Abstract
We analytically and numerically disclose the effects of the higher-order correction terms in the gravity and in the gauge field on the properties of s-wave holographic superconductors. On the gravity side, we consider the higher curvature Gauss–Bonnet corrections and on the gauge field side, we add a quadratic correction term to the Maxwell Lagrangian. We show that, for this system, one can still obtain an analytical relation between the critical temperature and the charge density. We also calculate the critical exponent and the condensation value both analytically and numerically. We use a variational method, based on the Sturm–Liouville eigenvalue problem for our analytical study, as well as a numerical shooting method in order to compare with our analytical results. For a fixed value of the Gauss–Bonnet parameter, we observe that the critical temperature decreases with increasing the nonlinearity of the gauge field. This implies that the nonlinear correction term to the Maxwell electrodynamics makes the condensation harder. We also study the holographic conductivity of the system and disclose the effects of the Gauss–Bonnet and nonlinear parameters \(\alpha \) and b on the superconducting gap. We observe that, for various values of \(\alpha \) and b, the real part of the conductivity is proportional to the frequency per temperature, \(\omega /T\), as the frequency is large enough. Besides, the conductivity has a minimum in the imaginary part which is shifted toward greater frequency with decreasing temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
The correspondence between the gravity in a d-dimensional anti-de Sitter (AdS) spacetime and the conformal field theory (CFT) residing on the (\(d-1\))-dimensional boundary of this spacetime, known as the AdS/CFT correspondence, provides an established method for calculating correlation functions in a strongly interacting field theory using a dual classical gravity description [1,2,3]. It has been confirmed that this duality can be applied to solving the problem of high temperature superconductors in condensed matter physics [4]. This is due to the fact the high temperature superconductors are basically in a strong coupling regime, and thus one expects that the holographic method could give some insights into the pairing mechanism in these systems. Understanding the mechanism of high temperature superconductors has long been a mysteries problem in modern condensed matter physics. Recently, it was suggested that it is logical to understand the properties of high temperature superconductors on the boundary of spacetime by considering classical general relativity in one higher dimension. This idea is called holographic superconductors (HSCs) [5,6,7] and has got a lot of attention in the past decade. According to the HSC proposal, on the gravity side, a Maxwell field and a charged scalar field are introduced to describe the U(1) symmetry and the scalar operator in the dual field theory, respectively. This holographic model undergoes a phase transition from a black hole with no hair (normal phase/conductor phase) to the case with scalar hair at low temperatures (superconducting phase) [8].
Nowadays, the investigations on the HSC have attracted considerable attention and have become an active field of research. Let us review some work in this direction. In the background of Schwarzschild AdS black holes in Einstein gravity, the properties of HSCs have been explored in [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The studies were also generalized to higher-order gravity theories such as Gauss–Bonnet gravity [17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. It was argued that the critical temperature of the HSC decreases with increasing the backreaction, although the effect of the Gauss–Bonnet coupling is more subtle: the critical temperature first decreases then increases as the coupling tends towards the Chern–Simons value in a backreaction dependent fashion [20]. It was confirmed that the critical exponent of the condensation in Gauss–Bonnet HSCs still obeys the mean field theory and has the value 1 / 2 [19]. Other studies on the holographic superconductor have been carried out (see for example [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] and the references therein).
It is also interesting to investigate the electrical conductivity of HSC in the dual CFT as a function of frequency. In the AdS/CFT correspondence, the electrical conductivity can be computed by looking at the linear response of the system to fluctuations of the fields \(A_{x}\) and \(g_{tx}\) in the bulk. These fluctuations are dual to the electric current \(J_{x}\) and energy current \(T_{tx}\) operators in the CFT. In the context of linear Maxwell field, the conductivity of HSC was computed in [4, 6, 7]. In the presence of nonlinear electrodynamics, the conductivity of HSC has been investigated in [50, 51]. Also, in the context of Born–Infeld nonlinear electrodynamics, the optical properties of Lifshitz HSC have been explored in [52]. It was demonstrated that this superconductor exhibits a metamaterial property for low frequency of the external electric field for a certain region of the nonlinear parameter. The effects of the Weyl coupling parameter and the Lifshitz dynamic exponent on the conductivity of HSC have been explored in [53]. In Ref. [54], rotating BTZ black holes were considered as the gravity dual to a \((1+1)\) dimensional superconductor. In this case, the dependence on the angular momentum on the conductivity has been investigated. Recently, the authors of [55] have analytically computed the holographic conductivity of HSCs in the presence of Born–Infeld nonlinear electrodynamics by considering the backreaction of the matter field on the bulk metric. Further investigations on the holographic conductivity of HSCs have been performed in [56, 57].
In this work, we will address the effects of the higher-order corrections on the holographic conductivity of the s-wave HSC. On the gravity side, we will consider the Gauss–Bonnet curvature correction terms which is the most general action in the 5D spacetime and on the gauge field side we add the quadratic nonlinear gauge term. We shall investigate the effects of these correction terms on the imaginary and real parts of the electrical conductivity of the system. With these correction terms, especially including a Gauss–Bonnet correction to the 5D action, we have the most general action with second-order field equations in 5D [58], which provides the most general model for a s-wave HSC. Furthermore, in an effective action approach to string theory, the Gauss–Bonnet term corresponds to the leading-order quantum corrections to gravity, and its presence guarantees a ghost-free action [59]. The purpose of this work is to analytically and numerically explore the effects of these correction terms on the properties of the s-wave HSC.
