Abstract
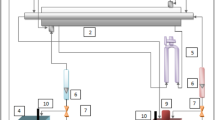
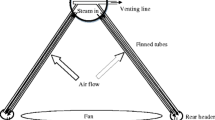
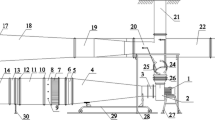
The influence of the configuration of flat fins on the thermal characteristics of a finned-tube heat exchanger is experimentally investigated. The configurations fins of four shapes are studied: plain (P), nozzle (N), diffuser (D), and nozzle-diffuser (ND). The bend angles of the N-fins were 10° and 20°, and the D‑fins were 10°, 20°, 30°, and 40°. It has been established that the configuration of the finning and the angle of bending of the fins play an important role in increasing the thermal characteristics of the finned-tube heat exchanger. The main advantage of the proposed finning method in comparison with those used earlier is an increase in heat transfer practically without an increase in the coefficient of friction inside the heat exchanger tube. The scheme of the experimental setup and its main characteristics are described. The obtained experimental data on heat transfer are graphically presented. It is shown that small bending angles of the nozzle and diffuser fins significantly increase heat transfer, while angles of more than 40° lead to its deterioration. A formula for calculating the Nusselt number is presented, which generalizes the experimental data for all investigated finning configurations with an error of ±14%.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Rivier, P. Sébastian, Th. Goli, G. Raffray, and A. Collignan, “Heat transfer enhancement of a circular tube heat exchanger fitted with an elliptic shaped turbulator designed in the context of developing countries,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 81, 92–101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.01.078
A. Kumar, S. Chamoli, and M. Kumar, “Experimental investigation on thermal performance and fluid flow characteristics in heat exchanger tube with solid hollow circular disk inserts,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 100, 227–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.01.081
N. Zheng, P. Liu, X. Wang, F. Shan, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Numerical simulation and optimization of heat transfer enhancement in a heat exchanger tube fitted with vortex rod inserts,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 123, 471–484 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.112
S. Chamoli, P. Yu, and Sh. Yu, “Multi-objective shape optimization of a heat exchanger tube fitted with compound inserts,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 117, 708–724 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.02.047
N. Zheng, P. Liu, F. Shan, J. Liu, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Numerical studies on thermo-hydraulic characteristics of laminar flow in a heat exchanger tube fitted with vortex rods,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 100, 448–456 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.09.008
P. Promvonge, N. Koolnapadol, M. Pimsarn, and C. Thianpong, “Thermal performance enhancement in a heat exchanger tube fitted with inclined vortex rings,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 62, 285–292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.09.031
N. Zheng, W. Liu, Z. Liu, P. Liu, and F. Shan, “A numerical study on heat transfer enhancement and the flow structure in a heat exchanger tube with discrete double inclined ribs,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 90, 232–241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.07.009
N. Zheng, P. Liu, F. Shan, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Effects of rib arrangements on the flow pattern and heat transfer in an internally ribbed heat exchanger tube,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 101, 93–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.10.035
N. Zheng, P. Liu, F. Shan, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Numerical investigations of the thermal-hydraulic performance in a rib-grooved heat exchanger tube based on entropy generation analysis,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 99, 1071–1085 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.02.008
N. Zheng, P. Liu, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Numerical simulation and sensitivity analysis of heat transfer enhancement in a flat heat exchanger tube with discrete inclined ribs,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 112, 509–520 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.05.019
W. M. Song, J. A. Meng, and Z. X. Li, “Numerical study of air-side performance of a finned flat tube heat exchanger with crossed discrete double inclined ribs,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 30, 1797–1804 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.04.013
N. Zheng, P. Liu, F. Shan, Z. Liu, and W. Liu, “Turbulent flow and heat transfer enhancement in a heat exchanger tube fitted with novel discrete inclined grooves,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 111, 289–300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2016.09.010
Z.-M. Lin, L.-B. Wang, and Y.-H. Zhang, “Numerical study on heat transfer enhancement of circular tube bank fin heat exchanger with interrupted annular groove fin,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 73, 1465–1476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.05.073
T. Välikangas, Sh. Singh, K. Sørensen, and T. Condra, “Fin-and-tube heat exchanger enhancement with a combined herringbone and vortex generator design,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 118, 602–616 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.006
J.-Sh. Leu, Y.-H. Wu, and J.-Y. Jang, “Heat transfer and fluid flow analysis in plate-fin and tube heat exchangers with a pair of block shape vortex generators,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 47, 4327–4338 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.04.031
N. Chimres, Ch.-Ch. Wang, and S. Wongwises, “Optimal design of the semi-dimple vortex generator in the fin and tube heat exchanger,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 120, 1173–1186 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.121
W. Dang, J. Nugud, Z.-M. Lin, Y.-H. Zhang, S. Liu, and L.-B. Wang, “The performances of circular tube bank fin heat exchangers with fins punched with quadrilateral vortex generators and flow re-distributors,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 134, 437–449 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.02.008
