Abstract
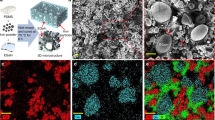
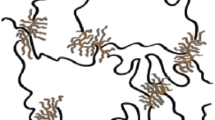
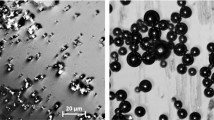
New metal-polymer composites based on mechanochemically synthesized magnetostrictive Fe-Ga phase particles with dimensions of up to 2 μm dispersed and spatially oriented in a polymer matrix have been studied. The polymer matrix for spatial anisotropic stabilization of particles was represented by modified polyurethane (PU). An increase in the magnetostrictive effect was achieved by directed orientation of particles in a magnetic field applied during polymerization of the PU matrix. The spatial anisotropy of the composite has been studied by the methods of conversion Mössbauer spectroscopy with resonant X-ray detection and scanning electron microscopy. It is shown that the mechanochemical synthesis is an effective method of obtaining particles with microstress-enhanced magnetostriction. The use of these particles for the formation of a functional elastomer composite provides a material with significant magnetostrictive effect, which can be several-fold increased due to orientation of particles in an applied magnetic field. The obtained anisotropic magnetostrictive composite is a promising material for the creation of smart functional components of positioning systems, attenuators, and sensors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Z. Lyakhov and T. F. Grigor’eva, Mechanocomposites-Precursors for Creating Materials with Unique Properties (Izd-vo SO RAN, Novosibirsk, 2009) [in Russian].
L. Nicolais and G. Carotenuto, Metal-Polymer Nano-composites (Wiley & Sons, 2005).
J. Atulaismba and A. B. Flatau, Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 043001 (2011).
S. Rafique, J. R. Cullen, M. Wuttig, and J. Cui, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 6939 (2004).
E. Hristoforou and A. Ktena, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 372 (2007).
T. Yu. Kiseleva, E. E. Levin, A. A. Novakova, et al., Proceedings of the 10th Int. Workshop “Optimization of Composition, Structure and Properties of Metals, Oxides, etc.” (Chernogolovka, 2011), pp. 1–9.
T. F. Grigor’eva, T. Yu. Kiseleva, S. A. Kovaleva, A. A. Novakova, S. V. Tsybulya, A. P. Barinova, and N. Z. Lyakhov, Phys. Met. Metallogr. 113, 575 (2012).
A. A. Novakova, A. A. Kiselev, R. N. Kuz’min, and G. V. Sidorova, JETP Lett. 43, 415 (1986).
A. A. Novakova, E. V. Smirnov, and T. S. Gendler, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 300, e354 (2006).
A. A. Novakova, O. V. Agladze, R. S. Gvozdover, et al., J. Surf. Investig. X-ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 16, 1863 (2001).
Yu. L. Raikher and O. V. Stolbov, Vychisl. Mekh. Splosh. Sred 2(2), 85 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.Yu. Kiseleva, S.I. Zholudev, I.A. Il’inykh, A.A. Novakova, 2013, published in Pis’ma v Zhurnal Tekhnicheskoi Fiziki, 2013, Vol. 39, No. 24, pp. 71–80.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiseleva, T.Y., Zholudev, S.I., Il’inykh, I.A. et al. Anisotropic magnetostrictive metal-polymer composites for functional devices. Tech. Phys. Lett. 39, 1109–1113 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785013120201
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785013120201