The plan of the work is as follows. In Sect. 2, we set up our model of the HSC in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with nonlinear electrodynamics in the probe limit and derive the equations of motion. In Sect. 3, we analytically and numerically compute the relationship between the critical temperature and the charge density of Gauss–Bonnet HSC. In Sect. 4, we study condensation operator near the critical temperature using analytical and numerical method. In Sect. 5 we investigate the electrical conductivity of the HSC in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with a nonlinear correction term to the Maxwell field. In particular, we shall find the ratio of the gap frequency in conductivity to the critical temperature. Finally, we summarize and discuss our results in Sect. 6.
2 HSC in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with nonlinear electrodynamics
We consider the 5D Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity in the background of AdS spaces which is described by the action [60]
where \(\Lambda =-6/l^{2}\) is the cosmological constant of 5-dimensional AdS spacetime with radius l, \(\alpha \) is the Gauss–Bonnet coefficient with dimension \((\mathrm{length})^2\), \(R_{\mu \nu \rho \sigma }\), \(R_{\mu \nu } \) and R are the Riemann curvature tensor, Ricci tensor, and the Ricci scalar, respectively. For convenience, hereafter we set the AdS radius \(l=1\). We consider the Lagrangian density of the matter field, \(L_{M}\), as
where \(\psi \) is a scalar field, q and m are, respectively, the charge and the mass of the scalar field, and the Lagrangian density of the nonlinear electrodynamics is given by [61, 62]
where \(\mathcal {F}=-\frac{1}{4}F^{\mu \nu }F_{\mu \nu }\) is the Maxwell Lagrangian and b is a parameter. The term \(b\mathcal {F}^{2}\) is the first-order leading nonlinear correction term to the Maxwell field. There are several motivations for choosing the nonlinear Lagrangian in the form of (3). First, the series expansion of the three well-known Lagrangians of nonlinear electrodynamics such as Born–Infeld, logarithmic and exponential nonlinear electrodynamics have the form of (3) [63]. Second, calculating a one-loop approximation of QED, it was shown [64] that the effective Lagrangian is given by (3). Besides, if one neglects all other gauge fields, one may arrive at the effective quadratic order of U(1) as \(\mathcal {F}^{2}\) [65, 66]. Furthermore, considering the next-order correction terms in the heterotic string effective action one can obtain the \(\mathcal {F}^{2}\) term as a correction to the bosonic sector of supergravity, which has the same order as the Gauss–Bonnet term [65,66,67,68],
The field equations can be obtained by varying the action (1) with respect to the metric \(g_{\mu \nu }\), the scalar field \(\psi \), and the gauge field \(A_{\mu }\). We find
where \(T_{\mu \nu }\) is the matter-stress tensor
The metric of a planar Schwarzschild–AdS black hole in 5D is [69]
with
The Hawking temperature at the horizon can be written in the form
It is worthwhile to note that in the limit \(r\rightarrow \infty \), we can obtain
so we can introduce the effective AdS radius by
We choose the gauge and the scalar fields in the form [4]
Inserting the metric (9) and the gauge and scalar fields (14) in the field equations (6) and (7), we arrive at
The horizon radius is defined as the root of \(f(r_{+})=0\). The regularity condition for the gauge field \(A_{t}\) on the horizon \(r_{+}\) implies the boundary condition \(\phi (r_+)=0\), which substituting in Eq. (15) yields
Near the AdS boundary (\(r\rightarrow \infty \)) the asymptotic behaviors of the solutions are given by
where \(\Delta _{\pm } =2\pm \sqrt{4+m^{2}L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}^{2}}\). It is clear that we should have \(m^{2}L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}^{2}\ge -\,4\). The value of \(\Delta _{\pm }\) depend on \(\tilde{m}^2=m^{2}L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}^{2}\). For example, setting \(\tilde{m}^2=-3\), we have \(\Delta _+=3\) and \(\Delta _-=1\). The coefficients \(\psi _{\pm }\) correspond to the vacuum expectation values of the condensate operator, namely \(\psi _{\pm }=<\mathcal {O}_{\pm }>\), where \(\mathcal {O}_{\pm }\) is the dual operator to the scalar field with the conformal dimension \(\Delta _{\pm }\). Following [4], we can impose the boundary condition in which either \(\psi _-\) or \(\psi _+\) vanishes, so that the theory is stable in the asymptotic AdS region. In what follows, we set \(\psi _{-}=0 \) and take \(\psi _{+}=\langle \mathcal {O}_{+} \rangle \) non-zero. The interpretation of the parameters \(\mu \) and \(\rho \), also comes from the gauge/gravity dictionary and they are, respectively, interpreted as the chemical potential and charge density of the conformal field theory on the boundary.
3 Relation between critical temperature and charge density
In this section, we are going to study the critical temperature of HSC, when the higher-order corrections to the gravity side and the gauge field are taken into account. We shall continue our study both analytically and numerically and compare the results of the two methods.
