Abstract
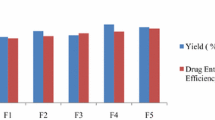
Raloxifene hydrochloride (R-HCl), a BCS class II drug, remains a mainstay in the prevention and pharmacologic therapy of osteoporosis. Its absolute bioavailability, however, is 2% due to poor solubility and extensive first pass metabolism. The present study describes two simultaneous approaches to improve its bioavailability, complexation of R-HCl with cyclodextrin(s), and formulation of mucoadhesive microspheres of the complex using different proportions of carbopol and HPMC. Microspheres were pale yellow in color, free-flowing, spherical, and porous in outline. The particle size ranged between 3 and 15 μm, and entrapment efficiency was found to be within 81.63% to 87.73%. A significant improvement in the solubility of R-HCl was observed, and it differed with the combination of excipients used. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry studies revealed that enhancement in drug solubility was resulted due to a change in its crystallinity within the formulation. Microspheres possessed remarkable mucoadhesion and offered controlled drug release, lasting up to 24 h. They produced a sharp plasma concentration–time profile of R-HCl within 30 min post-administration to Wistar rats. [AUC]0–24 h was found to be 1,722.34 ng h/ml, and it differed significantly to that of pure drug powder (318.28 ng h/ml). More than fivefold increase in AUC and more than twofold increase in MRT were observed. FT-IR studies evidenced no interaction among drug and excipients. The results of this study showed that mucoadhesive microspheres could be a viable approach to improve the pharmacokinetic profile of R-HCl.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein S. Update of current therapeutic options for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin Ther. 2006;28:151–73.
Vik SA, Maxwell CJ, Hanley-David A. Treatment of osteoporosis in an older home care population. BMC Musculoskel Disord. 2005;6:7.
Teeter JS, Meyerhoff RD. Environmental fate and chemistry of raloxifene hydrochloride. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2002;21:729–36.
Celnikier DH. Pharmacokinetics of raloxifene and its clinical application. Eur J Obs Gyn Reprod Biol. 1999;85:23–9.
Mizuma T. Intestinal glucuronidation metabolism may have a greater impact on oral bioavailability than hepatic glucuronidation metabolism in humans: a study with raloxifene, substrate for UGT1A1, 1A8, 1A9, and 1A10. Int J Pharm. 2009;378:140–1.
Jagadish B, Yelchuri R, Bindu K, Tangi H, Maroju S, Rao VU. Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of raloxifene hydrochloride by co-grinding with different superdisintegrants. Chem Pharm Bull. 2010;58:293–300.
Michael FW, Wacher VJ, Ruble KM, Ramsey MG, Edgar KJ, Buchanan NL, et al. Pharmacokinetics of raloxifene in male Wistar–Hannover rats: influence of complexation with hydroxybutenyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm. 2008;346:25–37.
Garg A, Singh S, Rao VU, Bindu K, Balasubramaniam J. Solid state interaction of raloxifene HCl with different hydrophilic carriers during co-grinding and its effect on dissolution rate. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35:455–70.
Skalko N, Brandl M, Bedirevic-Lacan M, Filipovic-Grcic J, Jalsenjak I. Liposomes with nifedipine and nifedipine-cyclodextrin complex: calorimetrical and plasma stability comparison. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1996;4:359–66.
Dhanaraju D, Kumaran KS, Baskaran T, Moorthy MSR. Enhancement of bioavailability of griseofulvin by its complexation with beta-cyclodextrin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1998;24:583–7.
Cappello B, Rosa GD, Giannini L, Rotonda MIL, Mensitieri G, Miro A, et al. Cyclodextrin-containing poly(ethyleneoxide) tablets for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: potential as buccal delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2006;319:63–70.
Melia CD, Washington N, Wilson CG. Advantages and disadvantages of multiparticulate delivery systems. In: Melia CD, Washington N, Wilson CG, editors. Multiparticulate oral dosage forms: technology and biopharmaceutics. Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press; 1994. p. 135–40.
Tao Y, Lu Y, Sun Y, Gu B, Lu W, Pan J. Development of mucoadhesive microspheres of acyclovir with enhanced bioavailability. Int J Pharm. 2009;378:30–6.
