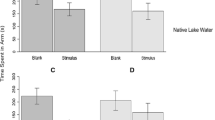
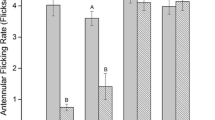
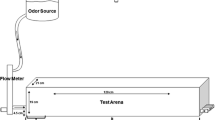
Abstract
Based on our own studies and on literature data, there are considered peculiarities of structural-functional organization of the crustacean olfactory system and effects of pollutants on it. The behavioral reaction changes based on chemoreception in the polluted aquatic environment are described. Usefulness of study of the crustacean olfactory system is substantiated as a perspective object of ecologo-toxicological investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derby, C.D. and Sorensen, P.W., Neural Processing, Perception, and Behavioral Responses to Natural Chemical Stimuli by Fish and Crustaceans, J. Chem. Ecol., 2008, vol. 34, pp. 898–914.
Hara, T.J., Is Morpholine an Effective Olfactory Stimulant in Fish?, J. Fish. Res. Bd Can., 1974, vol. 31, pp. 1547–1550.
Devitsina, G.V. and Malyukina, G.A., On Functional Organization of the Olfactory Organ in Micro- and Macrosmotics, Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1977, vol. 17, pp. 493–502.
Doroshenko, M.A., Gistofiziologiya organa obonyaniya ryb (Histophysiology of the Fish Olfactory Organ), Vladivostok, 2002.
Gdovsky, P.A., Structural and Functional Organization of the Fish Olfactory System, Doctorate Dissertation, Borok, 2005.
Zielinski, B.S. and Hara, T.J., Olfaction Fish Physiology, Zielinski, B.S. and Hara, T.J., Eds., New York: Elsevier/Academic, 2007, pp. 1–43.
Gdovsky, P.A. and Ruzhinskaya, N.N., The Effect of Copper Ions on the Peripheral Part of the Olfactory System in the Common Carp Cyprinus carpio L., Biol. Vnutr. Vod., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 90–95.
Devitsina, G.V., The Effect of Heavy Metal Salts on the Morphofunctional State of the Olfactory and Gustatory Epithelium in the Common Carp Cyprinus carpio L., Sensorn. Sistemy, 2002, vol. 16, pp. 164–169.
Tierney, K.B., Baldwin, D.H., Hara, T.J., Ross, P.S., Scholz, N.L., and Kennedy, C.J., Olfactory Toxicity in Fishes, Aquat. Toxicol., 2010, vol. 96, no. 1, pp. 2–26.
McClintock, T.S., Ache, B.W., and Derby, C.D., Lobster Olfactory Genomics, Integrat. Comp. Biol., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 940–947.
Shuranova, Zh.P. and Burmistrov, Yu.M., Neirofiziologiya rechnogo raka (Neurophysiology of the European Crayfish), Moscow, 1988.
Schmidt, M., Chien, H., Tadesse, T., Johns, M.E., and Derby, C.D., Rosette-type Tegumental Glands Associates with Aesthetasc Sensilla in the Caribbean Spiny Lobster, Panulirus argus, Cell Tissue Res., 2006, vol. 325, pp. 369–395.
Fedotov, V.P., Systems of Chemoperception in Decapod Crayfish, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2009, vol. 45, pp. 3–24.
Sandeman, R.E., and Sandeman, D.C., Development, Growth, and Plasticity in the Crayfish Olfactory System, Microsc. Res. Tech., 2003, vol. 60, pp. 266–277.
Blinova, N.K., Morphological Peculiarities of the Olfactory System in the Grass Shrimp Pandalus kessleri (Decapoda, Pandalidae), Vest. Zool., 2008, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 57–62.
Blinova, N.K., Aesthetasc Structure in the Grass Shrimp Pandalus latirostris, Zool. Zh., 1988, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 44–48.
Caprio, J. and Derby, C.D., Aquatic Animal Models in the Study of Chemoreception, The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference, Basbaum, A., Kaneko, A., Shepherd, G.M., and Westheimer, G., Eds., vol. 4, Olfaction and Taste, Firestein, S. and Beauchamp, G.K., Eds., San Diego, 2008, pp. 97–134.
Blinova, N.K. and Cherkashin, S.A., Development of Antennules in Larvae of the Grass Shrimp Pandalus kessleri, Biol. Morya, 1999, vol. 25, pp. 217–220.