3.1 Analytical method
Here, we analytically obtain the relation between the critical temperature and the charge density of Gauss–Bonnet HSC. To do this, we first transform the coordinate r to z, such that \(z={r_{+}}/{r}\). Using these new coordinates, the equations of motion (15) and (16) can be rewritten as
Near the critical temperature (\(T=T_{c}\)) we have \(\psi =0\), and thus Eq. (20) reduces to
Solving the above equation for a small value of the nonlinear parameter b, we find
where
Next, we consider the boundary conditions for \(\psi \) near the critical point (\(T\rightarrow T_{c}\)). We assume \(\psi \) has the following form [70]:
where F(z) is the trial function near the boundary \(z=0\), which satisfies the boundary conditions \(F(0)=1\) and \(F^{\prime }(0)=0\). Substituting Eqs. (23) and (25) in Eq. (21) one arrives at
where the prime now indicates the derivative with respect to z, and p(z), q(z) and w(z) read
It is a matter of calculations to convert Eq. (26) to the standard form of the Sturm–Liouville equation,
where
In the above equations we have only kept the terms up to order \(\alpha ^{3/2} \). Next, we perform a perturbative expansion \(b\lambda ^{2}\) and retain only the terms that are linear in b such that
where \(\lambda ^{2}|_{b=0}\) is the value of \(\lambda ^{2}\) for \(b=0\). Thus we can rewrite Eq. (33) as
Employing the Sturm–Liouville eigenvalues problem, the eigenvalues of Eq. (30) can be obtained by varying the following function:
where we also choose \(F(z)=1-az^{2}\) and \(m^{2}=-3/L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}^{2}\) to assess this expression. Finally, using Eqs. (11) and (24), for \(T\sim T_{c}\), one can obtain
where \(\zeta =\frac{1}{\pi \lambda _{{\mathrm {min}}}^{1/3}}\) and \(\lambda _{{\mathrm {min}}}\) is the minimum eigenvalue which can be obtained by variation of Eq. (36). Our strategy, in the analytical method, for calculating the critical temperature for condensation is to minimize the function (36) with respect to the coefficient a by fixing other parameters of the model such as b and \(\alpha \). Then we obtain \(\lambda _{{\mathrm {min}}}\) and hence the maximum value of \(T_{c}/\rho ^{1/3}\) can be deduced through Eq. (37). As an example, we present the details of our calculation for \(\alpha =0.01\) and \(b=0.01\). In this case Eq. (36) reduces to
whose minimum is \(\lambda _{{\mathrm {min}}}=25.6427\) at \(a =0.747087\). And thus according to Eq. (37), the critical temperature becomes \(T_{c}=0.185363\rho ^{1/3}\). In Tables 1, 2 and 3, we summarize our results for \(\lambda _{{\mathrm {min}}}\) and \(\zeta \) for different values of the parameters \(\alpha \), a and b. This table shows that, for a small and fixed value of \(\alpha \), with increasing the nonlinear parameter b, the value of \(\zeta =T_{c}/\rho ^{1/3}\) decreases as well. As we shall see in the next section this result is in a very good agreement with the numerical results.
3.2 Numerical method
Now, we numerically investigate the critical behavior of the HSC in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with a quadratic correction term to the gauge field. For the numerical study we employ the shooting method [71]. For simplicity we assume \(r_{+}=1\), and thus Eqs. (20) and (21) for \(\phi \) and \(\psi \) reduce to
Near the horizon (\(z=1\)), we can expand \(\phi \) and \(\psi \) as
while near the AdS boundary (\(z=0\)), they behave like
We calculate \(\phi ^{^{\prime \prime }}(1)\), \(\psi ^{^{\prime }}(1)\) and \(\psi ^{^{\prime \prime }}(1)\) in the term of \(\psi (1)\) and \(\phi ^{^{\prime }}(1)\) by using the equations of motion for \(\phi \) and \(\psi \), namely Eqs. (39) and (40), respectively. Since near the critical point \(\psi \) is very small, thus we choose \(\psi (1)=0.0001\). Our strategy for using the shooting method is as follows. For a specific value of the reduced scalar field mass \(\tilde{m}^{2}\), we can perform a numerical calculation near the horizon boundary with one shooting parameter \(\phi ^{^{\prime }}(1)\) to get proper solutions at the infinite boundary. For specific values of \(\phi ^{^{\prime }}(1)\), we impose the boundary condition \(\psi _{-}=0\). We also calculate the analytical values and numerical values of \(\zeta \) for different b. We compare our numerical results with analytical results in Tables 1, 2 and 3.
In Fig. 1, we plot \(\psi \) versus z for three first boundary condition \(\phi ^{^{\prime }}(1)\), \(\tilde{m}^{2}=-3\) and different values of the Gauss–Bonnet coefficient \(\alpha \) and nonlinear parameter b. In the absence of a quadratic correction term (\(b=0\)), our results exactly coincide with those presented in [19, 24]. The acceptable diagram for us is the red one in each plot, since there is nothing in the bulk to have effect on the speed of the wave, so the diagram of \(\psi \) will be stable. From Tables 1, 2 and 3, it is evident that when b becomes larger the condensation gets harder. A similar behavior can be seen for the fixed value of b and different values of \(\alpha \), namely the critical temperature reduces and condensation becomes harder when the Gauss–Bonnet coupling parameter \(\alpha \) gets larger.
