Abstract
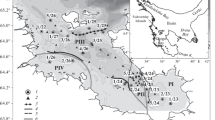
The abundance, biomass, size structure of small photosynthetic flagellates (SPF; 3–10 µm), chlorophyll a (Chl a), and the contribution of SPF to the total phytoplankton biomass were studied in Onega Bay of the White Sea in September 2019. The Chl a concentration in the surface water layer of the bay varies from 0.36 to 0.83 mg/m3. The contribution of photosynthetic algae to the total phytoplankton biomass ranges from 79 to 83%. The abundance and biomass of SPF in the photic layer varies from 0.04 × 109 to 0.22 × 109 cells/m3 and from 0.64 to 6.4 mg C/m3, respectively. Flagellates with a cell size of 6–10 µm dominate in the total SPF biomass and their share averages 82%. The SPF contribution to the total phytoplankton biomass in Onega Bay varies from 6 to 58% and does not depend on the phase of the tidal cycle. The obtained data on the SPF abundance evidenced that this group of protists plays a significant role in phytoplankton communities, and their estimate results in higher values of the total phytoplankton biomass of the White Sea in the fall compared to data obtained earlier.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Analytical, Kinetic, and Calculation Methods in Hydroengineering, Ed. by P. A. Lozovik and N. A. Efremenko (Nestor-Istoriya, St. Petersburg, 2017) [in Russian].
T. A. Belevich, L. V. Ilyash, I. A. Milyutina, et al., “Metagenomics of bolidophyceae in plankton and ice of the White Sea,” Biochemistry (Moscow) 82, 1538–1548 (2017).
T. A. Belevich, L. V. Ilyash, A. V. Zimin, et al., “Peculiarities of summer phytoplankton spatial distribution in Onega Bay of the White Sea under local hydrophysical conditions,” Moscow Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 71, 135–140 (2016).
V. Ya. Berger, Studies of Marine Fauna, Vol. 60 (68): Production Potential of the White Sea (Zoological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, 2007) [in Russian].
Hydrometeorology and Hydrochemistry of Seas of the USSR, Vol. 2: White Sea (Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, 1991) [in Russian].
Yu. S. Dolotov, N. N. Filatov, V. P. Shevchenko, et al., “Monitoring tidal conditions in estuaries of the Karelian coast of the White Sea,” Water Resour. 32, 611–628 (2005).
A. V. Drits, T. A. Belevich, L. V. Ilyash, et al., “Does zooplankton control phytoplankton development in White Sea coastal waters in spring?” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 58, 558–572 (2018).
L. V. Il’yash, T. I. Kol’tsova, and V. D. Fedorov, “Spatial distribution of phytoplankton in the White Sea in summer,” Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. 16: Biol., No. 4, 34–40 (2002).
L. V. Ilyash, L. S. Zhitina, and V. D. Fedorov, Phytoplankton of the White Sea (Yanus-M, Moscow, 2003) [in Russian].
L. V. Ilyash, I. G. Radchenko, V. P. Shevchenko, et al., “Spatial distribution of phytoplankton in the White Sea in the late summer period with regard to the water structure and dynamics,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 51, 993–1003 (2011).
L. V. Ilyash, T. N. Rat’kova, I. G. Radchenko, et al., “The White Sea phytoplankton,” in The White Sea System, Vol. 2: Water Column and Interacting Atmosphere, Cryosphere, River Run-Off, and Biosphere (Nauchnyi Mir, Moscow, 2012), pp. 605–639.
L. V. Ilyash, T. A. Belevich, A. N. Stupnikova, et al., “Effects of local hydrophysical conditions on the spatial variability of phytoplankton in the White Sea,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 55, 216–225 (2015).
I. A. Kiselev, “Phytoplankton of the White Sea,” Issled. Russ. Morei, No. 2 (105), 1–43 (1925).
O. I. Mamaev, Thermohaline Analysis of the Waters of World Ocean (Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, 1987) [in Russian].
E. R. Nikishova, I. G. Radchenko, and T. A. Belevich, “Small photosynthetic flagellates of the White Sea: seasonal dynamics and their role in plankton and ice communities,” Moscow Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 75, 147–152 (2020).
I. G. Radchenko, L. V. Ilyash, V. P. Shevchenko, et al., “Spatial distribution of phytoplankton in the subarctic estuary (Kem’ River, the White Sea),” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 59, 305–315 (2019).