J. M. Wu, H. Zhang, C. H. Yan, and Y. Wang, “Experimental study on the performance of a novel fin-tube air heat exchanger with punched longitudinal vortex generator,” Energy Convers. Manage. 57, 42–48 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.12.009
J. Gong, Ch. Min, Ch. Qi, E. Wang, and L. Tian, “Numerical simulation of flow and heat transfer characteristics in wavy fin-and-tube heat exchanger with combined longitudinal vortex generators,” Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 43, 53–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2013.01.004
W. Wang, Y. Bao, and Y. Wang, “Numerical investigation of a finned-tube heat exchanger with novel longitudinal vortex generators,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 86, 27–34 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.04.041
L. Li, X. Du, Y. Zhang, L. Yang, and Y. Yang, “Numerical simulation on flow and heat transfer of fin-and-tube heat exchanger with longitudinal vortex generators,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 92, 85–96 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.01.030
A. Joardar and A. M. Jacobi, “Heat transfer enhancement by winglet-type vortex generator arrays in compact plain-fin-and-tube heat exchangers,” Int. J. Refrig. 31, 87–97 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2007.04.011
Y.-L. He, P. Chu, W.-Q. Tao, Y.-W. Zhang, and T. Xie, “Analysis of heat transfer and pressure drop for fin-and-tube heat exchangers with rectangular winglet-type vortex generators,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 61, 770–783 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.02.040
A. A. Gholami, M. A. Wahid, and H. A. Mohammed, “Heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop for fin-and-tube compact heat exchangers with wavy rectangular winglet-type vortex generators,” Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 132–140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2014.02.016
A. Sinha, H. Chattopadhyay, A. K. Iyengar, and G. Biswas, “Enhancement of heat transfer in a fin-tube heat exchanger using rectangular winglet type vortex generators,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 101, 667–681 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.05.032
K. W. Song, Z. P. Xi, M. Su, L. Ch. Wang, X. Wua, and L. B. Wang, “Effect of geometric size of curved delta winglet vortex generators and tube pitch on heat transfer characteristics of fin-tube heat exchanger,” Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 82, 8–18 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.11.002
Sh. K. Sarangi and D. P. Mishra, “Effect of winglet location on heat transfer of a fin-and-tube heat exchanger,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 116, 528–540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.106
M. J. Li, H. Zhang, J. Zhang, Y. T. Mu, E. Tian, D. Dan, X. D. Zhang, and W. Q. Tao, “Experimental and numerical study and comparison of performance for wavy fin and a plain fin with radiantly arranged winglets around each tube in fin-and-tube heat exchangers,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 133, 298–307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.01.012
S. Skullong, P. Promvonge, Ch. Thianpong, N. Jayranaiwachira, and M. Pimsarn, “Thermal performance of heat exchanger tube inserted with curved-winglet tapes,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 129, 1197–1211 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.10.110
L. Chen, Z. Li, and Z.-Y. Guo, “Experimental investigation of plastic finned-tube heat exchangers, with emphasis on material thermal conductivity,” Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 33, 922–928 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2009.04.001
A. Lemouedda, A. Schmid, E. Franz, M. Breuer, and A. Delgado, “Numerical investigations for the optimization of serrated finned-tube heat exchangers,” Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 1393–1401 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.12.035
L. Bilir, Z. İlken, and A. Erek, “Numerical optimization of a fin-tube gas to liquid heat exchanger,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 52, 59–72 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.09.010
P. Pongsoi, S. Pikulkajorn, and S. Wongwises, “Effect of fin pitches on the optimum heat transfer performance of crimped spiral fin-and-tube heat exchangers,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 6555–6566 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.06.061
P. Kumar, A. Kumar, S. Chamoli, and M. Kumar, “Experimental investigation of heat transfer enhancement and fluid flow characteristics in a protruded surface heat exchanger tube,” Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 71, 42–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2015.10.014
X. Liu, J. Yu, and G. Yan, “A numerical study on the air-side heat transfer of perforated finned-tube heat exchangers with large fin pitches,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 100, 199–207 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.04.081
Y. Q. Kong, L. J. Yang, X. Z. Du, and Y. P. Yang, “Effects of continuous and alternant rectangular slots on thermo-flow performances of plain finned tube bundles in in-line and staggered configurations,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 93, 97–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.10.008
Y. Wang, H. Tian, G. Shu, G. Yu, X. Ma, and X. Li, “Simulation and optimization of metal-foam tube banks for heat transfer enhancement of exhaust heat exchangers,” Energy Procedia 142, 3863–3869 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.12.289
A. Gholami, M. A. Wahid, and H. A. Mohammed, “Thermal–hydraulic performance of fin-and-oval tube compact heat exchangers with innovative design of corrugated fin patterns,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 106, 573–592 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.09.028
ANSI/ASME PTC 19. Measurement Uncertainty (1986), Part 1.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provides by the Yasouj university. Also, the author appreciates Mr. Adel Abolpour of undergraduate students for collaborating on conducting experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goudarzi, K. Investigation of the Effect of Fin Configuration and Fin Angle on Thermal Performance of Finned-Tube Heat Exchanger. Experimental Study. Therm. Eng. 68, 556–563 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601521070065
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601521070065