4 Critical exponent and condensation values
In this section, our aim is to calculate the critical exponent of HSC with first-order correction terms in gravity and gauge field. Again, we continue our studying both analytically and numerically.
4.1 Analytical method
We would like to obtain the critical exponent and the condensation values of the condensation operator near the critical temperature using the analytical method. Inserting Eq. (25) into Eq. (20), we get
and
Near the critical temperature, \(\frac{\langle \mathcal {O}_{+} \rangle ^{2}}{r_{+}^{4}}\) is a very small and thus we can expand \(\phi (z)\) as
where \(\chi \) satisfies the following boundary condition:
With the help of Eq. (47), and comparing the coefficient of \(\frac{\langle \mathcal {O}_{+} \rangle ^{2}}{r_{+}^{4}}\) on both sides, Eq. (45) leads to
From Eq. (49) we figure out, in the limit \(z\rightarrow 0\), the following equation:
It is a matter of calculations to show that Eq. (49) can be written
where \(\Gamma (z)=1+z^{2}+z^{4}+25z^{6}\). Integrating both sides of the above equation in the interval [0, 1] and using the boundary condition (48), we arrive at
where
Combining Eqs. (18) and (47), we obtain
where in the last step we have expanded \(\chi (z)\) around \(z = 0\). Equating the coefficients of \(z^2\) on both sides of Eq. (53), we find
Using \(\lambda ={\rho }/{r^3_{+c}}\) and definition (11), we can obtain the order parameter \(\langle \mathcal {O}_{+} \rangle \) near the critical temperature \(T_{c}\) as
where
From Eq. (55) we observe that the critical exponent has the mean field value 1 / 2, which is independent of the nonlinear parameter b and Gauss–Bonnet parameter \(\alpha \). It is worth noting that \(\langle \mathcal {O} \rangle \) is zero at \(T = T_{c}\) and condensation occurs for \(T < T_{c}\). We shall come back to calculation of the condensation value \(\gamma \) in the next subsection.
4.2 Numerical method
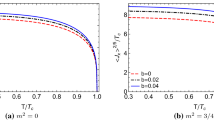
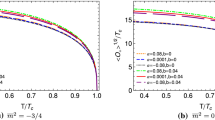
We use the numerical method to explore the behavior of the condensate operator \(\langle \mathcal {O}_{+}\rangle \) in terms of temperature for different values of \(\alpha \) and b (see Fig. 2). These curves are obtained by the shooting method which we described in the previous section. As one can see from this figure there is a critical temperature \(T_{c}\) below which the condensate appears, then it increases quickly as the system is cooled and finally goes to a constant for sufficiently low temperatures. This behavior is qualitatively similar to that obtained in BCS theory and observed in many materials.
Now we are going to study the condensation operator \(\langle \mathcal {O}_{+}\rangle \) in a close neighborhood of the superconductor’s critical temperature to compute the critical exponents and the condensation value \(\gamma \) of the Gauss–Bonnet HSC with quadratic nonlinear electromagnetic. For this purpose, we first take the logarithm of Eq. (55). We arrive at
We have plotted the behavior of the above function in Fig. 3. From this figure, we observe that the numerical results are fitted to the above analytic form in the vicinity of the critical temperature. We summarize our results in Fig. 3 and also Tables 4, 5 and 6 for different values of b and \(\alpha \). We see that, for a fixed value of \(\alpha \), the condensation operator \(\gamma \) increases with increasing b, while for a fixed value of b, it decreases with increasing \(\alpha \).
5 Holographic conductivity
In this section, we study the energy gap in the holographic superconductor phase which is constructed on the boundary of the background spacetime. In particular, we investigate the influence of the Gauss–Bonnet and nonlinear parameters on the superconducting gap. In order to do this, we must compute the electrical conductivity of holographic superconductor by turning on a small perturbation \(\delta A_{x}=A_{x}(r)\exp (-i\omega t)\) to the gauge field in the bulk where \(\omega \) is the frequency. At linearized order in the perturbation (\(\delta A_{x}\)), the equation of motion for the gauge field \(A_{x}(r)\), which obeys Eq. (7), is
In the absence of the nonlinear correction (\(b=0\)), this differential equation reduces to the Maxwell case as presented in [4, 5]. To determine the conductivity, we need the asymptotic (\(r\rightarrow \infty \)) form of the second-order differential equation (58),
which admits the following solution near the boundary:
where \(A_{x}^{(0)}\), \(A_{x}^{(1)}\) are two constants and K is also a constant parameter with length dimension which is considered so as to have a dimensionless logarithmic argument.
