J Pharm. 2007;336(1):42–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.11.029.
Horton ES, Clinkingbeard C, Gatlin M, Foley J, Mallows S, Shen S. Nateglinide alone and in combination with metformin improves glycemic control by reducing mealtime glucose levels in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(11):1660–5.
Takeuchi H, Nagira S, Yamamoto H, Kawashima Y. Solid dispersion particles of tolbutamide prepared with fine silica particles by the spray-drying method. Powder Technol. 2004;141(3):187–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2004.03.007.
Einfalt T, Planinšek O, Hrovat K. Methods of amorphization and investigation of the amorphous state. Acta Pharma. 2013 Sep 30;63(3):305–34. https://doi.org/10.2478/acph-2013-0026.
Planinšek O, Kovačič B, Vrečer F. Carvedilol dissolution improvement by preparation of solid dispersions with porous silica. Int J Pharm. 2011;406(1–2):41–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.12.035.
Chan HK, Clark AR, Feeley JC, Kuo MC, Lehrman SR, Pikal-Cleland K, et al. Physical stability of salmon calcitonin spray-dried powders for inhalation. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93(3):792–804. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.10594.
Jain V, Dhaked DK, Kasetti Y, Bharatam PV. Computational study on the conformational preferences in nateglinide. J Phys Org Chem. 2012;25(8):649–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.1956.
Heinz A, Strachan CJ, Gordon KC, Rades T. Analysis of solid-state transformations of pharmaceutical compounds using vibrational spectroscopy. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61(8):971–88.
Allesø M, Chieng N, Rehder S, Rantanen J, Rades T, Aaltonen J. Enhanced dissolution rate and synchronized release of drugs in binary systems through formulation: amorphous naproxen–cimetidine mixtures prepared by mechanical activation. J Control Release. 2009;136(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.01.027.
Remko M. Theoretical study of molecular structure, pKa, lipophilicity, solubility, absorption, and polar surface area of some hypoglycemic agents. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM. 2009;897(1–3):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theochem.2008.11.021.
Wairkar S, Gaud R, Jadhav N. Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of Nateglinide by microenvironmental ph-regulated ternary solid dispersion: in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017;69(9):1099–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12756.
Gao P, Shi Y. Characterization of supersaturatable formulations for improved absorption of poorly soluble drugs. AAPS J. 2012;14(4):703–13. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-012-9389-7.
Gupta P, Thilagavathi R, Chakraborti AK, Bansal AK. Role of molecular interaction in stability of celecoxib− PVP amorphous systems. Mol Pharm. 2005;2(5):384–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp050004g.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), India for assistance on XRPD and SEM analysis. The authors are highly thankful to Cipla Ltd., India, and Sanofi Ltd., India for providing gift sample of nateglinide and metformin hydrochloride respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wairkar, S., Gaud, R. Development and Characterization of Microstructured, Spray-Dried Co-Amorphous Mixture of Antidiabetic Agents Stabilized by Silicate. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1352-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1352-9