Abstract
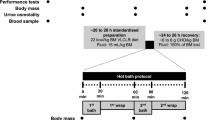
Metabolic effects of physical countermeasures against deficient weight-bearing were studied in three groups of 21- to 30 year-old volunteers during seven-day dry immersion (DI). Blood serum was investigated for 38 biochemical parameters that characterize the myocardium, skeletal musculature, hepatobiliary system, kidney, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract, as well as prostate, protein-nucleic, carbohydrate, electrolyte and mineral metabolisms. Seven-day DI without countermeasures (n = 5) increased the concentration of conjugated bilirubin, suppressed the activities of muscular (creatine phosphokinase CPK MM) and myocardial enzymes (CPK MB, OBDH), and caused an upward trend in cholesterol, its atherogenic LDP fraction and triglycerides. Mechanic foot stimulation (n = 6) intensified, within the physiologically normal limits, erythrocyte hemolysis, raising total bilirubin and potassium. Despite the stimulation, activity of muscle and myocardial enzymes decreased. Blood creatinine decreased to a lesser extent than in the immersed group without stimulation; however, lipid parameters did not rise. High-frequency stimulation of the lower leg and hip muscles in the course of immersion (n = 5) was found to heighten the activity of muscle enzymes and potassium level in blood beyond the physiologically normal range. Change in creatinine did not reach statistical significance, and lipid metabolism parameters were not different from baseline values. The use of these physical methods of counteracting weight-bearing deficiency did not interfere with redistribution of body liquids due to immersion. The parameters under study were mostly within the normal limits throughout the experimental exposure, suggesting the absence of pathological developments during DI or as a consequence of physical stimulation. Therefore, the reactions were obviously of normal adaptive nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
At’kov, O.Yu. and Bednenko, V.S., Gipokineziya. Nevesomost’. Klinicheskie i fiziologicheskie aspekty (Hipokinesia and Weightlessness: Clinical and Physiological Aspects), Moscow, 1989.
Bazarnova, M.A. and Morozova, V.T., Rukovodstvo po klinicheskoi laboratornoi diagnostike (Guide on Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics), Kiev, 1986.
Bravyi, Ya.R., Bersenev, E.Yu., Missina, S.S., et al., Effect of dry immersion on the mechanisms of metabolic reflex control of hemodynamic parameters during muscle work, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2008, vol. 42, no. 5, p. 39.
Dixon, M. and Webb, E.C., Enzymes, London: Longmans, Green and Co., 1979, 3rd edition.
Eshmanova, A.K., Luchitskaya, E.S., and Baevskii, R.M., Study of the autonomic control of circulation during seven-day dry immersion, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2008, vol. 42, no. 5, p. 45.
Zacks, S., The theory of Statistical Inference, Wiley, 1971.
Kamyshnikov, V.S., Spravochnik po klinikobiokhimicheskim issledovaniyam v laboratornoi diagnostike (Handbook of Clinical and Biochemical Studies in the Laboratory Diagnosis), Moscow, 2009.
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Pestov, I.D., and Egorov, A.D., The system of medical prevention in long-term spaceflights, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2008, vol. 42, no. 6, p. 66.
Markin, A.A., Zhuravleva, O.A., Morukov, B.V., et al., Characteristics of metabolism in cosmonauts after long-term missions at the International Space Station, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2005, vol. 39, no. 4, p. 36.
Markin, A.A., Morukov, B.V., Zhuravleva, O.A., et al., Time course of biochemical blood parameters in an experiment with seven-day immersion, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2008, vol. 42, no. 5, p. 56.
Epstein, M., Cardiovascular and renal effects of head-out water immersion in man, Circulat. Res., 1976, vol. 39, no. 5, p. 619.
Epstein, M., Water immersion and the kidney: Implications for volume regulations, Undersea Biomed. Res., 1984, vol. 11, no. 2, p. 113.
Markin, A., Strogonova, L., Balashov, O., et al., The dynamics of blood biochemical parameters in cosmonauts during long-term space flights, Acta Astronaut., 1998, vol. 42, nos. 1–8, p. 247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Markin, O.A. Zhuravleva, B.V. Morukov, I.V. Zabolotskaya, L.V. Vostrikova, D.S. Kuzhichkin, 2011, published in Aviakosmicheskaya i Ekologicheskaya Meditsina, 2011, Vol. 45, No. 4, pp. 28–34.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markin, A.A., Zhuravleva, O.A., Morukov, B.V. et al. Metabolic effects of physical countermeasures against deficient weight-bearing in an experiment with seven-day immersion. Hum Physiol 40, 752–758 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S036211971407010X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S036211971407010X