According to the AdS/CFT correspondence, the two point correlation function of the current operators in a system is given by its on-shell action where the action is evaluated on the equations of motion. Here, the on-shell action is
which, in the quadratic approximation for the gauge field perturbation, becomes
After performing an integration by parts and using Eq. (58), we get
Substituting Eqs. (12), (18) and (60) in the above expression, one arrives at
thus we can obtain \(S_\mathrm{o.s.}\) as follows:
in which logarithmic divergences appears. In order to cancel out this divergence, we obtain the boundary counterterm as described in the appendix by using Skenderis’ method of holographic renormalization [72]. Therefore, the finite on-shell action may be written as
where the gauge invariant counterterm \(S_\mathrm{c.t.}\) is given by Eq. (79). Now, we can obtain the current operator in the boundary field theory [4, 5] as
According to Ohm’s law, the electrical conductivity can be expressed as
where \(E_{x}=-\partial _{t}\delta A_{x}\). Hence, using the current (67), the holographic conductivity is given by
Consequently, the holography conductivity is calculated by solving numerically a differential equation (58) such that the in-falling boundary condition is imposed at the event horizon
in which T is the Hawking temperature and
where \(a_{1},a_{2},\ldots \) are calculated by Taylor series expansion of Eq. (58) around the horizon.
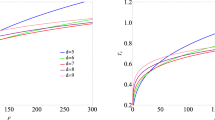
The numerical results for holographic conductivity associated with the condensation operator \(<\mathcal {O}_{+}>\) are plotted in Figs. 4, 5, 6 and 7. The real and imaginary parts of the electrical conductivity versus frequency are illustrated at different temperatures below \(T_c\) in Figs. 4 and 5, respectively. As one can see from Fig. 4, the superconducting gap has opened below the critical temperature, which became deeper with decreasing the temperature. Besides, for various values of \(\alpha \) and b, the real part of the conductivity is proportional to the frequency per temperature, \(\omega /T\), as the frequency is large enough. According to Fig. 5 the divergence in the imaginary part, at \(\omega =0\), points out a delta function in the real part, \(Re[\sigma ]\), at \(\omega =0\), which is not displayed in Fig. 4. As one can see from Fig. 5, the holographic conductivity of the HSC has a minimum in the imaginary part. Thus with decreasing the temperature the minimum in the imaginary part shifts toward greater frequency for various values of the Gauss–Bonnet and nonlinear parameters.
To study the formation of the superconducting gap with changing \(\alpha \) and b at low temperature, e.g., \(T\approx 0.1T_c\), the real and the imaginary parts of holographic conductivity as a function of \(\omega /{<\mathcal {O}_{+}>}^{1/3}\) are plotted in Figs. 6 and 7, respectively. For a fixed value of the Gauss–Bonnet coefficient \(\alpha \), the energy gap (\(\omega /{<\mathcal {O}_{+}>}^{1/3}\)) enlarges with increasing nonlinear parameter b. It is evident from Figs. 6 and 7 that the energy gap of HSC for various \(\alpha \) exhibits different behaviors based on the nonlinear correction b. In the case of the Maxwell field (\(b=0\)), the superconducting energy gap decreases as \(\alpha \) increases at low temperature (see Fig. 6d). When we take into account the nonlinear correction b, the energy gap of the HSC increases with increasing \(\alpha \) (see Fig. 6d, g). From Fig. 7, we see that, for a fixed value of \(\alpha \), the minimum of the imaginary part of the conductivity goes to the larger value of \(\omega /<\mathcal {O}_{+}>^{1/3}\) when b increases. In the absence of a correction (\(b=0\)), it decreases with enhancing Gauss–Bonnet coefficient (Fig. 6d). Besides, for a fixed value of b, the minimum of \(\mathrm {Im[\sigma ]}\) increases with increasing \(\alpha \), while for a fixed value of \(\alpha \), it increases with increasing b.
6 Conclusions
In this paper, we continue the studies on the s-wave holographic superconductors (HSC) by taking into account the higher correction terms both on the gravity side and on the gauge field side of the system. We considered the Gauss–Bonnet HSC when the Maxwell Lagrangian has a nonlinear correction term and is written in the form \(\mathcal {L}=\mathcal {F}+b \mathcal {F}^2\), where \(\mathcal {F}\) is the Maxwell Lagrangian. We have provided several motivations for choosing this kind of Lagrangian for the gauge field. For example, all well-known nonlinear Lagrangians have a series expansion of which the first two terms are exactly in the above form.
First, we have analytically and numerically investigated the relation between the critical temperature of the phase transition and charge density which depends on both the Gauss–Bonnet parameter \(\alpha \) and the nonlinear parameter b. For this purpose, we employed the analytical Sturm–Liouville eigenvalue problem and the numerical shooting method. We find that, for a fixed value of \(\alpha \), with increasing nonlinear parameter b, the value of \(T_{c}/\rho ^{1/3}\) decreases. This implies that when b becomes larger, the condensation gets harder. A similar behavior can be seen for the fixed value of b and different values of \(\alpha \), namely the critical temperature decreases and the condensation becomes harder when the Gauss–Bonnet coupling parameter \(\alpha \) gets larger. We confirmed that these results are in a very good agreement with our numerical results. Then we obtained the critical exponent of the Gauss–Bonnet HSC with a nonlinear gauge field. We observed that the critical exponent has the mean field value 1 / 2, which is independent of the nonlinear parameter b and the Gauss–Bonnet parameter \(\alpha \).
