Abstract
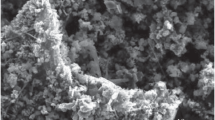
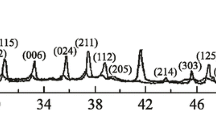
This paper describes a study of boron powders and powder compounds, obtained by various methods, including metallothermal, electrolytic, and borane cracking methods. The crystal state, particle size and microstructure, presence and composition of impurities, and chemical composition of the oxide layer of boron particles are profoundly investigated. The effects of the above-mentioned characteristics on the particle oxidation parameters during heating with a constant rate are analyzed. The determining influence of chemical composition of the particle surface layer on the initial temperature of their intense oxidation is established. It is shown that the maximum increase in the mass and heat release value during oxidation of the boron powders is almost independent of microstructural features, crystal state, and chemical composition of and oxide layer thickness of the particles, and cannot serve as indicators of completeness of boron oxidation during heating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramjet Rocket Engines on Solid and Pasty Fuels. Basics of Design and Experimental Development, Ed. by Yu. M. Milekhin and V. A. Sorokin (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2010) [in Russian].
A. Gany and D. W. Netzer, “Combustion Studies of Metallized Fuels for Solid-Fuel Ramjets,” J. Propul. Power 2 (2), 423–427 (1986).
R. Foelsche, R. Burton, and H. Krier, “Boron Particle Ignition and Combustion at 30–150 atm,” Combust. Flame 117 (1–2), 32–58 (1999).
A. G. Korotkikh et al., “Effect of Iron and Boron Ultrafine Powders on Combustion of Aluminized Solid Propellants,” Combust. Flame 178, 195–204 (2017).
S. Karmakar et al., “Effects of Rare-Earth Oxide Catalysts on the Ignition and Combustion Characteristics of Boron Nanoparticles,” Combust. Flame 160 (12), 3004–3014 (2013).
L. Liu, P. Liu, and G. He, “Ignition and Combustion Characteristics of Compound of Magnesium and Boron,” J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 121 (3), 1205–1212 (2015).
J. Xi et al., “Effect of Metal Hydrides on the Burning Characteristics of Boron,” Thermochim. Acta. 597, 58–64 (2014).
J. Xi et al., “Metal Oxides as Catalysts for Boron Oxidation,” J. Propul. Power 30 (1), 47–53 (2014).
P. Z. Si et al., “Amorphous Boron Nanoparticles and BN Encapsulating Boron Nano-Peanuts Prepared by Arc-Decomposing Diborane and Nitriding,” J. Mater. Sci. 38 (4), 689–692 (2003).
J. D. Casey and J. S. Haggerty, “Laser-Induced Vapour-Phase Syntheses of Boron and Titanium Diboride Powders,” J. Mater. Sci. 22 (2), 737–744 (1987).
A. L. Pickering et al., “Room Temperature Synthesis of Surface-Functionalised Boron Nanoparticles,” Chem. Commun., No. 6, 580 (2007).
R. A. Yetter, G. A. Risha, and S. F. Son, “Metal Particle Combustion and Nanotechnology,” Proc. Combust. Inst. 32 (2), 1819–1838 (2009).
E. L. Dreizin, “Metal-Based Reactive Nanomaterials,” Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 35 (2), 141–167 (2009).
G. Young, C. W. Roberts, and C. A. Stoltz, “Ignition and Combustion Enhancement of Boron with Polytetrafluoroethylene,” J. Propul. Power 31 (1), 386–392 (2015).
W. Yang et al., “Impacts of Particle Size and Pressure on Reactivity of Boron Oxidation,” J. Propul. Power 29 (5), 1207–1213 (2013).
B. E. Nikol’skii, N. L. Patratii, and Yu. V. Frolov, “Combustion of Boron-Containing Condensed Systems,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 28 (1), 51–53 (1992) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 28 (1), 45–47 (1992)].
A. Ulas, K. K. Kuo, and C. Gotzmer, “Ignition and Combustion of Boron Particles in Fluorine-Containing Environments,” Combust. Flame 127 (1–2), 1935–1957 (2001).
T. L. Connell et al., “Boron and Polytetrafluoroethylene as a Fuel Composition for Hybrid Rocket Applications,” J. Propul. Power 31 (1), 373–385 (2015).
K.-L. Chintersingh, M. Schoenitz, and E. L. Dreizin, “Oxidation Kinetics and Combustion of Boron Particles with Modified Surface,” Combust. Flame 173 288–295 (2016).
B. J. Bellott et al., “Nanoenergetic Materials: Boron Nanoparticles from the Pyrolysis of Decaborane and Their Functionalisation,” Chem. Commun., No. 22, 3214 (2009).
I. Glassman, F. A. Williams, and P. Antaki, “A Physical and Chemical Interpretation of Boron Particle Combustion,” Symp. Int. Combust. 20 (1), 2057–2064 (1985).
R. Nuzzo and G. Girolami, High Energy Nanomaterials: Aluminum and Boron: Army Research Office Review of Nano Engineered Energetic Materials (NEEM) MURI (HEAT Center, Aberdeen, 2010).
