Abstract
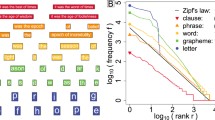
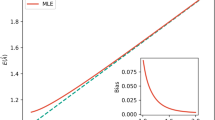
We show that the Zipf’s law for Chinese characters perfectly holds for sufficiently short texts (few thousand different characters). The scenario of its validity is similar to the Zipf’s law for words in short English texts. For long Chinese texts (or for mixtures of short Chinese texts), rank-frequency relations for Chinese characters display a two-layer, hierarchic structure that combines a Zipfian power-law regime for frequent characters (first layer) with an exponential-like regime for less frequent characters (second layer). For these two layers we provide different (though related) theoretical descriptions that include the range of low-frequency characters (hapax legomena). We suggest that this hierarchic structure of the rank-frequency relation connects to semantic features of Chinese characters (number of different meanings and homographies). The comparative analysis of rank-frequency relations for Chinese characters versus English words illustrates the extent to which the characters play for Chinese writers the same role as the words for those writing within alphabetical systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Wyllys, Library Trends 30, 53 (1981)
C.D. Manning, H. Schütze, Foundations of Statistical natural Language Processing (MIT Press, Cambridge, 1999)
H. Baayen, Word Frequency Distribution (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 2001)
W.T. Li, Glottometrics 5, 14 (2002)
N. Hatzigeorgiu, G. Mikros, G. Carayannis, J. Quantitative Linguistics 8, 175 (2001)
B.D. Jayaram, M.N. Vidya, J. Quantitative Linguistics 15, 293 (2008)
L. Lü, Z.K. Zhang, T. Zhou, PLoS ONE 5, e14139 (2010)
J. Baixeries, B. Elvevag, R. Ferrer-i-Cancho, PLoS ONE 8, e53227 (2013)
J.B. Estoup, Gammes Sténographiques (Institut Sténogra- phique de France, Paris, 1916)
R. Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. Solé, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100, 788 (2003)
M. Prokopenko et al., J. Stat. Mech. 2010, P11025 (2010)
B. Mandelbrot, An Information Theory of the Statistical structure of language, in Communication Theory, edited by W. Jackson (London, Butterworths, 1953)
B. Mandelbrot, Fractal Geometry of Nature (W.H. Freeman, New York, 1983)
B. Corominas-Murtra et al., Phys. Rev. E 83, 036115 (2011)
D. Manin, Cogn. Sci. 32, 1075 (2008)
G.A. Miller, Am. J. Psyc. 70, 311 (1957)
W.T. Li, IEEE Inform. Theory 38, 1842 (1992)
M.V. Arapov, Yu.A. Shrejder, in Semiotics and Informatics, (Moscow, VINITI, 1978), Vol. 10, p. 74
I. Kanter, D.A. Kessler, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4559 (1995)
B.M. Hill, J. Am. Stat. Ass. 69, 1017 (1974)
G. Troll, P. beim Graben, Phys. Rev. E 57, 1347 (1998)
A. Czirok et al., Phys. Rev. 53, 6371 (1996)
K.E. Kechedzhi et al., Phys. Rev. E 72, 046138 (2005)
A.E. Allahverdyan, W. Deng, Q.A. Wang, Phys. Rev. E 88, 062804 (2013)
D. Howes, Am. J. Psyc. 81, 269 (1968)
R. Ferrer-i-Cancho, B. Elveva, PLoS ONE 5, 9411 (2010)
K.H. Zhao, Am. J. Phys. 58, 449 (1990)
R. Rousseau, Q. Zhang, Scientometrics 24, 201 (1992)
D.H. Wang et al., Physica A 358, 545 (2005)
S. Shtrikman, J. Info. Sci. 20, 142 (1994)
Le Quan Ha et al., Extension of Zipf’s Law to Words and Phrases, in Proceedings of the 19th international conference on Computational linguistics (2002), Vol. 1, pp. 1–6
Q. Chen, J. Guo, Y. Liu, J. Quantitative Linguistics 19, 232 (2012)
D. Aaronson, S. Ferres, J. Memory and Language 25, 136 (1986)
H.C. Chen, Reading comprehension in Chinese, in Language processing in Chinese, edited by H.C. Chen, O.J.L. Tzeng (Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1992), pp. 175–205
R. Hoosain, Speed of getting at the phonology and meaning of Chinese words, in Cognitive Neuroscience Studies of Chinese Language, edited by H.S.R. Kao, C.K. Leong, D.G. Gao (Hong kong University Press, Hong kong, 2002)
G.K. Zipf, Selected Studies of the Principle of Relative Frequency in Language (Harvard University Press, Cambridge MA, 1932)
