Abstract
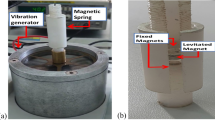
This paper deals with a description and modelling of a spring-less electromagnetic vibration energy harvesting system. The presented unique electromagnetic vibration energy harvester consists of a nonlinear resonance mechanism, magnetic circuit with a coil and an electronic load. The mechanical vibrations excite the nonlinear resonance mechanism and the relative movement of the magnetic circuit against fixed coil induces voltage due to Faraday’s Law. When the electronics is connected the current flows through the load and output power is harvested. There are several nonlinearities which affects operations of the presented electromagnetic energy harvesting system. The significant nonlinearity of the system is stiffness of the resonance mechanism and it causes extending of an operation bandwidth. The harvesting of electrical energy from mechanical vibrations provides electromagnetic damping feedbacks of the coil to moving magnetic circuit. The feedback depends on the current flow through the electronic load and coil. The using of modern power management circuit with optimal power point provides other nonlinear operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Paradiso, T. Starner, IEEE Pervasive Comput. 4, 18 (2005)
T. Becker, M. Kluge, J. Schalk, K. Tiplady, C. Paget, U. Hilleringmann, T. Otterpohl, IEEE Sens. J. 9 (2009)
P. Glynne-Jones, M.J. Tudor, S.P. Beeby, N.M. White, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 110, 344 (2004)
S.P. Beeby, M.J. Tudor, N.M. White, Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, R175 (2006)
B.H. Calhoun, D.C. Daly, N. Verma, D.F. Finchelstein, D.D. Wentzloff, A. Wang, S.H. Cho, A.P. Chandrakasan, Ieee Trans. Comput. 54, 727 (2005)
D.P. Arnold, IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 3940 (2007)
S. Priya, D.J. Inman (eds.), Energy Harvesting Technologies (Springer US, Boston, MA, 2009)
L. Mateu, F. Moll, in VLSI Circuits Syst. II, Pts 1 2, edited by J.F. Lopez, F.V. Fernandez, J.M. Lopez-Villegas, J.M. de la Rosa (2005), p. 359
Z. Hadas, C. Ondrusek, V. Singule, Microsyst. Technol. 16, 691 (2010)
Cammarano, A. Gonzalez-Buelga, S. a Neild, S.G. Burrow, D.J. Inman, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 476, 012071 (2013)
L. Gammaitoni, I. Neri, H. Vocca, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 (2009)
T.-W. Ma, H. Zhang, N.-S. Xu, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 28, 323 (2012)
S.D. Nguyen, E. Halvorsen, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 20, 1225 (2011)
E. Sardini, M. Serpelloni, Sensors Actuators, A Phys. 172, 475 (2011)
S.W. Guan, X.B. Shan, T. Xie, R.J. Song, Z.L. Xu, Appl. Mech. Mater. 444–445, 879 (2013)
S.G. Burrow, L.R. Clare, in Proc. IEEE Int. Electr. Mach. Drives Conf. IEMDC 2007 (2007), p. 715
J. Yang, Y.M. Wen, P. Li, X.L. Bai, Sci. China Technol. Sci. 54, 1419 (2011)
C.B. Williams, R.B. Yates, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 52, 8 (1996)
S.P. Beeby, M.J. Tudor, N.M. White, Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, R175 (2006)
T. von Büren, G. Tröster, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 135, 765 (2007)
Y. Zhu, J.W. Zu, IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 3344 (2012)
C. Lee, D. Stamp, N.R. Kapania, J.O. Mur-Miranda, in Energy, edited by N.K. Dhar, P.S. Wijewarnasuriya, A.K. Dutta (SPIE, 2010), p. 76830Y–76830Y–12
Z. Hadas, V. Singule, C. Ondrusek, Solid State Phenom. 164, 291 (2010)
Z. Hadas, V. Vetiska, Z. Ancik, C. Ondrusek, V. Singule, Smart Sensors, Actuators, Mems IV 87631F (2013)
Z. Hadas, V. Vetiska, R. Huzlik, V. Singule, Microsyst. Technol. 20, 831 (2014)
Z. Hadas, J. Kurfurst, C. Ondrusek, V. Singule, Microsyst. Technol. 18, 1003 (2012)
Z. Hadas, M. Kluge, V. Singule, C. Ondrusek, in 2007 IEEE Int. Symp. Diagnostics Electr. Mach. Power Electron. Drives (IEEE, 2007), p. 451
Z. Hadas, V. Singule, C. Ondrusek, Solid State Phenom. 147–149, 426 (2009)
Z. Hadas, R. Huzlik, in Mechatronics 2013 Recent Technol. Sci. Adv. (2014), p. 371
D. Niyato, E. Hossain, M. Rashid, V. Bhargava, IEEE Wirel. Commun. 14, 90 (2007)
E. Lefeuvre, D. Audigier, C. Richard, D. Guyomar, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 22, 2018 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadas, Z., Ondrusek, C. Nonlinear spring-less electromagnetic vibration energy harvesting system. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 224, 2881–2896 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2015-02595-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2015-02595-3