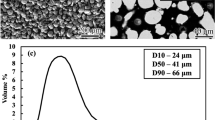
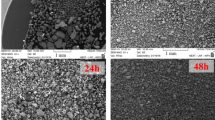
Abstract
The effect of main parameters of the selective laser melting (SLM) process on the structure and properties of permanent magnets made from an Alnico alloy is studied. Series of samples were prepared using various combinations of SLM conditions and spherical powder particles of an Alnico alloy prepared by melt spraying. A suitable range of manufacturing parameters is determined, which allows us to fabricate permanent magnets with an optimum structure. Conclusions about the effect of the main parameters of the SLM process on the surface morphology of the deposited alloy are inferred. The optimization of scanning conditions allows us to decrease the cracking and, therefore, to reach a high level of physical and mechanical properties of Alnico alloy samples.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Jaćimović, F. Binda, L. G. Herrmann, F. Greuter, J. Genta, M. Calvo, T. Tomše, and R. A. Simon, “Net shape 3D printed NdFeB permanent magnet,” Adv. Eng. Mater. 19, 1700098 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700098
A. S. Zhukov, B. K. Barakhtin, V. V. Bobyr, P. A. Kuznetsov, and I. V. Shakirov, “The experience of magnets manufacturing from metal powder using a laser,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1791, 012122 (2021).
F. Bittner, J. Thielsch, and W. G. Drosse, “Laser powder bed fusion of Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets,” Prog. Addit. Manuf. 5, 3–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-020-00117-7
V. Chaudhary, S. A. Mantri, R. V. Ramanujan, and R. Banerjee, “Additive manufacturing of magnetic materials,” Prog. Mater. Sci. 114, 100688 (2020). ISSN 0079-6425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100688
E. A. Périgo, J. Jacimovic, F. García Ferré, and L. M. Scherf, “Additive manufacturing of magnetic materials,” Addit. Manuf. 30, 100870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100870
A. B. Baldissera, P. Pavez, P. A. P. Wendhausen, C. H. Ahrens, and J. M. Mascheroni, “Additive manufacturing of bonded Nd–Fe–B–effect of process parameters on magnetic properties,” IEEE Trans Magn. 53, 1–4 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2017.2715722
L. Li, A. Tirado, I. C. Nlebedim, O. Rios, B. Post, V. Kunc, R. R. Lowden, E. Lara-Curzio, R. Fredette, J. Ormerod, T. A. Lograsso, and M. P. Paranthaman, “Big area additive manufacturing of high performance bonded NdFeB magnets,” Sci. Rep. 6, 36212 (2016).
T. Kolb, F. Huber, B. Akbulut, C. Donocik, N. Urban, D. Maurer, and J. Franke, “Laser beam melting of NdFeB for the production of reare-earth magnets,” Proc. EDCP Conf. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/EDPC.2016.7851311
C. Huber, H. Sepehri-Amin, M. Goertler, M. Groenefeld, Iu. Teliban, K. Hono, and D. Suess, “Coercivity enhancement of selective laser sintered NdFeB magnets by grain boundary infiltration,” Acta Mater. 172, 66–71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.04.037
D. Goll, D. Vogelgsang, U. Pflanz, D. Hohs, T. Grubesa, J. Schurr, T. Bernthaler, D. Kolb, H. Riegel, and G. Schneider, “Refining the microstructure of Fe–Nd–B by selective laser melting,” Phys. Status Solidi 13, 1800536 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssr.201800536
N. Urban, A. Meyer, S. Kreitlein, F. Leicht, and J. Franke, “Efficient near net-shape production of high energy rare earth magnets by laser beam melting,” Appl. Mech. Mater. 871, 137–144 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.871.137
A. S. Volegov, S. V. Andreev, N. V. Selezneva, I. A. Ryzhikhin, N. V. Kudrevatykh, L. Mädler, and I. V. Okulov, “Additive manufacturing of heavy rare earth free high-coercivity permanent magnets,” Acta Mater. 188, 733–739 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.02.058
C. Huber, G. Mitteramskogler, M. Goertler, Iu. Teliban, M. Groenefeld, and D. Suess, “Additive manufactured polymer-bonded isotropic ndfeb magnets by stereolithography and their comparison to fused filament fabricated and selective laser sintered magnets,” Materials 13, 1916 (2020). https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/ 13/8/1916.
