Abstract
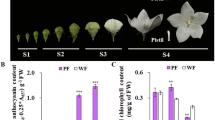
Paeonia suffruticosa “Shima Nishiki” is a extremely precious double-color cultivar in the world because of its unique and attractive flower color. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of its double-color formation have not been completely unravelled until now. In the present study, firstly, the full-length cDNA sequence, genomic DNA sequence, promoter region sequence of the key structural gene (PsDFR) in the red and pink petals of the “Shima Nishiki” cultivar were cloned and analyzed, respectively. Meanwhile, the methylation level of CpG island and promoter region of this gene in the red and pink petals was also measured. Moreover, the identification of regulatory effect of PsMYB114L/PsMYB12L and PsDFR was performed. Here, we found that the full-length cDNA sequence, genomic DNA sequence, promoter region sequence of PsDFR were identical in the red and pink petals. There were some differences for the methylation level of this gene in the red and pink petals, but these differences were little and did not show obvious regularity. Therefore, the differential expression of PsDFR should be not caused by its own sequence differences. In addition, the regulatory effect of PsMYB12L and PsDFR was successfully identified. Based on these above results, we concluded that PsMYB12L regulating the differential expression of PsDFR may be a key reason for the double-color formation. These results will advance our understanding of the molecular regulatory mechanisms of double-color formation in P. suffruticosa “Shima Nishiki”.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zhang, J.J., Shu, Q.Y., Liu, Z.A., Ren, H.X., Wang, L.S., and De Keyser, E., Two EST-derived marker systems for cultivar identification in tree peony, Plant Cell Rep., 2011, vol. 31, p. 299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1164-1
Zhao, D.Q., Tang, W.H., Hao, Z.J., and Tao, J., Identification of flavonoids and expression of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in two coloured tree peony flowers, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2015, vol. 459, p. 450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.126
Zhang, X.P., Zhao, M.Y., Guo, J., Zhao, L.Y., and Xu, Z.D., Anatomical and biochemical analyses reveal the mechanism of double-color formation in Paeonia suffruticosa ‘Shima Nishiki’, 3 Biotech, 2018, vol. 8, p. 420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1459-9
Zhao, D.Q. and Tao, J., Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants, Front. Plant Sci., 2015, vol. 6, p. 261. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00261
Noman, A., Aqeel, M., Deng, J.M., Khalid, N., Sanaullah, T., and He, S.H., Biotechnological advancements for improving floral attributes in ornamental plants, Front. Plant Sci., 2017, vol. 8, p. 530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00530
Nishihara, M. and Nakatsuka, T., Genetic engineering of flavonoid pigments to modify flower color in floricultural plants, Biotechnol. Lett., 2011, vol. 33, p. 433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0461-z
Miyagawa, N., Miyahara, T., Okamoto, M., Hirose, Y., Sakaguchi, K., Hatano, S., and Ozeki, Y., Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase activity is associated with the intensity of flower colors in delphinium, Plant Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 32, p. 249. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.15.0702b
Sánchez-Cabrera, M., Jiménez-López, F.J., Narbona, E., Arista, M., Ortiz, P.L., Romero-Campero, F.J., Ramanauskas, K., Igić, B., Fuller, A.A., and Whittall, J.B., Changes at a critical branchpoint in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway underlie the blue to orange flower color transition in Lysimachia arvensis, Front Plant Sci., 2021, vol. 12, p. 247. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.633979
Chen, S.M., Li, C.H., Zhu, X.R., Deng, Y.M., Sun, W., Wang, L.S., Chen, F.D., and Zhang, Z., The identification of flavonoids and the expression of genes of anthocyanin biosynthesis in the chrysanthemum flowers, Biol. Plant, 2012, vol. 56, p. 458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0069-3
Zhu, Y.J. and Bao, Y., Genome-wide mining of MYB transcription factors in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway of Gossypium hirsutum, Biochem. Genet., 2021, vol. 59, p. 678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10027-0
Nakatsuka, T., Nishihara, M., Mishiba, K., and Yamamura, S., Temporal expression of flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes regulates flower pigmentation in gentian plants, Plant Sci., 2005, vol. 168, p. 1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.01.009
Petroni, K. and Tonelli, C., Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs, Plant Sci., 2011, vol. 181, p. 219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.05.009
