Abstract
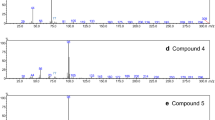
Synthetic cathinones (SC) continue to represent the second largest group of substances on the drug market among new psychoactive substances (NPS). They have gained their fame mainly due to their amphetamine-like effects. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction currently monitors over 830 NPS among which 156 are synthetic cathinone derivatives. The constant introduction of new derivatives often makes their identification in the examined evidence much more difficult. This is most often caused by the presence of isomers within the same group of substances as well as SC with similar chemical structures. Gas chromatography coupled to electron ionization mass spectrometry (GC-EI-MS) is the gold standard in their toxicological analysis. The aim of this study was to analyze 49 certified NPS standards from the SC group in the parent form and/or acetyl or trimethylsilyl derivatives by GC-EI-MS and to characterize their electron mass spectra. Additionally, an integrated application with the MassHunter software was used to create an authors’ library of SC including such parameters as retention times and mass spectra. The developed method allowed to achieve chromatographic separation of derivatives within a given group of positional isomers and SC with similar chemical structures. In the case of chloromethcathinone isomers, trimethylsilylation was necessary to achieve complete separation of these derivatives. The analysis of mass spectra of acetyl derivatives of SC allowed for their classification depending on the presence of characteristic m/z values. The obtained data allowed for the development of an automated library of mass spectra of these compounds with application potential for the purposes of forensic toxicology.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
European Drug Report 2021: Trends and Developments, Luxembourg: European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, 2021. https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/edr/trends-developments/2021_en. Accessed June 15, 2021.
Kelly, J.P., Drug Test. Anal., 2013, vol. 3, p. 439.
May, M.C., Pavone, D.C., and Lurie, I.S., J. Sep. Sci., 2020, vol. 43, p. 3756.
Silva, B., Fernandes, C., Tiritan, M.E., Pinto, M.M., Valente, M.J., Carvalho, M., de Pinho, P.G., and Remião, F., Forensic Toxicol., 2016, vol. 34, p. 372.
Mohr, S., Taschwer, M., and Schmid, M.G., Chirality, 2012, vol. 24, no. 6, p. 486.
Wang, D., Chen, X., Ming, Z., Jiang, L., and Zhou, Y., Separations, 2022, vol. 9, no. 3.
Westphal, F. and Junge, T., Forensic Sci. Int., 2012, vol. 223, p. 97.
Helfer, A.G., Turcant, A., Boels, D., Ferec, S., Lelièvre, B., Welter, J., Meyer, M.R., and Maurer, H.H., Drug Test. Anal., 2015, vol. 7, p. 368.
Merola, G., Fu, H., Tagliaro, F., Macchia, T., and McCord, B.R., Electrophoresis, 2014, vol. 35, p. 3231.
Schmid, M.G. and Hägele, J.S., J. Chromatogr. A, 2020, vol. 1624, 461256.
Pascual-Caro, S., Borrull, F., Calull, M., and Aguilar, C., J. Anal. Toxicol., 2021, vol. 45, no. 7, p. 693.
Concheiro, M., Anizan, S., Ellefsen, K., and Huestis, M.A., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2013, vol. 405, no. 29, p. 9437.
Lau, T., Concheiro, M., and Cooper, G., J. Anal. Toxicol., 2020, vol. 44, no. 7, p. 679.
Power, J.D., McGlynn, P., Clarke, K., McDermott, S.D., Kavanagh, P., and O’Brien, J., Forensic Sci. Int., 2012, vol. 212, p. 6.
Kavanagh, P., O’Brien, J., Fox, J., O’Donnell, C., Christie, R., Power, J.D., and McDermott, S.D., Forensic Sci. Int., 2012, vol. 216, p. 19.
Mohamed, K.M. and Bakdash, A., Anal. Chem. Insights, 2017, vol. 12, p. 1.
Alsenedi, K.A. and Morrison, C., Anal. Methods, 2017, vol. 9, p. 2732.
Kohyama, E., Chikumoto, T., Tada, H., Kitaichi, K., Horiuchi, T., and Ito, T., Anal. Sci., 2016, vol. 32, p. 831.
Meyer, M.R., Vollmar, C., Schwaninger, A.E., Wolf, E.U., and Maurer, H.H., J. Mass Spectrom., 2012, vol. 47, p. 253.
Bakdash, A., Open Chem., 2019, vol. 17, p. 902.
Zuba, D., TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2012, vol. 32, p. 15.
Abiedalla, Y., DeRuiter, J., Abdel-Hay, K.M., and Randall Clark, C., Forensic Chem., 2016, vol. 2, p. 46.
Levitas, M.P., Andrews, E., Lurie, I., and Marginean, I., Forensic Sci. Int., 2018, vol. 288, p. 107.
Kranenburg, R.F., Verduin, J., Stuyver, L.I., de Ridder, R., van Beek, A., Colmsee, E., and van Asten, A.C., Forensic Chem., 2020, vol. 20, 100273.
Cayman Spectral Library. https://www.caymanchem.com/forensics/publications/csl. Accessed March 16, 2022.
Meyer, M.R., Wilhelm, J., Peters, F.T., and Maurer, H.H., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2010, vol. 397, p. 1225.
Maurer, H.H., Pfleger, K., Weber, A.A., Mass Spectral Library of Drugs, Poisons, Pesticides, Pollutants, and Their Metabolites, New York: Wiley, 2016, 5th ed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Synowiec, K., Rojek, S., Maciów-Głąb, M. et al. The Role of GC-EI-MS and Derivatization in the Detection of New Psychoactive Substances Exemplified by 49 Synthetic Cathinones. J Anal Chem 77, 1315–1324 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106193482210015X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106193482210015X