Abstract
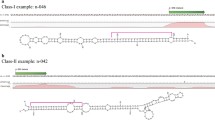
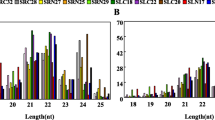
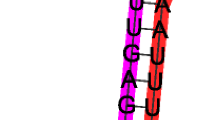
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous RNAs, involved in plant growth and development as well as in stress responses. Among them, some are highly evolutionally conserved in the plant kingdom, which provides a powerful strategy for identifying miRNAs in a new species. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) is one of the important food crops in the world, but few of its miRNAs have been determined. In this study, a total of 24 conserved miRNAs belonged to 14 miRNA families, and 16 novel miRNAs were identified by deep sequencing. Using previously established protocols, a total of 48 potential target genes were predicted for the conserved and novel miRNAs. These target genes are involved in transcription, metabolism, defense response, oxidationreduction processes, etc. Overall, this study provides information concerning the miRNAs precursors in I. batatas, mature miRNAs, and miRNA targets, and it is valuable as the basis for the future research of miRNA functions in I. batatas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EST:
-
Expressed Sequence Tag
- miRNAs:
-
microRNAs
- nt:
-
nucleotide
- sRNA:
-
small RNA
- snRNA:
-
small nuclear RNA
- snoRNA:
-
small nucleolar RNA
- ncRNAs:
-
noncoding RNAs
- NCBI:
-
national center for biotechnology information
- MFE:
-
minimum free energy
- MFEI:
-
minimum free energy index
- ARF:
-
auxin response factor
- AGO:
-
Agonaute
- SBP:
-
squamosa promoter-binding-like protein
References
Pashkovskiy, P.P. and Ryazansky, S.S., Biogenesis, evolution, and functions of plant microRNAs, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2013, vol. 78, pp. 627–637.
Jones-Rhoades, M.W., Bartel, D.P., and Bartel, B., MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2006, vol. 57, pp. 19–53.
Zhang, B., Wang, Q., and Pan, X., MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants, J. Cell Physiol., 2007, vol. 210, pp. 279–289.
Kozomara, A. and Griffiths-Jones, S., MiRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data, Nucleic Acids Res., 2013, vol. 42: D68–73. doi 10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Sunkar, R., Zhou, X., Zheng, Y., Zhang, W., and Zhu, J.K., Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing, BMC Plant Biol., 2008, vol. 8, p. 25.
Song, C., Wang, C., Zhang, C., Korir, N.K., Yu, H., Ma, Z., and Fang, J., Deep sequencing discovery of novel and conserved microRNAs in trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliate), BMC Genomics, 2010, vol. 11, p. 431.
Zhao, C.Z., Xia, H., Frazier, T.P., Yao, Y.Y., Bi, Y.P., Li, A.Q., Li, M.J., Li, C.S., Zhang, B.H., and Wang, X.J., Deep sequencing identifies novel and conserved microRNAs in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.), BMC Plant Biol., 2010, vol. 10, p. 3.
Zhang, R., Marshall, D., Bryan, G.J., and Hornyik, C., Identification and characterization of miRNA transcriptome in potato by high-throughput sequencing, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, pp. e57233.
Zhu, Q.H. and Helliwell, C.A., Regulation of flowering time and floral patterning by miR172, J. Exp. Bot., 2010, vol. 62, p. 9.
Sakaguchi, J. and Watanabe, Y., MiR165/166 and the development of land plants, Dev. Growth Differ., 2012, vol. 54, pp. 93–99.
Williams, L., Grigg, S.P., Xie, M., Christensen, S., and Fletcher, J.C., Regulation of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem and lateral organ formation by microRNA miR166g and its AtHD-ZIP target genes, Development, 2005, vol. 132, pp. 3657–3668.
Guo, H.S., Xie, Q., Fei, J.F., and Chua, N.H., MicroRNA directs mRNA cleavage of the transcription factor NAC1 to downregulate auxin signals for Arabidopsis lateral root development, Plant Cell Online, 2005, vol. 17, pp. 1376–1386.
