Abstract
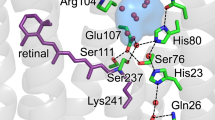
Three-dimensional X-ray models of the wild-type bacteriorhodopsin structure are investigated by means of the program PyMOL. Construction of the surfaces accessible to the solvent at the cytoplasmic side visualized a cavity near the proton carrier Asp96. The cavity shortens the way of the proton from the membrane surface to this carrier. The distance between the cavity surface and the centre of the carbonic atom of the Asp96 carboxylic group is ∼6 Å. Besides, for model structures 1c3w, 1qhj, and 1BRR, a channel of radius 1.1 Å is revealed between the cytoplasmic surface and Asp96carboxyl. The channel diameter is narrower than the characteristic diameter of the water molecule and apparently does not create conductivity in the nonexcited pigment. It is possible however that along this channel a hydrated “gap” opens at the second phase of a bacteriorhodopsin photocycle related with reprotonation of Asp96.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oesterhelt D., Stoeskenius W. 1971. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium, Nature New Biol. 233(39), 149–152.
Lanyi J.K. 2006. Proton transfers in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1757(8), 1012–1018.
Khitrina L.V., Ksenofontov A.L. 2004. Bacteriorhodopsin. Correspondence of the photocycle and electrogenesis with sites of molecule. Biokhimia (Moscow), (Rus.). 69(12), 1725–1728.
Skulachev V.P. 1992. Rhodopsin: From ion pumps to specialized photoreceptors. In: Proc. Vth Intern. Conf.: Structures and Functions of Retinal Proteins (Dourdan). Ed. Rigaud J.L. Montrouge, France: Collogue INSERM/John Libbey Eurotext Ltd. 221, 229–232.
Danshina S.V., Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Korana Kh.G., Marti T., Mogi T., Skulachev V.P. 1992. The mechanism of H+ transport by bacteriorhodopsin: A study on Asp-96 mutant forms. Biokhimia (Moscow) (Rus.). 57, 1574–1585.
Skulachev V.P. 1993. Interrelations of bioenergetic and sensory functions of the retinal proteins. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 26(2), 177–199.
Kaulen A.D. 2000. Electrogenic processes and protein conformational changes accompanying the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1460(1), 204–219.
Kalaidzidis I.V., Kaulen A.D., Radionov A.N., Khitrina L.V. 2001. Photoelectrochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biokhimia (Moscow) (Rus.). 66(11), 1511–1526.
Khitrina L.V. 2004. Bacteriorhodopsin. Is water no. 420 the terminal group in the proton transport chain? Biol. membrany (Rus.). 21(6), 473–475.
Shishkov A.V., Ksenofontov A.L., Bogacheva E.N., Kordyukova L.V., Badun G.A., Alekseevsky A.V., Tsetlin V.I., Baratova L.A. 2002. Studying the spatial organization of membrane proteins by means of tritium stratigraphy: Bacteriorhodopsin in purple membrane. Bioelectrochemistry. 56(1), 147–149.
Luecke H., Schobert B., Richter H.T., Cartailler J.P., Lanyi J.K. 1999. Structure of bacteriorhodopsin at 1.55 resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 291(4), 899–911.
Essen L., Siegert R., Lehmann W.D., Oesterhelt D. 1998. Lipid patches in membrane protein oligomers: Crystal structure of the bacteriorhodopsin-lipid complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95(20), 11673–11678.
Schätzler B., Dencher N.A., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D., Yaniv-Checover S., Nachliel E., Gutman M. 2003. Subsecond proton-hole propagation in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. J. 84(1), 671–686.
Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Khitrina L.V., Skulachev V.P. 1981. Fast stages of photoelectric processes in biological membranes. I. Bacteriorhodopsin. Eur. J. Biochem. 117(3), 461–470.