Wong SM, Kellaway IW, Murdan S. Enhancement of the dissolution rate and oral absorption of a poorly water soluble drug by formation of surfactant-containing microparticles. Int J Pharm. 2006;317:61–8.
Myung KC, Hongkee S, Hoo-Kyung C. Preparation of mucoadhesive microspheres containing antimicrobial agents for eradication of H. pylori. Int J Pharm. 2005;297:172–9.
Tiwari S, Singh S, Rawat M, Tilak R, Mishra B. L9 orthogonal design assisted formulation and evaluation of chitosan-based buccoadhesive films of miconazole nitrate. Curr Drug Deliv. 2009;6:305–16.
Khanna R, Agarwal SP, Ahuja A. Mucoadhesive buccal tablets of clotrimazole for oral candidiasis. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1997;23:831–7.
Li S, Lin S, Daggy BP, Mirchandani HL, Chien YW. Effect of HPMC and carbopol on the release and floating properties of gastric floating drug delivery system using factorial design. Int J Pharm. 2003;253:13–22.
Jug M, Beirevi-Laan M, Bengez S. Novel cyclodextrin-based film formulation intended for buccal delivery of atenolol. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35:796–807.
Gibaud S, Zirar SB, Mutzenhardt P, Isabelle F, Astier A. Melarsoprol–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Int J Pharm. 2005;306:107–21.
Patil SB, Murthy RSR. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive chitosan microspheres of amlodipine besylate for nasal administration. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2006;68:64–7.
Albrecht K, Greindl M, Kremser C, Wolf C, Debbage P, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Comparative in vivo mucoadhesion studies of thiomer formulations using magnetic resonance imaging and fluorescence detection. J Control Release. 2006;115:78–84.
Yang ZY, Zhang ZF, He XB, Zhao GY, Zhang YQ. Validation of a novel HPLC method for the determination of raloxifene and its pharmacokinetics in rat plasma. Chromatographia. 2007;65:197–201.
Koester LS, Bertuol JB, Groch KR, Xavier CR, Moellerke R, Mayorga P, et al. Bioavailability of carbamazepine: β-cyclodextrin complex in beagle dogs from hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrix tablets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004;22:201–7.
Marcon F, Mathiron D, Pilard S, Lemaire-Hurtel AS, Dubaele JM, Djedaini-Pilard F. Development and formulation of a 0.2% oral solution of midazolam containing γ-cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm. 2009;379:244–50.
Vippangunta SR, Maul KA, Tallavajhala S, Grant DJW. Solid state characterization of nifedipine solid dispersion. Int J Pharm. 2002;236:111–26.
Bilensoy E, Rouf MA, Vural I, Şen M, Hıncal AA. Mucoadhesive, thermosensitive, prolonged-release vaginal gel for clotrimazole: β-cyclodextrin complex. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006;7:E3–7.
Schaefer MJ, Singh J. Effect of isopropyl myristic acid ester on the physical characteristics and in vitro release of etoposide from PLGA microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2000;1:article 32.
Singla AK, Chawla M, Singh A. Potential applications of carbomer in oral mucoadhesive controlled drug delivery system: a review. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26:913–24.
Chun M, Kwak B, Choi CH. Preparation of buccal patch composed of carbopol, poloxamer and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Arch Pharm Res. 2003;26:973–8.
Han RY, Fang JY, Sung KC, Hu OYP. Mucoadhesive buccal disks for novel nalbuphine prodrug controlled delivery: effect of formulation variables on drug release and mucoadhesive performance. Int J Pharm. 1999;177:201–9.
Gavini E, Rassu G, Haukvik T, Lanni C, Racchi M, Giunchedi P. Mucoadhesive microspheres for nasal administration of cyclodextrins. J Drug Target. 2009;17:168–79.
Park SH, Chun MK, Choi HK. Preparation of an extended-release matrix tablet using chitosan/carbopol interpolymer complex. Int J Pharm. 2008;347:39–44.
Acknowledgments
The first author acknowledges the financial assistance of the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, in carrying out this research work. The support of Prof. O.N. Srivastava, Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, is thankfully acknowledged for providing the facility of SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, R.K., Tiwari, S. & Mishra, B. Bioadhesive Microspheres for Bioavailability Enhancement of Raloxifene Hydrochloride: Formulation and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 12, 650–657 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-011-9619-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-011-9619-9