Fujii, H., Chiou, T.J., Lin, S.I., Aung, K., and Zhu, J.K., A miRNA involved in phosphate-starvation response in Arabidopsis, Curr. Biol., 2005, vol. 15, pp. 2038–2043.
Sunkar, R., Kapoor, A., and Zhu, J.K., Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance, Plant Cell Online, 2006, vol. 18, pp. 2051–2065.
Zhao, B., Ge, L., Liang, R., Li, W., Ruan, K., Lin, H., and Jin, Y., Members of miR-169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription factor, BMC Mol. Biol., 2009, vol. 10, p. 29.
Lin, J.S., Lin, C.C., Lin, H.H., Chen, Y.C., and Jeng, S.T., MicroR828 regulates lignin and H2O2 accumulation in sweet potato on wounding, New Phytol., 2012, vol. 196, pp. 427–440.
Xie, F., Burklew, C.E., Yang, Y., Liu, M., Xiao, P., Zhang, B., and Qiu, D., De novo sequencing and a comprehensive analysis of purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) transcriptome, Planta, 2012, vol. 236, pp. 101–113.
Firon, N., LaBonte, D., Villordon, A., Kfir, Y., Solis, J., Lapis, E., Perlman, T.S., Doron-Faigenboim, A., Hetzroni, A., and Althan, L., Transcriptional profiling of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) roots indicates downregulation of lignin biosynthesis and up-regulation of starch biosynthesis at an early stage of storage root formation, BMC Genomics, 2013, vol. 14, p. 460.
Zhang, B., Pan, X., Cox, S., Cobb, G., and Anderson, T., Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2006, vol. 63, pp. 246–254.
Allen, E., Xie, Z., Gustafson, A.M., and Carrington, J.C., MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants, Cell, 2005, vol. 121, pp. 207–221.
Berezikov, E., Cuppen, E., and Plasterk, R.H.A., Approaches to microRNA discovery, Nat. Genetics, 2006, vol. 38, pp. S2–S7.
Dehury, B., Panda, D., Sahu, J., Sahu, M., Sarma, K., Barooah, M., Sen, P., and Modi, M., In silico identification and characterization of conserved miRNAs and their target genes in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) expressed sequence tags (ESTs), Plant Signal. Behav., 2013, vol. 8: e26543.
Farh, K.K.-H., Grimson, A., Jan, C., Lewis, B.P., Johnston, W.K., Lim, L.P., Burge, C.B., and Bartel, D.P., The widespread impact of mammalian microRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution, Science, 2005, vol. 310, pp. 1817–1821.
Patanun, O., Lertpanyasampatha, M., Sojikul, P., Viboonjun, U., and Narangajavana, J., Computational identification of microRNAs and their targets in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz.), Mol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 257–269.
Xie, F., Frazier, T.P., and Zhang, B., Identification, characterization and expression analysis of microRNAs and their targets in the potato (Solanum tuberosum), Gene, 2011, vol. 473, pp. 8–22.
Wang, Y., Li, K., Chen, L., Zou, Y., Liu, H., Tian, Y., Li, D., Wang, R., Zhao, F., and Brett, J.F., MicroRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors, GmARF8a and GmARF8b, is required for soybean (Glycine max L.) nodulation and lateral root development, Plant Physiol., 2015, doi 10.1104/pp.15.00265
Gursinsky, T., Pirovano, W., Gambino, G., Friedrich, S., Behrens, S.-E., and Pantaleo, V., Homeologs of the Nicotiana benthamiana antiviral ARGONAUTE1 show different susceptibilities to microRNA168-mediated control, Plant Physiol., 2015, vol. 168, pp. 938–952. doi 10.1104/pp.15.00070
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, X., E, Z., Ma, P. et al. Identification of miRNAs in sweet potato by Solexa sequencing. Russ J Plant Physiol 63, 283–292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716020060
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716020060