Blinova, N.K. and Cherkashin, S.A., Development of Olfactory Organs in Larvae of the Grass Shrimp Pandalus kessleri (Decapoda, Pandalidae) in Ontogenesis, Vestn. Zool., vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 413–419.
Steullet, P., Cate, H.S., and Derby, C.D., A Spatiotemporal Wave of Turnover and Functional Maturation of Olfactory Receptor Neurons in the Spiny Lobsters Panulirus argus, J. Neirosci., 2000, vol. 20, pp. 3282–3294.
Tierney, A.J., Tompson, C.D., and Dunham, D.W., Fine Structure of the Aesthetasc Chemoreceptors in the Crayfish Orconectes propinquus, Can. J. Zool., 1986, vol. 64, pp. 392–399.
Guse, G.-W., Ultrastructure, Development and Moulting of the Aesthetascs of Neomysis integer and Idotea baltica (Crustacea, Malacostraca), Zoomorfology, 1983, vol. 103, no. 2, pp. 121–133.
Schmidt, M. and Ache, B.W. Antennular Projections to the Midbrain of the Spiny Lobster. II. Sensory Innervation of the Olfactory Lobe, J. Comp. Neurol., 1992, vol. 318, pp. 291–303.
Tsvileneva, V.A., Titova, V.A., and Kvashina, T.V., Brain Topography of the Shore Crab Hemigrapsus sanguineus, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1985, vol. 21, pp. 578–585.
Beltz, B.S., Kordas, R., Lee, M.M., Long, G.B., Benton, J.L., and Sandeman, D., Ecological, Evolutionary, and Functional Correlates of Sensilla Number and Glomerular Density in the Olfactory System of Decapod Crustaceans, J. Comp. Neirol., 2003, vol. 455, pp. 260–269.
Blaustein, D.N., Derby, C.D, Simmons, R.B., and Beall, A.C., The Structure of the Brain and Medulla Terminalis of the Spiny Lobster (Panulirus argus) and Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), with an Emphasis of Olfactory Centers, J. Crustac. Biol., 1988, vol. 8, pp. 493–519.
Derby, C.D., Why Have Neurogenesis in Adult Olfactory Systems?, Chem. Senses, 2007, vol. 32, pp. 361–363.
Song, C.K., Johnstone, L.M., Edwards, D.H., Derby, C.D., and Schmidt, M., Cellular Basis of Neurogenesis in the Brain of Crayfish, Procambarus clarkii: Neurogenic Complex in the Olfactory Midbrain from Hatchlings to Adults, Arthrop. Struct. Dev., 2009, vol. 38, pp. 339–360.
Wachowiak, M. and Ache, B.W., Dual Inhibitory Pathways Mediated by GABA- and Histaminergyc Interneurons in the Lobster Olfactory Lobe, J. Comp. Physiol., 1997, vol. 180A, pp. 357–372.
Maynard, E., Microscopic Localization of Cholinesterases in the Nervous System of the Lobsters Panulirus argus and Homarus americanus, Cell Tissue Res., 1971, vol. 3, pp. 215–250.
Barker, D., Herbert, E., Hildebrand, J., and Kravitz, E., Acetylcholine and Lobster Sensory Neurons, J. Physiol., 1972, vol. 226, pp. 508–512.
Blinova, N.K., Morphofunctional Specificities of Olfactory Reception in the Grass Shrimp, Candidate Sci. Dissertation, Vladivostok, 1991.
Johanson, K.U.I. and De Mellon, F., Nitric Oxide as a Putative Messenger Molecule in the Crayfish Olfactory Midbrain, Brain Res., 1998, vol. 807, pp. 237–242.
Scholz, N.L., Chang, E.S., Graubard, K., and Truman, J.W., The NO/cGMP Pathway and the Development of Neural Networks in Postembryonic Lobsters, J. Neurobiol., 1998, vol. 34, pp. 208–226.
Carr, W.E.S., Gleeson, R.A., and Trapido-Rosenthal, H.G., The Role of Perireceptor Events in Chemosensory Processes, Trend. Neirosci., 1990, vol. 13, pp. 212–215.
Fedotov, V.P. and Karpenko, D.O., A Study of Chemoreceptors from the Claw of the European Crayfish Movement, Upravlenie dvizheniyami u rechnykh zhivotnykh (Management of Movements in Aquatic Animals), Leningrad, 1981, pp. 37–45.