C. P. Talley, “Combustion of Elemental Boron,” Aero/Space Engineering 18, 37–47 (1959).
A. Maceic and J. M. Semple, “Combustion of Boron Particles at Atmospheric Pressure,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 1 (3), 181–191 (1969).
Burning of Powdered Metals in Active Media, Ed. by P. F. Pokhil et al. (Nauka, Moscow, 1972) [in Russian].
Ignition and Combustion of Powdered Metals, Ed. by D. A. Yagodnikov (Bauman Moscow State Tech. Univ., Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
W. Ao, J. H. Zhou, W. J. Yang, et al., “Ignition, Combustion, and Oxidation of Mixtures of Amorphous and Crystalline Boron Powders,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 50 (6), 51–53 (2014) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 50 (6), 45–47 (2014)].
A. S. Nechepurenko, V. M. Shamrikov, Yu. Ya. Lasychenkov, et al., “Boron, Its Oxygen-Free Compounds, and Their Application in Modern Technology,” Tr. Ural. Nauch.-Issled. Khim. Inst. 72, 1–6 (2005).
A. Jain et al., “Characterization of Electrodeposited Elemental Boron,” Mater. Charact. 59 (7), 890–900 (2008).
A. Jain et al., “Structural Characterization of Electrodeposited Boron,” Bull. Mater. Sci. 36 (7), 1323–1329 (2013).
B. Callmer, “An Accurate Refinement of the β-Rhombohedral Boron Structure,” Acta Crystallogr. B 33 (6), 1951–1954 (1977).
S. Brutti et al., “Synchrotron Powder Diffraction Rietveld Refinement of MgB20 Crystal Structure,” Intermetallics 10 (8), 811–817 (2002).
I. Higashi, “Aluminum Distribution in the Boron Framework of γ-AlB12,” J. Solid State Chem. 47 (3), 333–349 (1983).
B. Van Devener et al., “Oxide-Free, Catalyst-Coated, Fuel-Soluble, Air-Stable Boron Nanopowder As Combined Combustion Catalyst and High Energy Density Fuel,” Energy Fuels 23 (12), 6111–6120 (2009).
W. E. Moddeman et al., “Surface Oxides of Boron and B12O2 as Determined by XPS,” Surf. Interface Anal. 14 (5), 224–232 (1989).
M. Ennaceur and B. Terreault, “XPS Study of the Process of Oxygen Gettering by Thin Films of PACVD Boron,” J. Nucl. Mater. 280 (1), 33–38 (2000).
C. Ronning et al., “Ion Beam Synthesis of Boron Carbide Thin Films,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 158–159, 382–387 (2002).
P. J. Kervalishvili et al., “Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Oxygen Behavior in Boron,” J. Mater. Res. 7 (7), 1822–1828 (1992).
D. N. Hendrickson, J. M. Hollander, W. L. Jolly, “Core-Electron Binding Energies for Compounds of Boron, Carbon, and Chromium,” Inorg. Chem. 9 (3), 612–615 (1970).
J. J. Pireaux et al., “High Resolution ESCA Study of Uranium Fluorides: UF4 and K2UF6,” Chem. Phys. Lett. 46 (2), 215–219 (1977).
C. D. Wagner, “Studies of the Charging of Insulators in ESCA,” J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 18 (3), 345–349 (1980).
A. I. Grigor’ev, V. I. Sigimov, and I. D. Grigor’eva, “Ignition of a Solid Particle of Boron,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 10 (4), 539–542 (1974) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 10 (4), 467–470 (1974)].
A. I. Grigor’ev, I. D. Grigor’eva, and V. I. Sigimov, “Oxidation Kinetics of Boron,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 12 (1), 52–56 (1976) [Combust., Expl., ShockWaves 12 (1), 44–47 (1976)].
D. Z. Safaneev, L. Ya. Kashporov, Yu. M. Grigoriev, “Heat-Liberation Kinetics in Boron–Oxygen Interaction,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 17 (2), 109–114 (1981) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 17 (2), 210–214 (1981)].
M. A. Trunov et al., “Effect of Polymorphic Phase Transformations in Al2O3 Film on Oxidation Kinetics of Aluminum Powders,” Combust. Flame. 140 (4), 310–318 (2005).
D. Meerov et al., “Boron Particles Agglomeration and Slag During Combustion of Energetic Condensed Systems,” Phys. Procedia 72, 85–88 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.N. Pivkina, N.V. Muravyev, K.A. Monogarov, D.B. Meerov, I.V. Fomenkov, E.A. Skryleva, M.Yu. Presnyakov, A.L. Vasiliev, N.I. Shishov, Yu.M. Milekhin.
Published in Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 54, No. 4, pp. 73–83, July–August, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pivkina, A.N., Muravyev, N.V., Monogarov, K.A. et al. Comparative Analysis of Boron Powders Obtained by Various Methods. I. Microstructure and Oxidation Parameters during Heating. Combust Explos Shock Waves 54, 450–460 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508218040093
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508218040093