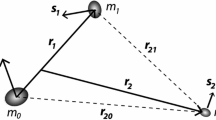
Abstract
Two methods have been developed to study secular (apsidal and nodal) orbital precession in circumbinary systems consisting of a binary star and an exoplanet. The first method is based on a model of three R-toroids and is intended to study the precession of test orbits. For exosystems Kepler-413 and Kepler-453, the mutual orientation of the angular momenta of the stellar pair \({{L}_{{12}}}\) and the planet \({{L}_{p}}\) was found relative to the Laplace plane, the ratio \(\gamma = {{L}_{{12}}}{\text{/}}{{L}_{p}}\) and zonal harmonics of the potential of R-toroids were calculated. Equations for the frequencies of both types of precession were obtained and solved, and the dominant influence of the toroids of the stellar pair was established. The second method is based on the model of interacting Gaussian rings and is intended to study the secular evolution of the orbits of the stars and the planet of the circumbinary system itself. This approach made it possible to accurately calculate the periods of nodal precession for the stars and the planet; for example, in the Kepler-413 system, these periods are, respectively, \(T_{1}^{0} = 11.63 \pm 0.28\) years, \(T_{2}^{0} = 11.39 \pm 0.28\) years, \(T_{p}^{0} = 11.49 \pm 0.28\) years. A subtle effect of the planet’s influence on the disruption of the 1 : 1 resonance for the periods of nodal precession of the stars was revealed.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
B. P. Kondratyev and V. S. Kornoukhov, Astron. Rep. 65 (2021, in press).
St. Raetz, T. O. B. Schmidt, S. Czesla, T. Klocová, et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 460, 2834 (2016).
J. W. Barnes, J. C. van Eyken, B. K. Jackson, D. R. Ciardi, and J. J. Fortney, Astrophys. J. 774, 53 (2013).
Ch. Chen, A. Franchini, S. H. Lubow, R. G. Martin, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 490, 5634 (2019).
B. C. Bromley and S. J. Kenyon, Astron. J. 161, 25 (2021).
A. S. Hamers, M. X. Cai, J. Roa, and N. Leigh, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 480, 3800 (2018).
B. P. Kondratyev, Solar Syst. Res. 46, 352 (2012).
V. B. Kostov, P. R. McCullough, J. A. Carter, M. Deleuil, et al., Astrophys. J. 784, 14 (2014).
Y. Judkovsky, A. Ofir, and O. Aharonson, Astron. J. 160, 195 (2020).
W. F. Welsh, J. A. Orosz, D. R. Short, W. D. Cochran, et al., Astrophys. J. 809, 26 (2015).
B. P. Kondratyev and V. S. Kornoukhov, Astron. Rep. 64, 434 (2020).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of Moscow State University “Fundamental and Applied Space Research.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by M. Chubarova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondratyev, B.P., Kornoukhov, V.S. Study of the Secular Evolution of Circumbinary Systems Using R-Toroid and Gaussian Ring Models. Astron. Rep. 65, 588–597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772921080072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772921080072