Abstract
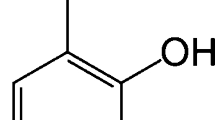
Several laws governing ampholyte transport through ion-exchange membranes are established by a comparative analysis of the concentration dependence of electrical conductivity for homogeneous (CMX, AMX) and heterogeneous (MK-40, MA-41) membranes in NaCl, LysHCl, and NaH2PO4 solutions. The increase in the electrical conductivity of membranes in ampholyte solutions as the solutions become more dilute is explained by the increased fraction of divalent ions of the amino acid (cation-exchange membrane) or from phosphoric acid (anion-exchange membrane) in the membrane as a result of Donnan exclusion of hydrolysis products (hydroxide ions or protons, respectively).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nefedova, G.Z., Klimova, Z.G., and Sapozhnikova, G.S., Ionitovye membrany: Granulyaty, Poroshki (katalog) (Ion-Exchange Membranes: Granules and Powders (catalog)), Pashkov, A.B., Ed., Moscow: NIITEKhim, 1977.
NEOSEPTA Ion-Exchange Membranes (catalog), Tokyo: Tokuyama Soda Co. Ltd.
Gurskaya, G.V., Struktury aminokislot (Structure of Amino Acids), Moscow: Nauka, 1966.
Koryta, J., Dvorjak, J., and Bohackova, V., Electrochemistry, London: Methuen, 1970.
Bobreshova, O.V., Faustov, A.S., Chubirko, M.I., Popov, V.I., Aristov, I.V., and Kulintsov, P.I., Lizinodna iz vazhneishikh nezamenimykh aminokislot v obespechenii polnotsennogo pitaniya (Lysine: One of the Most Important Essential Amino Acids in Guaranteeing Optimal Nutrition), Voronezh: Voronezh. Gos. Univ., 2003.
Roques, H., Fondements theoriques du traitment chimique des eaux (Theoretical Fundamentals of the Chemical Treatment of Waters), 2 vols., Paris: Technique et Documentation-Lavoisier, 1990.
Dobosh, D., Elektrokhimicheskie konstanty (Electrochemical Constants), Moscow: Mir, 1980.
Strel’nikova, O.Yu., Bobreshova, O.V., Kulintsov, P.I., and Stepanenko, L.V., Kondensirovannye sredy i mezhfaznye granitsy, 2001, vol. 3, No. 1, p. 92.
Novikova, L.A., Kulintsov, P.I., Bobreshova, O.V., and Bobylkina, O.V., Elektrokhimiya, 2002, vol. 38, p. 1016 [Russ. J. Electrochem. (Engl. Transl.), 2002, vol. 38, pp. 909–912].
Belaid, N.N., Dammak, L., Ngom, B., Larchet, C., and Auclair, B., Eur. Polym. J., 1998, vol. 34, p. 564.
Damaskin, B.B., Petrii, O.A., and Tsirlina, G.A., Elektrokhimiya (Electrochemistry), Moscow: Khimiya, 2001.
Zabolotskii, V.I., and Nikonenko, V.V., Perenos ionov v membranakh (Ion Transport in Membranes), Moscow: Nauka, 1996.
Berezina, N.P., Gnusin, N.P., Demina, O.A., and Timofeev, S., J. Membr. Sci., 1994, vol. 86, p. 207.
Zabolotsky, V.I. and Nikonenko, V.V., J. Membr. Sci., 1993, vol. 79, p. 181.
Kotova, D.L. and Selemenev, V.F., Termicheskii analiz ionoobmennykh materialov (Thermal Analysis of Ion-Exchange Materials), Moscow: Nauka, 2002.
Mamaeva, O.Yu., Kulintsov, P.I., and Bobreshova, O.V., Elektrokhimiya, 2000, vol. 36, p. 1504 [Russ. J. Electrochem. (Engl. Transl.), 2000, vol. 36, pp. 1332–1334].
Kulintsov, P.I., Bobreshova, O.V., Aristov, I.V., Novikova, I.V., and Khrykina, L.A., Elektrokhimiya, 2000, vol. 36, p. 365 [Russ. J. Electrochem. (Engl. Transl.), 2000, vol. 36, pp. 327–329].
Bobreshova, O.V., Aristov, I.V., Kulintsov, P.I., Khrykina, L.A., and Mamaeva, O.Yu., Membrany, 2001, no. 7, p. 3.
Bobreshova, O., Novikova, L., Kulintsov, P., and Balavadze, E., Desalination, 2002, vol. 149, p. 363.
Pismenskaya, N., Laktionov, E., Nikonenko, V., El Attar, A., Auclair, B., and Pourcelly, G., J. Membr. Sci., 2001, vol. 181, p. 185.
Pismenskaya, N., Nikonenko, V., Volodina, E., and Pourcelly, G., Desalination, 2002, vol. 147, p. 345.
Helfferich, F., Ion Exchange, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1962.
Choi, J.-H. and Moon, S.-H., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, vol. 265, p. 93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.D. Pismenskaya, E.I. Belova, V.V. Nikonenko, C. Larchet, 2008, published in Elektrokhimiya, 2008, Vol. 44, No. 11, pp. 1381–1387.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pismenskaya, N.D., Belova, E.I., Nikonenko, V.V. et al. Electrical conductivity of cation-and anion-exchange membranes in ampholyte solutions. Russ J Electrochem 44, 1285–1291 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193508110141
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193508110141