Abstract
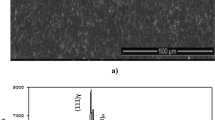
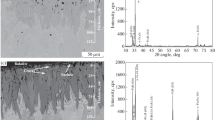
In this study, AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel surface was boronized with nanoboron and ekabor-III powders at 950 and 1000°C for 2 and 4 hours period by solid-state box boronizing method. Then, behaviors of the boronized specimen in the microstructure, three-point bending, and tensile strength characteristics were investigated. As a result of the boriding process, the boride layer thickness in the range of 23–67 µm and microhardness value in the range of 1020–2200 HV have been obtained according to the increase in processing time and temperature and to the particle size of the boron source (0, 1). The coating layer on boronized specimens did not exhibit any sign of reaction caused by the tensile strength applied until the yield point was in both tests. Although the particle size of the boron agents was more effective on the boronized specimen’s bending and tensile strength behaviors, it was observed that processing temperature and its duration are effective as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Atik, “Mechanical properties and wear strength in aluminum–alumina composites,” Mater. Struct. 31, 418–422 (1998).
E. Atik, U. Yunker, and C. Meric, “The effect of conventional heat treatment and boronizing on abrasive wear and corrosion of SAE 1010, SAE 1040, D2 and 304 steels,” Tribol. Int. 36, 155–161 (2003).
M. Mathew and P. K. Rajendrakumar, “Optimization of process parameters of boro-carburized low carbon steel for tensile strength by Taquchi method with grey relational analysis,” Mater. Design, 32, 3637–3644 (2011).
D. A. Brandt and J. C. Warner, Metallurgy Fundamentals, Goodheart-Willcox Company Inc., GoodheartWillcox Publisher, Tinley Park, Il., 301, 219–222 (2005).
M. Ulutan, “Investigation of mechanical behaviors of an AISI 4140 steel after surface hardening and coating processes,” Ph. D. Dissertation, Osmangazi Univ., Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2007.
E. Kaluç, “Effect of spot welding parameters on the tensile and shear strength and intergrannular corrosion of ferritic–austenitic stainless steel couple,” Ph. D. Dissertation, Istanbul Tech. Univ., Gradute School of Natural and Applied Sciences, 1988).
A. Abou-Elazm, R. Abdel-Karim, I. Elmahallawi, and R. Rashad, “Correlation between the degree of sensitization and stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of type 304H stainless steel,” Corr. Sci. 51, 203–208 (2009).
S. Taktak, “Some mechanical properties of borided AISI H13 and 304 steels,” Mater. Design 8, 1836–1843 (2004).
M. Keddam and S. M. Chentouf, “A diffusion model for describing the bilayer growth (FeB/Fe2B) during the iron powder-pack bonding,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 293–299 (2005). DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.01.016.
I. Usta, I. Ozbek, M. Ipek, C. Bindal, and A. H. Ucisik, “The characterization of boride pure tungsten,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 194, 330–334 (2005).
I. Uslu, H. Comert, M. Ipek, O. Ozdemir, and C. Bindal, “Evaluation of borides formed on AISI P20 steel,” Mater. Design 28, 55–61 (2007).
U. Sen, S. Sen, and F. Yilmaz, “An evaluation of some properties of borides deposited on boronized ductile iron,” J. Mater. Process. Technol. 148, 1–7 (2004).
M. Kulka and A. Pertek, “The importance of carbon content beneath iron borides after boriding of chromium and nickel-based lowcarbon steel,” Appl. Surf. Sci, 214, 161–171 (2003).
E. Rodn, G. Cabeo, G. Laudien, S. Biemer, K.-T. Rie, and S. Hoppe, “Plasma-assisted boriding of industrial components in a pulsed D.C. glow discharge,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 116, 229–233 (1999).
I. Campos, G. Ramirez, U. Figueroa, J. Martinez, and O. Morales, “Evaluation of boron mobility on the phases FeB, Fe2B and diffusion zone in AISI 1045 and M2 steels,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 3469–3475 (2007).
O. Özdemir, M.A. Omar, M. Usta, S. Zeytin, C. Bindal, A.H. Ucisik, “An investigation on boriding kinetics of AISI 316 stainless steel,” Vacuum 83, 175–179 (2009).
C. Martini, G. Palombarini, and M. Carbucicchio, “Mechanism of thermochemical growth of iron borides on iron,” J. Mater. Sci. 39, 933–937 (2004).
I. Uslu, H. Comert, M. Ipek, F.G. Celebi, O. Özdemir, and C. Bindal, “A comparison of borides formed on AISI 1040 and AISI P20 steels,” Mater. Design 28, 1819–1826 (2007).
A. Günen, M. S. Gök, A. Erdoğan, et. al. “Investigation of micro-abrasion wear behavior of boronized stainless steel with nanoboron powders,” Tribol. Trans., 274, 1065–1070 (2013).
H. J. Hunger and G. Trute, “Boronizing to produce wear-resistant surface layers,” Heat Treat. Metals, 2, 31–39 (1994).
X. Tian, Y. L. Yang, S. J. Sun, J. An, Y. Lu, Z. G. Wang, “Tensile properties of boronized N80 steel tube cooled by different methods,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 18, 162–167 (2009).
Y. Kayali, “Investigation of the diffusion kinetics of borided stainless steels,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 1061–1068 (2013).
R. Malik, D. Burch, M. Z. Bazant and G. Ceder, “Particle size dependence of the ionic diffusivity,” Nano Lett. 10, 4123–4127 (2010).
C. Meriç, S. Sahin, and S. S. Yilmaz, “Investigation of the effect on boride layer of powder particle size used in boronizing with solid boron-yielding substances,” Mater. Res. Bull. 35, 2165–2172 (2000).
A. Galibois, O. Boutenko, and B. Voyzelle, “Mécanisme de formation des couches borurées sur les aciers a haut Carbone.—Technique des pates,” Acta Metall. 28, 1753–1764 (1980).
K. Hulka, J. M. Gray, and F. Heisterkamp, Metallurgical Concept and Full-Scale Testing of a High Toughness H 2 S Resistant 0.03%–0.10%Nb Steel, Niobium Tech. Report, NbTR 16/90, (1990).
C. M. Suh, S. H. Kim, J. H. Lee, and N. S. Hwang, “Variation of boride layer characteristics by heating conditions and materials,” Int. J. Modern Phys. B 17, 1795–1800 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Günen, A., Kurt, B., Somunkιran, İ. et al. The effect of process conditions in heat-assisted boronizing treatment on the tensile and bending strength characteristics of the AISI-304 austenitic stainless steel. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 116, 896–907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15090021
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15090021