Shepheard, P., Chemoreception in the Antennule of the Lobsters Homarus americanus, Mar. Behav. Physiol., 1974, vol. 2, pp. 261–273.
Blinova, N.K., Sensitivity of Olfactory Receptors to Alimentary Attractants in the Grass Shrimp, Morskii Evol. Zh., 2009, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 53–58.
Fusser, S.M., Carr, W.B.S., and Ache, B.V., Antennular Chemo Sensitivity in the Spiny Lobster Panulirus argus: Studies of Taurine Sensitive Receptors, Biol. Bull., 1978, vol. 154, pp. 226–240.
Derby, C.D., Steullet, P., Horner, A.J., and Cate, H.S., The Sensory Basis of Feeding Behavior in the Caribbean Spiny Lobster, Panulirus argus, Mar. Freshwater Res., 2001, vol. 52, pp. 1339–1350.
Roethke, N., MacDiarmid, A.B., and Montgomery, J.C., The Role of Olfaction during Mating in the Southern Temperate Spiny Lobster Jesus Edwards, Hormones and Behavior, 2004, vol. 46, pp. 311–318.
Derby, C.D. and Ataman, J., Influence of Drilling Muds on the Primary Chemosensory Neurons in Walking Legs of the Lobster Homarus americanus, Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci., 1981, vol. 38, pp. 268–274.
Blinova, N.K. and Cherkashin, S.A., The Effect of Phenol on Antennular Chemoreception in the Grass Shrimp, Biol. Nuke, 1987, no.2, pp. 44–48.
Luk’yanenko, V.I., Physiologo-Biochemical Aspects of Aquatic Toxicology, Vliya nie zagryaznyayushchikh veshchestv na gi dro bi ontov i ekosistemy vodoemov (Effect of Pollutants on Hydrobionts and Ecosystems of Water Reservoirs), 1979, pp. 49–57.
Yakovlev, V.A., Action of Heavy Metals on Freshwater Zoobenthos: 2. Consequences for Communities, Ekolog. Khimiya, 2002, vol. 11, pp. 117–132.
Bergey, L.L. and Weis, J.S., Molting as a Mechanism of Depuration of Metals in the Fiddler Crab, Uca pugnax, Mar. Environ. Res., 2007, vol. 64, pp. 556–562.
Winner, R.W., Selenium Effects on Antennal Integrity and Chronic Copper Toxicity in Daphnia pulex (de Geer), Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1984, vol. 33, pp. 605–611.
Blinova, N.K., Effect of Heavy Metals on Development of Olfactory Organs in Pandalus kessleri Larvae, “Marine Coastal Ecosystems”: Tez. III Mezhdunar. nauch.-prakt. konf. (Abstr. III Intern. Sci.-Pract. Confer.), Vladivostok, 2008, pp. 225–226.
Sindermann, C.J., Bang, F.B., Christensen, N.O., Dethlefsen, V., Harshbarger, J.C., Mitchel, J.R., and Mulcany, M.F., The Role and Value of Pathology in Pollution Effects Monitoring Programmers, Pathology Panel Report. Rapp. P. v. Reun. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer., 1980, vol. 179, pp. 135–151.
Golovanova, I.L. and Frolova, T.V., Effects of Copper, Zinc, and Cadmium on Carbohydrase Activity in Aquatic Invertebrates, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 2005, vol. 4, pp. 73–83.
Santos, M.H.S., Cunha, N.T., and Bianchini, A., Effects of Copper and Zinc on Growth, Feeding and Oxygen Consumption of Farfantepenaeus pau lensis Postlarvae (Decapoda: Penaeidae), J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2000, vol. 247, pp. 233–242.
Sundelin, B., Ryk, C., and Malmberg, G., Effects on the Sexual Maturation of the Sediment-Living Amphipod Monoporeia affinis, Environ. Toxicol., 2000, vol. 15, pp. 518–526.
Luk’yanenko, V.I. and Cherkashin, S.A., Experimental Substantiation of a Possibility of Using Toxicant Avoidance Reaction by Hydrobionts in Water Quality Bioassays, Fiziologiya i biokhimiya gidrobiontov (Physiology and Biochemistry of Hydrobionts), Yaroslavl, 1987, pp. 48–57.