L. Lü, Z.K. Zhang, T. Zhou, Sci. Rep. 3, 1082 (2013)
C.K. Hu, W.C. Kuo, Universality and Scaling in the Statistical Data of Literary Works (POLA Forever, 2005), pp. 115–139
J. Elliott et al., Language identification in unknown signals, in Proceedings of the 18th conference on Computational linguistics (2000), Vol. 2, pp. 1021–1025
J. Elliot, E. Atwell, J. British Interplanetary Society 53, 13 (2000)
H.P. Luhn, IBM J. Res. Devel. 2, 159 (1958)
S.M. Huang et al., Decision Support Systems 46, 70 (2008)
D.M.W. Powers, Applications and explanations of Zipf’s law, in New Methods in Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (NEMLAP3/CONLL98), edited by D.M.W. Powers (ACL, 1998), pp. 151–160
G. Sampson, Linguistics 32, 117 (1994)
J. DeFrancis, Visible Speech: the Diverse Oneness of Writing Systems (University of Hawaii Press, Honulu, 1989)
J.L. Packard, The Morphology of Chinese: A linguistic and Cognitive Approach (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000)
K. Turner, Visualizing Zipf’s Law in Japanese, available at this link: http://classes.soe.ucsc.edu/cmps161/Winter12/projects/ katurner/proj/paper/paper.pdf
R. Hoosain, Psychological reality of the word in Chinese, in Language processing in Chinese, edited by H.C. Chen, J.L. Tseng (Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1992), pp. 111–130
I.M. Liu et al., Chinese J. Psyc. 16, 25 (1974)
S.H. Hsu, K.C. Huang, Perceptual and Motor Skills 91, 355 (2000)
S.H. Hsu, K.C. Huang, Perceptual and Motor Skills 90, 81 (2000)
X. Luo, A Maximum Entropy Chinese Character-based parser, in Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2003
Wm.C. Hannas, Asia’s Orthographic Dilemma (University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu, 1997)
C.Y. Chen et al., Some distributional properties of Madanrin Chinese, in Proceedings of the first Pasific Asia conference on Formal and Computational Linguistics, Taipei, 1993, p. 81
N.V. Obukhova, Quantitative Linguistics and Automatic Text Analysis (Proc. of Tartu university) 745, 119 (1986)
N.J.D. Nagelkerke, Biometrika 78, 691 (1991)
M.L. Goldstein, S.A. Morris, G.G. Yen, Eur. Phys. J. B 41, 255 (2004)
H. Bauke, Eur. Phys. J. B 58, 167 (2007)
A. Clauset, C.R. Shalizi, M.E.J. Newman, SIAM Rev. 51, 4 (2009)
R.E. Madsen et al., Modeling word burstiness using the Dirichlet distribution, in Proc. Intl. Conf. Machine Learning (2005)
S. Bernhardsson, L.E. Correa da Rocha, P. Minnhagen, Physica A 389, 330 (2010)
S. Bernhardsson, L.E. Correa da Rocha, P. Minnhagen, New J. Phys. 11, 123015 (2009)
T. Hofmann, Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis, in Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (1999)
W.J.M. Levelt et al., Beh. Brain Sciences 22, 1 (1999)
J. Tuldava, J. Quantitative Linguistics 3, 38 (1996)
D. Krallmann, Statistische Methoden in der Stilistischen Textanalyse (Inaug.-Dissert, Bonn, 1966)
S.K. Baek, S. Bernhardsson, P. Minnhagen, New J. Phys. 13, 043004 (2011)
Y. Dover, Physica A 334, 591 (2004)
E.V. Vakarin, J.P. Badiali, Phys. Rev. E 74, 036120 (2006)
E.T. Jaynes, IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybernet. 4, 227 (1968)
M. Jaeger, Int. J. Approx. Reas. 38, 217 (2005)
J. Haldane, Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 28, 55 (1932)
A.F. Healy, A. Drewnowski, Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 9, 413 (1983)
Reading Chinese Script: A Cognitive Analysis, edited by J. Wang, A.W. Imhoff, H.-C. Chen (Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, 1999)
A.N. Kolmogorov, Giornale dell’ Instituto Italiano degli Attuari 4, 77 (1933)
P.T. Nicholls, J. Am. Soc. Information Sci. 40, 379 (1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, W., Allahverdyan, A.E., Li, B. et al. Rank-frequency relation for Chinese characters. Eur. Phys. J. B 87, 47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2014-40805-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2014-40805-2