Albert, N.W., Davies, K.M., Lewis, D.H., Zhang, H.B., Montefiori, M., Brendolise, C., Boase, M.R., Ngo, H., Jameson, P.E., and Schwinn, K.E., A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots, Plant Cell, 2014, vol. 26, p. 962. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.122069
Zhang, X.P., Xu Z.D., Yu, X.Y., Zhao, L.Y., Zhao, M.Y., Han, X., and Qi, S., Identification of two novel R2R3-MYB transcription factors, PsMYB114L and PsMYB12L, related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in Paeonia suffruticosa, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, vol. 20, p. 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051055
Rouholamina, S., Zahedia, B., Nazarian-Firouzabadib, F., and Saei, A., Expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis key regulatory genes involved in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.), Sci. Hortic., 2015, vol. 186, p. 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.02.017
Hichri, I., Barrieu, F., Bogs, J., Kappel, C., Delrot, S., and Lauvergeat, V., Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, J. Exp. Bot., 2011, vol. 62, p. 2465. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq442
Schaart, J.G., Dubos, C., De La Fuente, I.R., van Houwelingen, A.M.M.L., de Vos, R.C.H., Jonker, H.H., Xu, W.J., Routaboul, J.M., Lepiniec, L., and Bovy, A.G., Identification and characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 regulatory complexes controlling proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) fruits, New Phytol., 2013, vol. 197, p. 454. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12017
Sakai, M., Yamagishi, M., and Matsuyama, K., Repression of anthocyanin biosynthesis by R3-MYB transcription factors in lily (Lilium spp.), Plant Cell Rep., 2019, vol. 38, p. 609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02391-4
Pérez-Díaz, J.R., Pérez-Díaz, J., Madrid-Espinoza, J., González-Villanueva, E., Moreno, Y., and Ruiz-Lara, S., New member of the R2R3-MYB transcription factors family in grapevine suppresses the anthocyanin accumulation in the flowers of transgenic tobacco, Plant Mol. Biol., 2016, vol. 90, p. 63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0394-y
Yamagishi, M. and Sakai, M., The microRNA828/MYB12 module mediates bicolor pattern development in Asiatic Hybrid Lily (Lilium spp.) flowers, Front. Plant Sci., 2020, vol. 11, p. 590791. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.590791
Borevitz, J.O., Xia, Y.J., Blount, J., Dixon, R.A., and Lamb, C., Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, Plant Cell, 2000, vol. 12, p. 2383. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.12.2383
Gonzalez, A., Zhao, M.Z., Leavitt, J.M., and Lloyd, A.M., Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings, Plant J., 2008, vol. 53, p. 814. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x
Gu, Z.Y., Zhu, J., Hao, Q., Yuan, Y.W., Duan, Y.W., Men, S.Q., Wang, Q.Y., Hou, Q.Z., Liu, Z.A., Shu, Q.Y., and Wang, L.S., A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor contributes to petal blotch formation by regulating organ-specific expression of PsCHS in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa), Plant Cell Physiol., 2019, vol. 60, p. 599. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy232
Zhang, Y.Z., Xu, S.Z., Ma, H.P., Duan, X.J., Gao, S.X., Zhou X.J., and Cheng, Y.W., The R2R3-MYB gene PsMY-B58 positively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in tree peony flowers., Plant Physiol. Biotech., 2021, vol. 164, p. 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.04.034
Hosoki, T., Hamada, M., Kando, T., Moriwaki, R., and Inaba, K., Comparative study of anthocyanins in tree peony flowers, J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 1991, vol. 60, p. 395. https://doi.org/10.2503/jjshs.60.395
Wang, L.S., Shiraishi, A., Hashimoto, F., Aoki, N., Shimizu, K., and Sakata, Y., Analysis of petal anthocyanins to investigate flower coloration of Zhongyuan (Chinese) and Daikon Island (Japanese) tree peony cultivars, J. Plant Res., 2001, vol. 114, p. 33. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013966
Zhang, C., Wang, W.N., Wang, Y.J., Gao, S.L., Du, D.N., Fu, J.X., and Dong, L., Anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation in developing flowers of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa) ‘Luoyang Hong’, Postharvest Biol. Technol., 2014, vol. 97, p. 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.05.019
Gao, L.X., Yang, H.X., Liu, H.F., Yang, J., and Hu, Y.H., Extensive transcriptome changes underlying the flower color intensity variation in Paeonia ostii, Front. Plant Sci., 2016, vol. 6, p. 1205. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01205
Zhang, Y.Z., Cheng, Y.W., Xu, S.Z., Ma, H.P., Han, J.M., and Zhang, Y., Tree peony variegated flowers show a small insertion in the F3’H gene of the acyanic flower parts, BMC Plant Biol., 2020, vol. 20, p. 211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02428-x