Then we explored, numerically, the holographic conductivity of the system. For this purpose, we plotted the real and imaginary parts of the electrical conductivity versus \(\omega /T\) and \(\omega /<\mathcal {O}_{+}>^{1/3}\) for \(T<T_c\). We observed that the superconducting gap has opened below the critical temperature, which became deeper with decreasing the temperature. Interestingly enough, we found that, for different values of \(\alpha \) and b, and for large frequency, the real part of the conductivity is proportional to \(\omega /T\). We observed that the holographic conductivity of HSC has a minimum in the imaginary part. Besides, with decreasing the temperature the minimum in the imaginary part shifts toward greater frequency for various values of the Gauss–Bonnet parameter \(\alpha \) and the nonlinear gauge field parameter b. Furthermore, for a fixed value of b, the minimum of \(\mathrm {Im[\sigma ]}\) increases with increasing \(\alpha \), while for a fixed value of \(\alpha \), it increases with increasing b.
References
J. Maldacena, The large \(N\) limit of superconformal field theories and supergravity. Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 2, 231 (1998). arXiv:hep-th/9711200
S.S. Gubser, I.R. Klebanov, A.M. Polyakov, Gauge theory correlators from non-critical string theory. Phys. Lett. B 428, 105 (1998). arXiv:hep-th/9802109
E. Witten, Anti de sitter space and holography. Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 2, 253 (1998). arXiv:hep-th/9802150
S.A. Hartnoll, C.P. Herzog, G.T. Horowitz, Building a holographic superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 031601 (2008). arXiv:0803.3295
G.T. Horowitz, M.M. Roberts, Holographic superconductors with various condensates. Phys. Rev. D 78, 126008 (2008). arXiv:0810.1563
S.A. Hartnoll, C.P. Herzog, G.T. Horowitz, Holographic superconductors. JHEP 12, 015 (2008). arXiv:0810.1563
G.T. Horowitz, Introduction to holographic superconductors. Lect. Notes Phys. 828, 313 (2011). arXiv:1002.1722
S.S. Gubser, Breaking an Abelian gauge symmetry near a black hole horizon. Phys. Rev. D 78, 065034 (2008). arXiv:0801.2977
D. Musso, Introductory notes on holographic superconductors. arXiv:1401.1504
R.G. Cai, L. Li, Li-Fang Li, Run-Qiu Yang, Introduction to holographic superconductor models. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 060401 (2015). arXiv:1502.00437
X.H. Ge, B. Wang, S.F. Wu, G.H. Yang, Analytical study on holographic superconductors in external magnetic field. JHEP 08, 108 (2010). arXiv:1002.4901
R. Banerjee, S. Gangopadhyay, D. Roychowdhury, A. Lala, Holographic \(s\)-wave condensate with non-linear electrodynamics: a nontrivial boundary value problem. Phys. Rev. D 87, 104001 (2013). arXiv:1208.5902v3
D. Momeni, M. Raza, R. Myrzakulov, More on superconductors via gauge/gravity duality with nonlinear Maxwell field. J Gravity 2013, Article ID 782512
C.M. Chen, M.F. Wu, An analytic analysis of phase transitions in holographic superconductors. Prog. Theor. Phys. 126, 387 (2011). arXiv:1103.5130
H.B. Zeng, X. Gao, Y. Jiang, H.S. Zong, Analytical computation of critical exponents in several holographic superconductors. JHEP 1105, 002 (2011). arXiv:1012.5564
R.G. Cai, H.F. Li, H.Q. Zhang, Analytical studies on holographic insulator/superconductor phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 83, 126007 (2011). arXiv:1103.5568
Q. Pan, B. Wang, E. Papantonopoulos, J. Oliveira, A.B. Pavan, Holographic superconductors with various condensates in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 81, 106007 (2010). arXiv:0912.2475
Q. Pan, B. Wang, General holographic superconductor models with Gauss–Bonnet corrections. Phys. Lett. B 693, 159 (2010). arXiv:1005.4743
H.F. Li, R.G. Cai, H.Q. Zhang, Analytical studies on holographic superconductors in Gauss–Bonnet gravity. JHEP 04, 028 (2011). arXiv:1103.2833
L. Barclay, R. Gregory, S. Kanno, P. Sutcliffe, Gauss–Bonnet holographic superconductors. JHEP 1012, 029 (2010). arXiv:1009.1991
R.G. Cai, Z.Y. Nie, H.Q. Zhang, Holographic \(p\)-wave superconductors from Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 82, 066007 (2010). arXiv:1007.3321
R.G. Cai, Z.Y. Nie, H.Q. Zhang, Holographic phase transitions of \(p\)-wave superconductors in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with back-reaction. Phys. Rev. D 83, 066013 (2011). arXiv:1012.5559
Q. Pan, J. Jing, B. Wang, Analytical investigation of the phase transition between holographic insulator and superconductor in Gauss–Bonnet gravity. JHEP 11, 088 (2011). arXiv:1105.6153
R. Gregory, S. Kanno, J. Soda, Holographic superconductors with higher curvature corrections. JHEP 0910, 010 (2009). arXiv:0907.3203
R.G. Cai, Z.Y. Nie, H.Q. Zhang, Holographic \(p\)-wave superconductors from Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 82, 066007 (2010). arXiv:1007.3321
