Abstract.
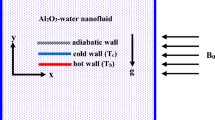
Hybrid nanofluids are made of a base fluid and at least two different types of nanoparticles. The main purpose of using hybrid nanofluids is that they have better thermophysical properties comparing to that of nanofluids with single nanoparticles. In this paper, a comparison between water-silver-magnesium oxide hybrid nanofluid and water-silver nanofluid’s influence on the flow field, heat transfer and entropy generation in an enclosure with rotating heat sources have been investigated. The study has been done for a Grashof number of 104, a Richardson number from 0.3 to 100 and for volume fractions of 0 to 0.01 of nanoparticles. The governing equations are solved numerically using the finite volume method and the SIMPLER algorithm with a computer program using FORTRAN programming language. The results show that in all of Richardson numbers with the increment in volume fraction of nanoparticles, the maximum size of the flow function has been reduced. For all of the investigated Richardson numbers and water-silver nanofluid and water-silver-magnesium oxide hybrid nanofluid with an increment in volume fraction of nanoparticles, the maximum size of the flow function has been reduced. The maximum values of the flow function for conventional nanofluid are greater than for hybrid nanofluid. The increment of the Nusselt number with increasing the volume fraction of nanoparticles in conventional nanofluid is more sensible comparing to hybrid nanofluid. Also with increasing the volume fraction of nanoparticles, the friction and thermal entropy generation is more sensible in conventional nanofluid comparing to hybrid nanofluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fatih Selimefendigil, Muneer A. Ismael, Ali J. Chamkha, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 124--125, 95 (2017)
Samy M. Elsherbiny, Mohamed A. Teamah, Atef R. Moussa, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 82, 459 (2017)
Tongsheng Wang, Zhu Huang, Guang Xi, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 106, 1063 (2017)
M. Muthtamilselvan, K. Periyadurai, Deog Hee Doh, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 115, 19 (2017)
A. Arefmanesh, A. Aghaei, H. Ehteram, Appl. Math. Model. 40, 815 (2016)
M. Hemmat Esfe, A. Abbasian Arani, W. Yan, H. Ehteram, A. Aghaie, M. Afrand, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 92, 76 (2016)
Abhipsit Kumar Singh, Nanda Kishore, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 122, 326 (2017)
N. Nithyadevi, A. Shamadhani Begum, Hakan F. Oztop, Nidal Abu-Hamdeh, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 113, 716 (2017)
K. Mehmood, S. Hussain, M. Sagheer, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 109, 397 (2017)
Faroogh Garoosi, Farhad Talebi, Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 1668 (2017)
Ali Arefmanesh, Alireza Aghaei, Hamidreza Ehteram, Appl. Math. Model. 40, 815 (2016)
M. Famouri, K. Hooman, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35, 492 (2008)
A. Mukhopadhyay, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37, 867 (2010)
M. Shahi, A.H. Mahmoudi, A. Honarbakhsh Raouf, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 972 (2011)
H. Khorasanizadeh, J. Amani, M. Nikfar, Sci. Iran. F 19, 1996 (2012)
C. Cho, C. Chen, K. Chen, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 61, 749 (2013)
M. Magherbi, H. Abbassi, A. Ben Brahim, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46, 3441 (2003)
L.B. Erbay Altac, B. Sulus, Entropy 5, 496 (2003)
S. Mahmud, A.K.M. Sadrul Islam, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 42, 1003 (2003)
P.K. Singh, K.B. Anoop, T. Sundararajan, S.K. Das, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 4757 (2010)
R.M. Kaluri, T. Basak, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 2578 (2011)
T. Basak, R.S. Kaluri, A.R. Balakrishnan, Numer. Heat Transf. 59, 372 (2011)
H. Oztop, M.M. Rahman, A. Ahsan, M. Hasanuzzaman, R. Saidur, Khaled Al-Salem, N.A. Rahim, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 1844 (2012)
Xu.Xu. Zi-Tao Yu, Hu. Ya-Cai, Li-Wu Fan, Ke-Fa Cen, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 1141 (2012)
E. Abu-Nada, Z. Masoud, A. Hijazi, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35, 657 (2008)
Frank P. Incropera, David P. De Witt, Theodore, L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine, Introduction to Heat Transfer, 5th Edition (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006)
Mohammad Hemmat Esfe, Seyfolah Saedodin, Mojtaba Biglari, Hadi Rostamia, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 74, 91 (2016)
Mohammad Hemmat Esfe, Ali Akbar Abbasian Arani, Mohammad Rezaie, Wei-Mon Yan, Arash Karimipour, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 66, 189 (2015)
A.J. Chamkhaa, E. Abu-Nada, Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 36, 82 (2012)
R.D.C. Oliveski, M.H. Macagnan, J.B. Copetti, Appl. Therm. Eng. 29, 1417 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamiatia, M. Numerical investigation in comparing the influence of water-silver-magnesium oxide hybrid nanofluid and water-silver normal nanofluid on fluid flow, heat transfer and entropy generation in an enclosure with rotating heat sources. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 405 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12750-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12750-7