Abstract
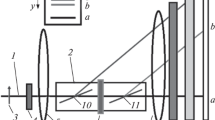
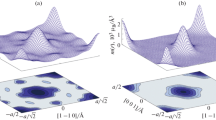
A new way of analyzing the polarization of thermal and cold neutron beams, based on the dependence of the neutron-scattering cross section on the neutron polarization upon diffraction from a magnetic spiral, is proposed. In this method, the working element of the neutron-polarization analyzer is a single-crystal noncentrosymmetric cubic helicoidal MnSi magnet, the spin spiral in which is formed at T < T c (T c = 29 K) in the magnetic-field range H < H C2 ∼ 500 mT. Since the spiral period d in MnSi is 180 Å, thermal and cold neutrons with wavelengths λ ≤ 2d diffract from this structure. It is established that the efficiency of neutron-polarization analysis is as high as 100% with the experimental geometry when the polarization vector P is parallel to the scattering vector Q.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. V. Maleev, Phys. Usp. 45, 569 (2002).
F. Bloch, Phys. Rev. 50, 259 (1936).
D. J. Hughes, J. R. Wallace, and R. H. Holzmann, Phys. Rev. 73, 1277 (1947).
L. V. Tarasov and I. I. Gurevich, Low-Energy Neutron Physics (North-Holland, Amsterdam 1968; Nauka, Moscow, 1965).
C. G. Shull, E. O. Wollan, and W. C. Koehler, Phys. Rev. 81, 626 (1951).
S. Tomiyoshi, Y. Yamaguchi, and Y. Ito, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 213–214, 932 (1995).
P. Boni, D. Clemens, M. Senthil Kumar, and C. Pappas, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 267–268, 320 (1999).
J. W. Lynn, J. K. Kjems, L. Passell, A. M. Saxena, and B. P. Schoenborn, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 9, 454 (1976).
C. F. Majkrzak and L. Passell, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A 41, 41 (1985).
Th. Krista, S. J. Kennedy, T. J. Hicks, and F. Mezei, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 241–243, 82 (1997).
T. E. Chupp, J. Neutron Res. 6, 205 (1997).
T. Shinohara, J. Suzuk, T. Oku, S. Takata, H. Kira, K. Suzuya, K. Aizawa, M. Arai, T. Otomo, and M. Sugiyama, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 404, 2640 (2009).
A. Ioffe, G. Gordeev, B. Ibrayev, Th. Krist, and F. Mezei, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 234–236, 1071 (1997).
S. Funahashi, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 137, 99 (1976).
D. B. McWhan, Rev. Phys. Appl. 19, 715 (1984).
L. D. Cussen, D. J. Goossens, and T. J. Hicks, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 440, 409 (2000).
P. J. Webster and K. R. A. Ziebeck, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 15–18, 473 (1980).
F. Tasset and E. Ressouche, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 359, 537 (1995).
T. Okua, K. Sakaia, T. Adachia, K. Ikedaa, H. M. Shimizua, R. Maruyamac, M. Hinoc, S. Tasakic, Y. Kiyanagid, T. Kamiyamad, H. Iwasad, K. Sasakid, T. Inoe, M. Furusakae, D. Yamazakif, J. Suzukif, and T. Ebisawaf, Phys. B: Condens. Matter 335, 226 (2003).
S. V. Grigoriev, S. V. Maleyev, A. I. Okorokov, Yu. O. Chetverikov, P. Boni, R. Georgii, D. Lamago, H. Eckerlebe, and K. Pranzas, Rev. Phys. B 74, 214414 (2006).
B. Lebech, J. Bernhard, and T. Freltoft, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1, 6105 (1989).
N. Kanazawa, Y. Onose, T. Arima, D. Okuyama, K. Ohoyama, S. Wakimoto, K. Kakurai, S. Ishiwata, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 156603 (2011).
N. Kanazawa, J.-H. Kim, D. S. Inosov, J. S. White, N. Egetenmeyer, J. L. Gavilano, S. Ishiwata, Y. Onose, T. Arima, B. Keimer, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 86, 134425 (2012).
O. L. Makarova, A. V. Tsvyashchenko, G. Andre, F. Porcher, L. N. Fomicheva, N. Rey, and I. Mirebeau, Phys. Rev. B 85, 205205 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.M. Chubova, V.A. Dyadkin, E.V. Moskvin, S.V. Grigoriev, 2014, published in Poverkhnost’. Rentgenovskie, Sinkhrotronnye i Neitronnye Issledovaniya, 2014, No. 10, pp. 64–70.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chubova, N.M., Dyadkin, V.A., Moskvin, E.V. et al. Method of analysis of neutron polarization using noncentrosymmetric cubic helicoidal magnets. J. Surf. Investig. 8, 1020–1026 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451014050267
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451014050267