R.G. Cai, H.F. Li, H.Q. Zhang, Analytical studies on holographic insulator/superconductor phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 83, 126007 (2011). arXiv:1103.5568
R.G. Cai, L. Li, L.F. Li, A holographic \(p\)-wave superconductor model. JHEP 1401, 032 (2014). arxiv:1309.4877
X.H. Ge, S.F. Tu, B. Wang, \(d\)-Wave holographic superconductors with backreaction in external magnetic fields. JHEP 09, 088 (2012). arXiv:1209.4272
X.M. Kuang, E. Papantonopoulos, G. Siopsis, B. Wang, Building a holographic superconductor with higher-derivative couplings. Phys. Rev. D 88, 086008 (2013). arXiv:1303.2575
Q. Pan, J. Jing, B. Wang, S. Chen, Analytical study on holographic superconductors with backreactions. JHEP 06, 087 (2012). arXiv:1205.3543
Q. Pan, J. Jing, B. Wang, Analytical investigation of the phase transition between holographic insulator and superconductor in Gauss–Bonnet gravity. JHEP 11, 088 (2011). arXiv:1105.6153
M. Kord Zangeneh, Y.C. Ong, B. Wang, Entanglement entropy and complexity for one-dimensional holographic superconductors. Phys. Lett. B 771, 235 (2017). arXiv:1704.00557
W. Yao, J. Jing, Analytical study on holographic superconductors for Born–Infeld electrodynamics in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with backreactions. JHEP 05, 101 (2013). arXiv:1306.0064
J. Jing, L. Wang, Q. Pan, S. Chen, Holographic superconductors in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with Born–Infeld electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 83, 066010 (2011). arXiv:1012.0644
J. Jing, Q. Pan, S. Chen, Holographic superconductor/insulator transition with logarithmic electromagnetic field in Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Phys. Lett. B 716, 385 (2012). arXiv:1209.0893
S. Chen, Q. Pan, J. Jing, Holographic superconductors in quintessence AdS black hole. Class. Quantum Gravity 30, 145001 (2013). arXiv:1206.2069
S. Gangopadhyay, D. Roychowdhury, Analytic study of properties of holographic \(p\)-wave superconductors. JHEP 08, 104 (2012). arXiv:1207.5605
A. Sheykhi, H.R. Salahi, A. Montakhab, Analytical and numerical study of Gauss–Bonnet holographic superconductors with Power–Maxwell field. JHEP 04, 058 (2016). arXiv:1603.00075
H.R. Salahi, A. Sheykhi, A. Montakhab, Effects of backreaction on Power–Maxwell holographic superconductors in Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 76, 575 (2016). arXiv:1608.05025
A. Sheykhi, F. Shaker, Analytical study of properties of holographic superconductors with exponential nonlinear electrodynamics. Can. J. Phys. 94(12), 1372 (2016). arXiv:1601.05817
A. Sheykhi, F. Shamsi, Holographic superconductors with logarithmic nonlinear electrodynamics in an external magnetic field. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 916 (2017). arXiv:1603.02678
A. Sheykhi, F. Shamsi, S. Davatolhagh, The upper critical magnetic field of holographic superconductor with conformally invariant Power–Maxwell electrodynamics. Can. J. Phys. 95, 450 (2017). arXiv:1609.05040
R.A. Konoplya, A. Zhidenko, Holographic conductivity of zero temperature superconductors. Phys. Lett. B 686, 199 (2010). arXiv:0909.2138
X.M. Kuang, W.J. Li, Y. Ling, Holographic superconductors in quasi-topological gravity. JHEP 12, 69 (2010). arXiv:1008.4066
M.R. Setare, D. Momeni, N. Majd, Holographic superconductors in a model of non-relativistic gravity. JHEP 5, 118 (2011). arXiv:1003.0376
J.P. Wu, Y. Cao, X.M. Kuang, W.J. Li, The (3+1)-holographic superconductor with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 697, 153 (2011). arXiv:1010.1929
M.R. Setare, D. Momeni, Gauss–Bonnet holographic superconductors with magnetic field. Eur. Phys. Lett. 96, 60006 (2011). arXiv:1106.1025
D. Ma, Y. Cao, J.P. Wu, The Stuckelberg holographic superconductors with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 704, 604 (2011). arXiv:1201.2486
J.P. Wu, P. Liu, Holographic superconductivity from higher derivative theory. Phys. Lett. B 774, 527 (2017). arXiv:1710.07971
A. Dehyadegari, A. Sheykhi, M.K. Zangeneh, Holographic conductivity for logarithmic charged dilaton-Lifshitz solutions. Phys. Lett. B 758, 226 (2016). arXiv:1602.08476
A. Dehyadegari, M. Kord Zangeneh, A. Sheykhi, Holographic conductivity in the massive gravity with power-law Maxwell field. Phys. Lett. B 773, 344 (2017). arXiv:1703.00975
M. Kord Zangeneh, S.S. Hashemi, A. Dehyadegari, A. Sheykhi, B. Wang, Optical properties of Born–Infeld-dilaton-Lifshitz holographic superconductors. arXiv:1710.10162
S.A. Hosseini Mansoori, B. Mirza, A. Mokhtari, F. Lalehgani Dezaki, Z. Sherkatghanad, Weyl holographic superconductor in the Lifshitz black hole background. JHEP 1607, 111 (2016). arXiv:1602.07245
P. Chaturvedi, G. Sengupta, Rotating BTZ black holes and one dimensional holographic superconductors. Phys. Rev. D 90, 046002 (2014). arXiv:1310.5128
D. Ghorai, S. Gangopadhyay, Conductivity of holographic superconductors in Born–Infeld electrodynamics. arXiv:1710.09630