T. N. Rat’kova, A. F. Sazhin, and K. N. Kosobokova, “Unicellular inhabitants of the White Sea underice pelagic zone during the early spring period,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 44, 240–246 (2004).
K. K. Sarukhan-Bek, I. G. Radchenko, and T. I. Kol’tsova, “Phytoplankton of the Chupa Bay (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea),” in Study of Phytoplankton during Monitoring of the Baltic Sea and Other Seas of the USSR (Moscow, 1991), pp. 111–119.
V. D. Fedorov, Analysis Methods of Phytoplankton and Its Activity (Moscow State Univ., Moscow, 1979) [in Russian].
E. J. Arar and G. B. Collins, Method 445.0: In Vitro Determination of Chlorophyll a and Pheophytin a in Marine and Freshwater Algae by Fluorescence (US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, 1997).
T. A. Belevich, L. V. Ilyash, I. A. Milyutina, et al., “Photosynthetic picoeukaryotes in the land-fast ice of the White Sea, Russia,” Microb. Ecol. 75 (3), 582–597 (2017).
V. Berger, S. Dahle, K. Galaktionov, et al., White Sea: Ecology and Environment (Derzavents, Tromsø, 2001).
D. A. Caron, “Technique for enumeration of heterotrophic and phototrophic nanoplankton, using epifluorescence microscopy, and comparison with other procedures,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46 (2), 491–498 (1983).
J. E. Cloern and A. D. Jassby, “Patterns and scales of phytoplankton variability in estuarine–coastal ecosystems,” Estuaries Coasts 33, 230–241 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-009-9195-3
D. W. Crawford, A. O. Cefarelli, I. A. Wrohan, et al., “Spatial patterns in abundance, taxonomic composition and carbon biomass of nano- and microphytoplankton in Subarctic and Arctic Seas,” Prog. Oceanogr. 162, 132–159 (2018).
M. D. Guiry and G. M. Guiry, AlgaeBase (National University of Ireland, Galway, 2021). http://www. a-lgaebase.org. Cited May 23, 2021.
Ø. Hammer, D. A. T. Harper, and P. D. Ryan, “PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis,” Palaeontol. Electron. 4 (1), 9 (2001).
H. Hillebrand, C. D. Durselen, D. Kirschtel, et al., “Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae,” J. Phycol. 35, 403–424 (1999).
M. D. Kravchishina, V. I. Burenkov, O. V. Kopelevich, et al., “New data on the spatial and temporal variability of the chlorophyll a concentration in the White Sea,” Dokl. Earth Sci. 448, 120–125 (2013).
A. M. Kubiszyn, J. M. Wiktor, J. M. Wiktor Jr., et al., “The annual planktonic protist community structure in an ice-free high Arctic fjord (Adventfjorden, West Spitsbergen),” J. Mar. Syst. 169, 61–72 (2017).
S. Menden-Deuer and E. J. Lessard, “Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 45, 569–579 (2000).
T. Rat’kova and V. Savinov, “Phytoplankton,” in White Sea: Ecology and Environment (Derzavets, Tromsø, 2001), pp. 23–30.
E. B. Sherr, B. F. Sherr, and L. Fessenden, “Heterotrophic protists in the central Arctic Ocean,” Deep Sea Res., Part II 44, 1665–1682 (1997).
V. R. Shevchenko, Y. S. Dolotov, N. N. Filatov, et al., “Biogeochemistry of the Kem’ River estuary, White Sea (Russia),” Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 9 (1–2), 57–66 (2005).
J. M. Sieburth, V. Smetacek, and J. Lenz, “Pelagic ecosystem structure: heterotrophic compartments of the plankton and their relationships to plankton size fractions,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 1256–1263 (1978).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the crew of the research vessel “Ecolog” for invaluable help in sampling and collecting materials for the study.
Funding
The work was carried out within the framework of the State Assignment of the Northern Water Problems Institute, Karelian Scientific Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, Lomonosov Moscow State University (topic no. 121032300135-7, part 2) and the Development Program of the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of Lomonosov Moscow State University “The Future of the Planet and Global Environmental Changes.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by D. Martynova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belevich, T.A., Nikishova, E.R., Tolstikov, A.V. et al. On the Role of Small Photosynthetic Flagellates in the Fall Phytoplankton Community of Onega Bay, White Sea. Oceanology 61, 944–953 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001437021060199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001437021060199