Kalaidzidis Y.L., Gavrilov A.V., Zaitsev P.V., Kalaidzidis A.L., Korolev E.V. 1997. Pluck —an environment for software development environment. Programmirovaniye (Rus.). 4, 38–46. [Translated.version: Kalaidzidis Y.L., Gavrilov A.V., Zaitsev P.V., Kalaidzidis A.L., Korolev E.V. 1997. Programming and Computer Software. 23 (4), 206–211]
Shinoda T., Ogawa H., Cornelius F., Toyoshima C. 2009. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4 resolution. Nature. 459(7245), 446–450.
Pedersen B.P., Buch-Pedersen M.J., Morth J.P., Palmgren M.G., Nissen P. 2007. Crystal structure of the plasma membrane proton pump. Nature. 450(7172), 1111–1114.
Yu E.W., Aires J.R., Nikaido H. 2003. AcrB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli: Composite substratebinding cavity of exceptional flexibility generates its extremely wide substrate specificity. J. Bacteriol. 185(19), 5657–5664.
Belrhali H., Nollert P., Royant A., Menzel C., Rosenbuch J.P., Landau E.M., Pebay-Peyroula E. 1999. Protein, lipid and water organization in bacteriorhodopsin crystals: A molecular view of the purple membrane at 1.9 Å resolution. Structure (London). 7(8), 909–917.
Subramaniam S., Henderson R. 2000. Molecular mechanism of vectorial proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Nature. 406(6796), 653–657.
Nekrasov B.N. 1969. Osnovy obshchey khimii (Bases of General Chemistry), in 3 vols. Vol. 2. Moscow: Khimiya.
Stoeckenius W., Lozier R.H., Bogomolni R.A. 1979. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 505(3–4), 215–278.
Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Skulachev V.P., Khitrina L.V., Chekulayeva L.N. 1981. Phases of photoelectrical response of bacteriorhodopsin. Biokhimiya (Moscow) (Rus.). 46(6), 998–1004.
Khitrina L.V., Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Chekulayeva L.N. 1982. Inhibition of bacteriorhodopsin by formalin and lanthanum. Biokhimiya (Moscow) (Rus.). 47(11), 1763–1772.
Drachev A.L., Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Khitrina L.V. 1984. The action of lanthanum ions and formaldehyde on the proton-pumping function of bacteriorhodopsin. Eur. J. Biochem. 138(2), 349–356.
Friedman R., Nachliel E., Gutman M. 2003. The role of small intraprotein cavities in the catalytic cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. J. 85(2), 886–896.
Hirai T., Subramaniam S., Lanyi J.K. 2009. Structural snapshots of conformational changes in a seven-helix membrane protein: Lessons from bacteriorhodopsin. Curr. Opin Struct. Biol. 19(4), 433–439.
Lanyi J.K., Schobert B. 2006. Propagating structural perturbation inside bacteriorhodopsin: Crystal structures of the M state and the D96A and T46V mutants. Biochemistry. 45(39), 12003–12010.
Hayakawa N., Kasahara T., Hasegawa D., Yoshimura K., Murakami M., Kouyama T. 2008. Effect of xenon binding to a hydrophobic cavity on the proton pumping cycle in bacteriorhodopsin. J. Mol. Biol. 384(4), 812–823.
Drachev L.A., Kaulen A.D., Skulachev V.P. 1984. Correlation of photochemical cycle, H+ release and uptake, and electric events in bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 178(2), 331–335.
Heberle J., Riesle J., Thiedemann G., Oesterhelt D., Dencher N.A. 1994. Proton migration along the membrane surface and retarded surface to bulk transfer. Nature. 370(6488), 379–382.
Nachliel E., Gutman M., Kiryati S., Dencher N.A. 1996. Protonation dynamics of the extracellular and cytoplasmic surface of bacteriorhodopsin in the purple membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 93(20), 10747–10752.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.V. Khitrina, 2011, published in Biologicheskie Membrany, 2011, Vol. 28, No. 2, pp. 137–144.
The article was translated by the author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khitrina, L.V. Cavity depth on the bacteriorhodopsin peptide surface near the proton carrier Asp96: Data of X-ray structure models. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 5, 198–204 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747811010065
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747811010065