Abstract
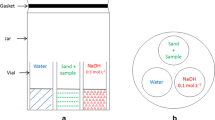
In the work, the effect of 120-day exposure to distilled water and seawater at 23°C on the structure and properties of polylactide was studied. It was found that the melting and glass transition temperature of polylactide decreased by 2°C in distilled water, while the crystallinity degree increased by 9 and 5% in distilled water and in seawater, respectively. Atomic force microscopy revealed pores defects with a diameter of 150–200 and 170–230 μm after exposure to seawater and distilled water, respectively. Elongation and tensile strength at break were significantly reduced during the hydrolytic degradation of polylactide.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. K. A. Barnes, A. Walters, and L. Goncalves, “Macroplastics at sea around Antarctica,” Mar. Environ. Res. 70, 250–252 (2010).
Yu. V. Tertyshnaya and L. S. Shibryaeva, “Degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its blends during treatment with UV light and water,” Polym. Sci., Ser. B 55, 164–168 (2013).
M. V. Podzorova, Yu. V. Tertyshnaya, and A. A. Popov, “The effect of environmental factors on biodegradable polylactide-based materials,” Polym. Sci., Ser. D 10, 289–292 (2017).
L.-T. Lim, R. Auras, and M. Rubino, “Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid),” Prog. Polym. Sci. 33, 820 (2008).
D. Garlotta, “A literature review of polylactid acid,” J. Polym. Environ. 9, 63–84 (2001).
Y. Young, S. W. Lee, S. J. Lee, and W. H. Park, “Thermal interfiber bonding of electrospun poly(L-lactid acid) nanofiber,” Mater. Lett. 60, 1331–1333 (2006).
M. Obarzanek-Fojt, Yv. Elbs-Glatz, E. Lizundia, L. Diener, S.-R. Sarasua, and A. Bruinink, “From implantation to degradation—are poly (L-lactide)/multiwall carbon nanotube composite materials really cytocompatible?,” Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 10 (5), 1041 (2014).
R. Ortiz, S. Moreno-Flores, I. Quintana, Md. M. Vivanco, J. R. Sarasua, and J. L. Toca-Herrera, “Ultra-fast laser microprocessing of medical polymers for cell engineering applications,” Mater. Sci. Eng: C 37, 241 (2014).
Yu. V. Tertyshnaya, S. G. Karpova, and A. A. Popov, “Effect of aqueous medium on the molecular mobility of polylactide,” Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 36 (6), 84–91 (2017).
V. K. Holm, S. Ndoni, and J. Risbo, “The stability of poly(lactic acid) packaging films as influenced by humidity and temperature,” J. Food Sci. 71, 40–44 (2006).
V. Piemonte and F. Gironi, “Kinetics of hydrolytic degradation of PLA,” J. Polym. Environ. 21, 313–318 (2013).
C. Stathokostopoulou and P. A. Tarantili, “Preparation, characterization and drug release studies from poly(D,L-lactic acid)/organoclay nanocomposites films,” J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 51, 117–124 (2014).
Q. Zhou and M. Xanthos, “Nanoclay and crystallinity effects on the hydrolytic degradation of polylactides,” Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 1450–1459 (2008).
E. Olewnik-Kruszkowska, “Influence of the type of buffer solution on thermal and structural properties of polylactide-based composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stab. 129, 87–95 (2016).
G. H. Yew, A. M. Mohd Yusof, Z. A. Mohd Ishak, and U. S. Ishiaku, “Water absorption and enzymatic degradation of polylactic acid/rice starch composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stab. 90, 488– 500 (2005).
G. E. Johnson, in Water in Polymers, Ed. by S. P. Rowland (Am. Chem. Soc., Washington, D.C., 1980), p. 441.
M. O. Gallyamov, Diffusion in Polymers. Visualization of Solutions to Typical Diffusion Problems (Krasand, 2014) [in Russian].
Y. Ohtani, K. Okumura, and A. Kawaguchi, “Crystallization behavior of amorphous poly(L-lactide),” J. Macromol. Sci., Part B: Phys. 42, 875–888 (2003).
Yu. V. Tertyshnaya, S. G. Karpova, O. V. Shatalova, A. V. Krivandin, and L. S. Shibryaeva, “Effect of temperature on the molecular mobility in polylactide,” Polym. Sci., Ser. A 58 (1), 50 (2016).
M. Deroine, A. Le Duigou, Y.-M. Corre, P.-Y. Le Gac, P. Davies, G. Cesar, and S. Bruzaud, “Accelerated aging of polylactide in aqueous environment: Comparative study between distilled water and seawater,” Polym. Degrad. Stab. 108, 319–329 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to NT-MDT Spectrum Instruments (Moscow) and S.I. Nesterov for their help in performing experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by D. Kharitonov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tertyshnaya, Y.V., Popov, A.A. Hydrolytic Degradation of Polylactide in Distilled Water and Seawater. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 13, 306–310 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995421220030211
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995421220030211