Abstract
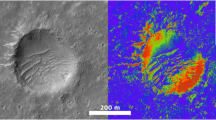
The relief of polygonal structures at the Phoenix landing site on Mars has been determined with the improved photoclinometry method from the images acquired with the HiRISE camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The investigations showed that, within 1 km from the landing site, the topography amplitude of the relief on the surface scales of 5.5–65 m varies within the range of ∼40 to 70 cm. The polygonal structures of 2–6 m across correspond to the small-scale relief with the topography amplitude ranging from 20 to 30 cm and the standard deviation of about 3 cm. Within 1 km from the landing site, the variations of these characteristics are small. For the small polygons that are less than 5.5 m in size, the typical height is 10–15 cm. The polygons of 18–22 m in size are up to 28 cm in height, while the polygons of 60–90 m in size reach about 44 cm in height. The error in determining the relief heights was ±5.5%. The investigations showed that the improved photoclinometry method is promising for the study of small-scale features of the Martian surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dulova, I.A., Kornienko, Yu.V., and Skuratovskii, S.I., The way to determine surface relief by means of clinometric method under initial data insufficiency or excess, Radiofiz. Elektron., 2007, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 408–415.
Dulova, I.A., Skuratovsky, S.I., Bondarenko, N.V., and Kornienko, Yu.V., Reconstruction of the surface topography from single images with the photometric method, Solar Syst. Res., 2008, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 522–535.
Ershov, E.D., Obshchaya geokriologiya (General Geocryology), Moscow: MSU, 2002.
Grumpe, A.M. and Wöhler, C., DEM construction and calibration of hyperspectral image data using pairs of radiance images, in Proc. 7th Int. Symp. Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, Dubrovnik, 2011, pp. 609–614.
Kirk, R.L., Howington-Kraus, E., Rosiek, M.R., Anderson, J.A., Archinal, B.A., Becker, K.J., Cook, D.A., Galuszka, D.M., Geissler, P.E., Hare, T.M., Holmberg, I.M., Keszthelyi, L.P., Redding, B.L., Delamere, W.A., Gallagher, D., Chapel, J.D., Eliason, E.M., King, R., and McEwen, A.S., Ultrahigh resolution topographic mapping of Mars with HiRISE stereo images: methods and first results, in Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Mars, Pasadena: Lunar and Planet. Inst., July 9–13, 2007.
Korteniemi, J. and Kreslavsky, M.A., Patterned ground in Martian high northern latitudes: morphology and age constraints, Icarus, 2013, vol. 225, no. 2, pp. 960–970. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2012.09.032
Kuzmin, R.O. and Zabalueva, E.V., Polygonal terrains on Mars: preliminary results of global mapping of their spatial distribution, in Proc. 34th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., Houston, 2003, Abstract no. 1912.
Kuzmin, R.O., Ground ice in the Martian regolith, in Water on Mars and Life, Tokano, T., Ed., Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer-Verlag, 2005, pp. 152–189.
Levy, J.S., Head, J.W., and Marchant, D.R., Cold and dry processes in the Martian Arctic: geomorphic observations at the phoenix landing site and comparisons with terrestrial cold desert landforms, Geophys. Rev. Lett., 2009a, vol. 36, no. 21. doi: 10.1029/2009GL040634
Levy, J., Head, J., and Marchant, D., Thermal contraction crack polygons on Mars: classification, distribution, and climate implications from HiRISE observations, J. Geophys. Res. (Planets), 2009b, vol. 114, p. E01007.
Levy, J.S., Marchant, D.R., and Head, J.W., Thermal contraction crack polygons on Mars: a synthesis from HiRISE, Phoenix, and terrestrial analog studies, Icarus, 2010, vol. 206, pp. 229–252.
Lohse, V., Heipke, C., and Kirk, R.L., Derivation of planetary topography using multi-image shape-from-shading, Planet. Space Sci., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 661–674.
Mangold, N., High latitude patterned grounds on Mars: classification, distribution and climatic control, Icarus, 2005, vol. 174, pp. 336–359.
Marchant, D.R., Lewis, A.R., Phillips, W.M., Moore, E.J., Souchez, R.A., Denton, G.H., Sugden, D.E., Potter, N., Jr., and Landis, G.P., Formation of patterned ground and sublimation till over Miocene glacier ice in Beacon Valley, southern Victoria land, Antarctica, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 2002, vol. 114, pp. 718–730.
McEwen, A.S., Eliason, E.M., Bergstrom, J.W., Bridges, N.T., Hansen, C.J., Delamere, W.A., Grant, J.A., Gulick, V.C., Herkenhoff, K.E., Keszthelyi, L., Kirk, R.L., Mellon, M.T., Squyres, S.W., Thomas, N., and Weitz, C.M., Mars reconnaissance orbiter’s high resolution imaging science experiment (HiRISE), J. Geophys. Res. (Planets), 2007, vol. 112, p. E05S02.
Mellon, M.T., Malin, M.C., Arvidson, R.E., Searls, M.L., Sizemore, H.G., Heet, T.L., Lemmon, M.T., Keller, H.U., and Marshall, J., The periglacial landscape at the Phoenix landing site, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, p. E00E06. doi: 10.1029/2009JE003418
Mitrofanov, I.G., Zuber, M.T., Litvak, M.L., Demidov, N.E., Sanin, A.B., Boynton, W.V., Gilichinsky, D.A., Hamara, D., Kozyrev, A.S., Saunders, R.D., Smith, D.E., and Tretyakov, V.I., Water ice permafrost on Mars: layering structure and subsurface distribution according to HEND/Odyssey and MOLA/MGAs data, Geophys. Rev. Lett., 2007, vol. 34, no. 18. doi: 10.1029/2007GL030030
Parusimov, V.G. and Kornienko, Yu.V., The way to determine the most probable surface relief by using its optical image, Astrometr. Astrofiz., 1973, no. 19, pp. 20–24.
Romanovskii, N.N., Osnovy kriogeneza litosfery (Foundations of Lithosphere Cryogenesis), Moscow: MSU, 1993.
Skuratovsky, S.I., Dulova, I.A., Kornienko, Yu.V., and Bondarenko, N.V., Optimal observational conditions of the planetary surface for the relief reconstruction with photometric method, in Proc. 42nd Vernadsky-Brown Microsymp., Moscow, 2005, Abstract no. M42-61.
Smith, D.E., Zuber, M.T., Solomon, S.C., Phillips, R.J., Head, J.W., Garvin, J.B., Banerdt, W.B., Muhleman, D.O., Pettengill, G.H., Neumann, G.A., Lemoine, F.G., Abshire, J.B., Aharonson, O., Brown, D.C., Hauck, S.A., Ivanov, A.B., McGovern, P.J., Zwally, H.J., and Duxbury, T.C., The global topography of Mars and implications for surface evolution, Science, 1999, vol. 284, pp. 1495–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5419.1495
van Diggelen, J., A photometric investigation of the slopes and heights of the ranges of hills in the maria of the Moon, Neth. Astron. Inst. Bull., 1951, vol. 11, pp. 283–289.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.V. Bondarenko, I.A. Dulova, Yu.V. Kornienko, 2014, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 2014, Vol. 48, No. 4, pp. 263–279.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bondarenko, N.V., Dulova, I.A. & Kornienko, Y.V. Topography of polygonal structures at the Phoenix landing site on mars through the relief retrieval from the HiRISE images with the improved photoclinometry method. Sol Syst Res 48, 243–258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094614040030
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094614040030