Abstract
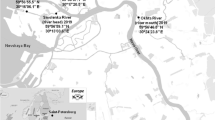
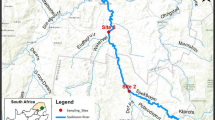
Chemoecological studies were carried out in the water areas of the Kagau and Longtau rivers in the Can Gio Biosphere Reserve (Vietnam). Mass-spectrometry analysis was used to determine the concentrations of 15 microelements (heavy metals and metalloids) in water and bottom sediments. The overall pollution level in the Can Gio rivers was found to be moderate. However, the concentrations of some heavy metals in several cases exceeded the maximum permissible concentration at short-time exposure; also, the limits of safe concentrations at chronic exposure were exceeded for some elements. The concentrations of some heavy elements amount to 30 to 80% of the MPC for water bodies used for fishery. Primarily, these are copper, zinc, arsenic, vanadium, iron, and molybdenum. It was found that, according to the Regulations of Vietnam, the waters of the examined water areas showed concentrations of suspended matter in excess of the standards for category A1 sources, and the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water was below the standard. The obtained results suggest the need to monitor the chemical–ecological conditions of rivers in Can Gio as protected natural objects, which are also used to some extent for social and economic purposes.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alekseeva, N.N., V’etnam. Priroda: fiziko-geograficheskii ocherk, Bol`shaya sovetskaya enciklopediya (Great Soviet Encyclopedia). http://bigenc.ru (Accessed: May 21, 2022).
Vodyanitskii, Yu.N., Standards for the contents of heavy metals and metalloids in soils, Eurasian Soil Sci., 2012, no. 3, pp. 321–328.
Geografiya V’etnama. Geograficheskoe opisanie V’etnama (Vietnam Geography. Geographic Description of Vietnam). http://www.world-globe.ru/countries/vietnam/geography. Accessed May 21, 2022.
Glavnoe statisticheskoe upravlenie V’etnama (Main Statistical Department of Vietnam). www.gso.gov.vn/default_en.aspx?tabid=467&idmid=3&ItemID=14454. Accessed May 21, 2022.
GOST (State Standard) R 56 219-2014. Determination of the concentrations of 62 elements by the method of mass spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma, M.: Standartinform, 2015.
Znamenitye reki V’etnama (Famous Rivers of Vietnam). (Electronic Resource). zen.yandex.ru. Accessed: May 27, 2022.
Zolotokopova, S.V. and Ngo, T.K., Effect of industrial production on the environmental conditions of the Sherepok R. (Vietnam), Vestn. nauch. konf. (Bull. Sci. Conf.), Tambov, 2017, no. 4, Pt. 1, pp. 60–61.
Le Bin’ Zyong, Effect of coal-mining plants in Vietnam on the hydrosphere, Izv. Tul’sk. GU. Nauki Zemle, 2015, no. 1, pp. 14–21.
Le Tkhi Vin’, Heavy metals in the sphere of the Van Fong Bay (Khanh Hoa Strait), Zhurn. Nauk Morsk. Tekhnol., 2012, no. 3, pp. 12–23.
Mass-spektrometry s induktivno svyazannoi plazmoi (ISP-MS): PlasmaQuant MS i Plasma Quant MS Elite. Instruktsiya po ekspluatatsii (Mass Spectrometers with Inductively Coupled Plasma (ISP-MS). Operation Manual), Iena: Analytik Jena AG, 2014.
Mirzoeva, N.Yu., Tereshchenko, N.N., Paraskiv, A.A., Proskurnin, V.Yu., and Morozov, E.G., Heavy metals in the surface water of the Atlantic sector of the Antarctic in the 79th voyage of RV Akademik Mstislav Keldysh, Morskoi Biol. Zhurn., 2020, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 56–68.
Ngo Tkhe Kyong, The concentration and regularities in the distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in river ecosystems in industrial regions of Vietnam: case study of the Sherepok R., Daklak province, Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow: RUDN Univ., 2018, p. 199.
Nguen Van Zung, Ecological problems of the Mekong R. delta, Sb. dokl. VI Vseros. nauch.-prakt. konf. “Nauchnaya initsiativa inostrannykh studentov i aspirantov rossiiskikh vuzov” (Coll. Pap. VI All-Russ. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Scientific Initiative of Foreign Students and Postgraduates of Russian Higher Education Institutions”), Tomsk, 2013, vol. I, pp. 96–98.
PND F 16.2.2:2.3.71-2011 Metodika izmerenii massovykh dolei metallov v osadkakh stochnykh vod, donnykh otlozheniyakh, obraztsakh rastitel’nogo proiskhozhdeniya spektral’nymi metodami (Procedure for Measuring Mass Fractions of Metals in Wastewater Sediments and Vegetation Samples by Spectral Methods), Moscow: Federal. Sluzh. Nadz. Sfer. Prirodopol’z., 2011.
Longtau River [Electronic Resource] www.hmong. press/wiki/Long_Tau_ river (Accessed: June 5, 2022).
Dongnai River [Electronic Resource] http://wiki5.ru (Accessed June 5, 2022).