E. White, E. Rinko, T. Prost, T. Horn, C. Ledford, C. Rock, and I. Anderson, “Processing of alnico magnets by additive manufacturing,” Appl. Sci. 9, 4843 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224843
I. A. Radulov, V. V. Popov, A. Koptyug, F. Maccari, A. Kovalevsky, S. Essel, J. Gassmann, K. P. Skokov, and M. Bamberger, “Production of net-shape Mn–Al permanent magnets by electron beam melting,” Addit. Manuf. 30, 100787 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100787
M. S. K. K. Y. Nartu, S. Dasari, A. Sharma, V. Chaudhary, S. M. Varahabhatla, S. A. Mantri, E. Ivanov, R. V. Ramanujan, N. B. Dahotre, and R. Banerjee, “Reducing coercivity by chemical ordering in additively manufactured soft magnetic Fe–Co (Hiperco) alloys,” J. Alloys Compd. 861, 157998 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157998
V. Chaudhary, N. M. S. K. K. Yadav, S. A. Mantri, S. Dasari, A. Jagetia, R. V. Ramanujan, and R. Banerjee, “Additive manufacturing of functionally graded Co–Fe and Ni–Fe magnetic materials,” J. Alloys Compd. 823, 153817 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153817
E. M. H. White, A. G. Kassen, E. Simsek, W. Tang, R. T. Ott, and I. E. Anderson, “Net shape processing of alnico magnets by additive manufacturing,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, No. 11, 2101606 (2017).
R. Skomski, P. Manchanda, P. Kumar, B. Balamurugan, A. Kashyap, and D. J. Sellmyer, “Predicting the future of permanent-magnet materials,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, No. 7, 3215–3220 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2248139
P. F. Rottmann, A. T. Polonsky, T. Francis, M. G. Emigh, M. Krispin, G. Rieger, McL. P. Echlin, C. G. Levi, and T. M. Pollock, “TriBeam tomography and microstructure evolution in additively manufactured Alnico magnets,” Mater. Today 49, 23–34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2021.05.003
L. Zhou, M. K. Miller, Lu. Ping, Ke. Liqin, R. Skomski, H. Dillon, Q. Xing, A. Palasyuk, M. R. McCartney, D. J. Smith, S. Constantinides, R. W. McCallum, I. E. Anderson, V. Antropov, and M. J. Kramer, “Architecture and magnetism of alnico,” Acta Mater. 74, 224–233 (2014). ISSN 1359-6454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.04.044
P. A. Kuznetsov, I. V. Shakirov, A. S. Zukov, V. V. Bobyr’, and M. V. Starytsin, “Effect of particle size distribution on the structure and mechanical properties in the process of laser powder bed fusion,” J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1758, 012021 (2021).
V. Bobyr, A. Zhukov, I. Shakirov, and P. Kuznetsov, “Selection of the selective laser melting modes—As the method of achieving an item’s complex shape with the specified physical and mechanical properties,” Mater. Today: Proc. 19, 2129–2133 (2019).
P. Kuznetsov, I. Shakirov, A. Mozhayko, A. Zhukov, and V. Bobyr, “Comparison of sequential and circular scanning thermal fields and their influence on microstructure of Alnico alloy produced by laser powder bed fusion,” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1967, 012064 (2021).
Funding
The experimental studies were performed using equipment of the Center of Collective Access “Composition, Structure, and Properties of Structural and Functional Materials” at the Scientific Research Center Kurchatov Institute, Gorynin Central Research Institute of Structural Materials Prometei and were supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (agreement no. 13.CKP.21.0014, unique identifier RF-2296.61321X0014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by N. Kolchugina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakirov, I.V., Zhukov, A.S., Perevislov, S.N. et al. The Effect of Selective Laser Melting Conditions on the Structure of an Alnico Alloy. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 227–237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22030103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22030103