Flerov, B.A., Ekologo-fiziologicheskie aspekty toksikologii presnovodnykh zhivotnykh (Ecologo-Physiological Aspects of Freshwater Animal Toxicology), Leningrad, 1989.
Pynnnen, K., Heavy Metal-Induced Changes in the Feeding and Burrowing Behaviour of a Baltic Isopod, Saduria (Mesidotea) entomon L., Mar. Environ. Res., 1996, vol. 41, pp. 145–156.
Matishov, G.G., Kreneva, S.V., Muraveiko, V.M., Shparkovsky, I.A., and Il’in, G.V., Biotestirovanie i prognoz izmenchivosti vodnykh ekosistem pri anropogennom zagryaznenii (Biotesting and Prediction of Variability in Aquatic Ecosystems at Anthropogenic Pollution), Apatity, 2003.
Cherkashin, S.A., Biotesting: Terminology, Tasks, the Main Requirements, and Use in Fish Toxicology, Izv. TINRO, 2001, vol. 128, pp. 1020–1035.
Evans, G.W., Lye, M., and Lockwood, A.P.M., Some Effect of Oil Dispersants on the Feeding Behavior of the Brown Shrimp, Crangon crangon, Mar. Behav. Physiol., 1977, vol. 4, pp. 171–181.
Atema, J. and Stein, L.S., Effect of Crude Oil on the Feeding Behavior of the Lobster Homarus americanus, Envir. Pollut., 1974, vol. 6, pp. 77–86.
Kittredge, J.S., The Effects of Crude Oil Pollution on the Behavior of Marine Invertebrates-Final Report, Arlington, 1973.
Pearson, W.H. and Olla, B.L., Threshold for Detection of Naphthalene and Other Behavioural Responses by Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus, Estuaries, 1980, vol. 3, pp. 224–229.
McLeese, D.W., Chemosensory Response of Lobster Homarus americanus in the Presence of Copper and Phoshamidon, J. Fish. Res. Bd Can., 1975, vol. 32, pp. 2055–2060.
Atema, J., Leavitt, D.F., Barshaw, D.E., and Cuomo, M.C., Effect of Drilling Muds on Primary Chemosensory Neurons in Walking Legs of the Lobster, Homarus americanus, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1982, vol. 38, pp. 675–690.
Blaxter, J.H.S. and Ten Hallers-Tjabbes, C.C., The Effects of Pollutants on Sensory Systems and Behavior of Aquatic Animals, Netherl. J. Aquat. Ecol., 1992, vol. 26, pp. 43–58.
McLeese, D.W., Toxicity of Copper at Two Temperatures and Three Salinities to the American Lobsters (Homarus americanus), J. Fish. Res. Bd Can., 1974, vol. 31, pp. 1949–1952.
Flerov, B.A. and Tagunov, B.B., Analysis of the Toxicant Avoidance Reaction in a Branchiopod Streptocephalus torvicomis (Waga), Inform. Bull. Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 1978, vol. 40, pp. 68–71.
Cherkashin, S.A., Some Aspects of the Effects of Oil Hydrocarbons on Fish and Crustaceans, Vestnik DVO RAN, 2005, vol. 3, pp. 83–91.
Luk’yanenko, V.I., Cherkashin, S.A., and Kandinskii, P.A., Juvenile Fish and Mysid Behavior in Solutions of Organic Toxicants, Gidrobiol. Zh., 1987, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 64–69.
Percy, J.A., Responses of Arctic Marine Crustaceans to Crude Oil and Oil-Tainted Food, Environ. Poll., 1976, vol. 10, pp. 155–162.
Percy, J.A., Responses of Arctic Marine Benthic Crustaceans to Sediments Contaminated with Crude Oil, Environ. Poll., 1977, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–10.
Percy, J.A. and Mullin, T.S., Effects of Crude Oils on the Locomotor Activity of Arctic Marine Invertebrates, Mar. Poll. Bull., 1977, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 35–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.K. Blinova, S.A. Cherkashin, 2011, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2012, Vol. 48, No. 2, pp. 133–141.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blinova, N.K., Cherkashin, S.A. The olfactory system of crustaceans as a model for ecologo-toxicological studies. J Evol Biochem Phys 48, 155–165 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093012020053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093012020053