RD 52.10.243-92 Rukovodstvo po khimicheskomu analizu morskikh vod (Guide on the Chemical Analyses of Seawater). URL http://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200042955 (Accessed February 27, 2022).
Rukovodstvo po metodam khimicheskogo analiza morskikh vod (Guide for Seawater Chemical Analyses), Oradovskii, S.G, Ed., Lenigrad: Gidrometeoizdat.
Spravochnik po geokhimicheskim poiskam poleznykh iskopaemykh (Guide on the Geochemical Methods for Mineral Exploration by Geochemical Methods), Solov, A.P, Arkhipov, A.Ya, Bugrov, V.A, Eds., Moscow: Nedra, 1990.
Spravochnik. Kharakteristiki zagryaznyayushchikh veshchestv. Razdel II. Dlya vodnykh ob’’ektov (Reference Book. Pollutant Characteristics. Section II. For Water Objects), Perm’: Ekologiya, 2016.
Khoang Tkhi Tkhan’ Tkhui, Heavy metals in the deposits in the Saigon R., Ho Chi Minh C., Zhurn. nauchn. razr. tekhnol., 2007, no. 1, pp. 27–37.
Fam Viet Nu, As pollution in the Mekong delta, Sel. Khoz. Razv. Sel. Mestn., 2011, no. 2, pp. 15–21.
Fiziko-geograficheskoe polozhenie V’etnam (Physiographic Position of Vietnam), [Elektronnyi resurs]. https://fb.ru/article/380112/vetnam-geograficheskoe-polojenie-i-obschie-svedeniya-o-strane. Accessed June 22, 2022.
Fung Tkhai Zyong., Ecological–geochemical conditions of the Mekong R. delta (the Republic of Vietnam), Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Geol.–Mineral.) Dissertation, Tomsk: NITPU, 2015, p. 26.
Biosphere reserves. http://www.unesco.org/new/en/natural-sciences/environment/ecological-sciences/biosphere-reserves/asia-and-the-pacific/vietnam/can-gio-mangrove/. Accessed October 22, 2021.
Cao, Vu., Hung, Bui DuyCam., Pham, Thi., Ngoc, Mai., and Bach, Quang., Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in municipal sewage sludge from a river in highly urbanized metropolitan area in Hanoi, Vietnam: levels, accumulation pattern and assessment of land application, Environ. Geochem. Health, 2015, no. 37, pp. 133–146.
Cenci, R.M. and Martin, J.M., Concentration and fate of trace metals in Mekong River delta, Sci. Total Environ., 2004, no. 332, pp. 167–182.
Grachev, V.A., The regularities of heavy metals and arsenic accumulation in the vegetation of riverside depending on the level of technogenic load, J. Pharm. Sci. Res., 2018, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 800–804.
Hurt, B.T., Jones, M.J., and Pistone, G., Transboundary Water Quality Issues in the Mekong River Basin, Mekong River Commission, Melbourne: Water Studies Centre, Monash Univ., 2001.
Nguyen Thanh Giao and Huynh Thi Hong Nhien, Assessment of surface water quality and monitoring in Southern Vietnam using multicriteria statistical approaches, Sustainable Environ. Res., 2022, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 2–12.
Nguyen, T.L.H., Ohtsubo, M., Li, L.Y., and Higashi, T., Heavy metal pollution of the To-Lich and Kim-Nguu River in Hanoi City and the industrial source of the pollutants, J. Fac. Agr. Kyushu Univ., 2007, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 141–146.
14QCVN 08-MT:2015/BTNMT. QUY CHUẨN KỸ THUẬT QUỐC GIA VỀ CHẤT LƯỢNG NƯỚC MẶT. National Technical Regulation on Surface Water Quality. HÀ NỘI – 2015. 13 tr. http://cem.gov.vn/storage/documents/5d6f3ecb26484qcvn-08-mt2015btnmt. pdf. Accessed November 29, 2021) (in Vietnamese).
15QCVN 43:2017/BTNMT. QUY CHUẨN KỸ THUẬT QUỐC GIA VỀ CHẤT LƯỢNG TRẦM TÍCH. National Technical Regulation on Sediment Quality. https://luatvietnam.vn/tai-nguyen/quy-chuan-qcvn-43-2017-btnmt-chat-luong-tram-tich-166191-d3.html. Accessed November 29, 2021 (in Vietnamese).
Prathumratana, L., Sthiannopkao, S., and Kim, K.W., The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the lower Mekong River, Environ. Int., 2008, no. 34, pp. 860–866.
Warmer Henk and Ronald vam Dokkum,s Water Pollution Control in the Netherlands: Policy and Practice the Netherlands, Lelystad: RIZA, 2002.
Funding
This study was carried out as a research of the Joint Russian–Vietnamese Tropic Research and Technological Center (Subject Ekolan E-3.4), and the governmental order to the FRC (the subject of the Kovalevskii Institute of Biology of Southern Seas, Russian Academy of Sciences, state registration 121031500515-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tereshchenko, N.N., Chuzhikova-Proskurnina, O.D., Proskurnin, V.Y. et al. Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Water and Bottom Sediments in the Rivers in the Can Gio Biospheric Reserve, Vietnam. Water Resour 50, 330–343 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S009780782302015X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S009780782302015X