Abstract
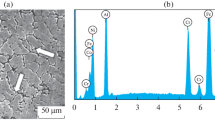
Using wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM), we produced samples of Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Ni high-entropy alloy (HEA) with a grain size of 4–15 µm. Inclusions of the second phase were found along the boundaries and in the volume of the grains. The near-boundary volumes of the alloy (volumes located along grain boundaries) are enriched in chromium and iron atoms, the volume of grains is enriched in nickel and aluminum atoms, and cobalt is quasi-uniformly distributed in the alloy. The inclusions of an elongated shape are enriched in chromium, iron, and oxygen atoms and may be carbides. Microhardness, modulus of elasticity, and tribological properties of the alloy are determined and the stretch curves are analyzed. Irradiation of the HEA with a pulsed electron beam is accompanied by the release of grain boundaries from precipitates of the second phase, which indicates the homogenization of the material. High-speed crystallization of the molten surface layer of HEA samples is accompanied by the formation of a columnar structure with a submicrometer-nanocrystalline structure. The electron-beam processing decreases the microhardness of the surface layer of the alloy with a thickness of up to 90 µm, which may be due to the relaxation of internal stress fields formed in the initial material during its manufacture. Irradiation of a high-entropy alloy with an intense pulsed electron beam improves the strength and plasticity of the material, increasing the compressive strength by 1.1–1.6 times.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. P. George, W. A. Curtin, and C. C. Tasan, Acta Mater. 188, 435 (2020).
V. Shivam, J. Basu, V. K. Pandey, Y. Shadangi, and N. K. Mukhopadhyay, Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 2221 (2018).
U. L. Ganesh and H. Raghavendra, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139, 207 (2020).
Y. A. Alshataif, S. Sivasankaran, F. A. Al-Mufadi, A. S. Alaboodi, and H. R. Ammar, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 1099 (2019).
K. C. Cheng, J. H. Chen, S. Stadler, and S. H. Chen, Appl. Surf. Sci. 478, 478 (2019).
J. Joseph, P. Hodgson, T. Jarvis, X. Wu, N. Stanford, and D. M. Fabijanic, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 733, 59 (2018).
R. Jian, L. Wang, S. Zhou, Y. Zhu, Y. J. Liang, B. Wang, and Y. Xue, Mater. Lett. 278, 128405 (2020).
L. Hou, J. Hui, Y. Yao, J. Chen, and J. Liu, Vacuum 164, 212 (2019).
Y. Zhang, T. T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M. C. Gao, K. A. Dahmen, P. K. Liaw, and Z. Lu, Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1 (2014).
B. Cantor, Entropy 16, 4749 (2014).
D. B. Miracle and O. N. Senkov, Acta Mater. 122, 448 (2017).
W. Zhang, P. K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang, Sci. China Earth Sci. 61, 2 (2018).
K. A. Osintsev, V. E. Gromov, S. V. Konovalov, Yu. F. Ivanov, and I. A. Panchenko, Izv. Ferr. Metall., No. 4, 1 (2021).
A. D. Pogrebnyak, A. A. Bagdasapuan, I. V. Yakushchenko, and V. M. Beresnev, Russ. Chem. Rev. 83, 1027 (2014).
A. S. Rogachev, Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 121, 807 (2020).
M. H. Tsai, R. C. Tsai, T. Chang, and W. F. Huang, Metals (Basel) 9, 1 (2019).
Y. Y. Zhao, Y. X. Ye, C. Z. Liu, R. Feng, K. F. Yao, and T. G. Nieh, Intermetallics 113, 106561 (2019).
D. Oleszak, A. Antolak-Dudka, and T. Kulik, Mater. Lett. 232, 160 (2018).
J. Wang, Y. Liu, B. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Cao, T. Li, and R. Zhou, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 689, 233 (2017).
N. Yurchenko, E. Panina, M. Tikhonovsky, G. Salishchev, S. Zherebtsov, and N. Stepanov, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 105322 (2020).
T. W. Lu, C. S. Feng, Z. Wang, K. W. Liao, Z. Y. Liu, Y. Z. Xie, J. G. Hu, and W. B. Liao, Appl. Surf. Sci. 494, 72 (2019).
Y. Geng, S. V. Konovalov, and X. Chen, Prog. Phys. Met. 21, 26 (2020).
Y. H. Zhou, Z. H. Zhang, Y. P. Wang, G. Liu, S. Y. Zhou, Y. L. Li, J. Shen, and M. Yan, Addit. Manuf. 25, 204 (2019).
Y. A. Alshataif, S. Sivasankaran, F. A. Al-Mufadi, A. S. Alaboodi, and H. R. Ammar, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 1099 (2019).
Yu. F. Ivanov, V. E. Gromov, D. V. Zagulyaev, S. V. Konovalov, Yu. A. Rubannikova, and A. P. Semin, Prog. Phys. Met. 21, 345 (2020).
V. E. Gromov, Yu. F. Ivanov, S. E. Vorobiev, and S. V. Konovalov, Fatigue of Steels Modified by High Intensity Electron Beams (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2015).
Q. Shen, X. Kong, and X. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 74, 136 (2021).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 20-19-00452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Zhukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanov, Y.F., Gromov, V.E., Konovalov, S.V. et al. Study of the Structure and Properties of a High-Entropy AlCoCrFeNi Alloy after Electron-Beam Processing. Phys. Solid State 64, 372–378 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783422080042
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783422080042