Zhang, X.P., Zhao, L.Y., Xu, Z.D., and Yu, X.Y., Transcriptome sequencing of Paeonia suffruticosa ‘Shima Nishiki’to identify differentially expressed genes mediating double-color formation, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2018, vol. 123, p. 114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.12.009
Ren, H., Wen, L.Z., Guo, Y.H., Yu, Y.Y., Sun, C.H., Fan, H.M., Ma, F.F., and Zheng, C.S., Expressional and functional verification of the involvement of CmEXPA4 in Chrysanthemum root development., J. Plant Growth Regul, 2019, vol. 38, p. 1375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09940-x
Wang, Y.J., Dong, L., Zhang, C., and Wang, X.Q., Reference gene selection for real-time quantitative PCR normalization in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.), J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 20, p. 521. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.05.008
Schmittgen, T.D. and Livak, K.J., Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method, Nat. Protoc., 2008, vol. 3, p. 1101. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Jia, N., Liu, J.Q., Sun, Y.F., Tan, P.H., Cao, H., Xie, Y.Y., BotingWen, B.T., Gu, T.Y., Liu, M.J., Li, M.M., Huang, Y.T., Lu, J., Jin, N., Sun, L.C., Xin, F.J., and Fan, B., Citrus sinensis MYB transcription factors CsMYB330 and CsMYB308 regulate fruit juice sac lignification through fine-tuning expression of the Cs4CL1 gene, Plant Sci., 2018, vol. 277, p. 334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.10.006
An, J.P., Yao, J.F., Xu, R.R., You, C.X., Wang, X.F., and Hao, Y.J., Apple bZIP transcription factor MdbZ-IP44 regulates abscisic acid-promoted anthocyanin accumulation, Plant Cell Environ., 2018, vol. 41, p. 2678. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13393
Inagaki, Y., Hisatomi, Y., Suzuki, T., Kasahara, K., and Iida, S., Isolation of a suppressor-mutator/enhancer-like transposable element, Tpn1, from Japanese morning glory bearing variegated flowers, Plant Cell, 1994, vol. 6, p. 375. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.3.375
Sato, M., Kawabe, T., Hosokawa, M., Tatsuzawa, F., and Doi, M., Tissue culture-induced flower-color changes in Saintpaulia caused by excision of the transposon inserted in the flavonoid 3’,5’ hydroxylase (F3’5’H) promoter, Plant Cell Rep., 2011, vol. 30, p. 929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1016-z
Suzuki, M., Miyahara, T., Tokumoto, H., Hakamatsuka, T., Goda, Y., Ozeki, Y., and Sasaki, N., Transposon-mediated mutation of CYP76AD3 affects betalain synthesis and produces variegated flowers in four o’clock (Mirabilis jalapa), J. Plant Physiol., 2014, vol. 171, p. 1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.010
Sasaki, N., Nishizaki, Y., Uchida, Y., Wakamatsu, E., Umemoto, N., Momose, M., Okamura, M., Yoshida, H., Yamaguchi, M., Nakayama, M., Ozeki, Y., and Itoh, Y., Identification of the glutathione S-transferase gene responsible for flower color intensity in carnations, Plant Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 29, p. 223. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.12.0120a
Liu, X.J., Chuang, Y.N., Chiou, C.Y., Chin, D.C., Shen, F.Q., and Yeh, K.W., Methylation effect on chalcone synthase gene expression determines anthocyanin pigmentation in floral tissues of two Oncidium orchid cultivars, Planta, 2012, vol. 236, p. 401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1616-z
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank Wenshuang Zhao for his invaluable help and assistance.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022MC013), Agricultural improved variety project of Shandong Province (2020LZGC011-1) and Doctoral fund project of Shandong Jianzhu University (X20021S0101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.P. Zhang and X. Han have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship. Z.D. Xu and J.Q. Chen conceived and designed the research. X.P. Zhang and X. Han participated in the specific design of the study. X.P. Zhang and X. Han performed the experiments and the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. M.Y. Zhao, S.J. Lu, X.Y. Yu, Y.F. Fang, C. Li contributed analysis tools and helped analyze the data. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants as objects of research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Abbreviations: ANS—anthocyanidin synthase gene; CHS—chalcone synthase gene; CHI—chalcone isomerase gene; DFR—dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene; F3H—flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene; F3'H—flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase gene; SN-Pink—pink petal; SN-Red—red petal; TFs—transcription factors.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.P., Han, X., Zhao, M.Y. et al. Identification of a Regulatory Module (PsMYB12L/PsDFR) with Potential Involved in Double-Color Formation in Paeonia suffruticosa “Shima Nishiki”. Russ J Plant Physiol 70, 26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443722601823
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443722601823