K. Lin, E. Abdalla, A. Wang, Holographic superconductors in Horava–Lifshitz gravity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 24, 1550038 (2015). arXiv:1406.4721
C.-J. Luo, X.-M. Kuang, F.-W. Shu, Lifshitz holographic superconductor in Horava–Lifshitz gravity. Phys. Lett. B 759, 184 (2016). arXiv:1605.03260
D. Lovelock, J. Math. Phys. 12, 498 (1971)
B. Zwiebach, Phys. Lett. B 156, 315 (1985)
S. Gangopadhyay, D. Roychowdhury, Analytic study of properties of holographic superconductors in Born–Infeld electrodynamics. JHEP 5, 2 (2012). arXiv:1201.6520
S.H. Hendi, S. Panahiyan, Thermodynamic instability of topological black holes in Gauss–Bonnet gravity with a generalized electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 90, 124008 (2014). arXiv:1501.05481 [gr-qc]
S.H. Hendi, S. Panahiyan, M. Momennia, Extended phase space of AdS black holes in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity with a quadratic nonlinear electrodynamics. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 25, 1650063 (2016). arXiv:1503.03340
S.H. Hendi, Asymptotic charged BTZ black hole solutions. JHEP 03, 065 (2012)
A. Ritz, R. Delbourgo, The low-energy effective Lagrangian for photon interactions in any dimension. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 11, 253 (1996). arXiv:hep-th/9503160
J.T. Liu, P. Szepietowski, Higher derivative corrections to R-charged AdS5 black holes and field redefinitions. Phys. Rev. D 79, 084042 (2009). arXiv:0806.1026
Y. Kats, L. Motl, M. Padi, Higher-order corrections to mass-charge relation of extremal black holes. JHEP 12, 068 (2007). arXiv:hep-th/0606100
D. Anninos, G. Pastras, Thermodynamics of the Maxwell–Gauss–Bonnet anti-de Sitter black hole with higher derivative gauge corrections. JHEP 07, 030 (2009). arXiv:0807.3478
R.G. Cai, Z.-Y. Nie, Y.-W. Sun, Shear viscosity from effective couplings of gravitons. Phys. Rev. D 78, 126007 (2008). arXiv:0811.1665
R.G. Cai, Gauss–Bonnet black holes in AdS spaces. Phys. Rev. D 65, 084014 (2002). arXiv:hep-th/0109133
S. Gangopadhyay, D. Roychowdhury, Analytic study of Gauss–Bonnet holographic superconductors in Born–Infeld electrodynamics. JHEP 05, 156 (2012). arXiv:1204.0673
S.A. Hartnoll, Lectures on holographic methods for condensed matter physics. Class. Quantum Gravity 26, 224002 (2009). arXiv:0903.3246
K. Skenderis, Lecture notes on holographic renormalization. Class. Quantum Gravity 19, 5849 (2002). arXiv:hep-th/0209067
L. Barclay, R. Gregory, S. Kanno, P. Sutcliffe, Gauss–Bonnet holographic superconductors. JHEP 12, 29 (2010). arXiv:1009.1991
J.R. Sun, S.Y. Wu, H.Q. Zhang, Novel features of the transport coefficients in Lifshitz black branes. Phys. Rev. D 87, 086005 (2013). arXiv:1302.5309
Acknowledgements
We thank the Research Council of Shiraz University. The work of AS has been supported financially by Research Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics of Maragha (RIAAM), Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Holographic renormalization
Appendix: Holographic renormalization
To construct the boundary counterterm action, we utilize the holographic renormalization method of Skenderis, which was presented in [72,73,74]. To apply this method, the spacetime metric takes the form
which relates to the metric (9) via \(\tau =t/L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}\), \(\varrho =L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}^{2}/r\) and the asymptotic (\(\varrho \rightarrow 0\)) metric function is \(\mathcal {X}(\varrho )_{\varrho \rightarrow 0}=1\). Hence, the asymptotically metric becomes
where
According to the electromagnetic contribution, one can evaluate the on-shell action as
where \(\epsilon \) is a small constant parameter. On the new coordinates (72), the gauge field equation of the bulk motion near the boundary is given by
where \(\partial _{0}^{2}\) refers to the wave operator of the boundary metric \(\gamma _{\mu \nu }^{0}\) and the general solution of this equation is
where \(\psi =-1/4\partial _{0}^{2}A_{i}^{0}\). With \(A_{i}\) at hand, the on-shell electromagnetic action can be written as
which is logarithmically divergent. Now, according to Ref. [72], in order to determine the counterterm action, we first invert the solution (77) to find \(A_{i}^{0}=A_{i}+\mathcal {O}(\epsilon )\). Thus, the counterterm action is obtained:
It is notable that, since we consider \(A_{i}=A_{i}(\varrho )\exp (-i\omega L_{{\mathrm {eff}}}\tau )\), one can calculate
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Funded by SCOAP3
About this article
Cite this article
Sheykhi, A., Ghazanfari, A. & Dehyadegari, A. Holographic conductivity of holographic superconductors with higher-order corrections. Eur. Phys. J. C 78, 159 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-018-5650-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-018-5650-2