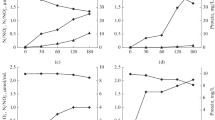
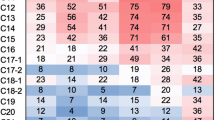
Abstract
Enrichment cultures of aerobic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria obtained from the injection and production wells of the Dagang oil field (China) were studied by molecular biological and microbiological methods. This work is the first to report simultaneous isolation of DNA and RNA from enrichment cultures of microorganisms from oil strata with further construction of clone libraries of 16S rRNA genes and 16S crDNA (complementary rDNA). Comparative analysis of the DNA- and RNA-derived clone libraries made it possible to determine the total genomic diversity of microorganisms, as well as to reveal metabolically active microorganisms in these cultures. Phylotypes of bacteria of the genus Geobacillus were found to be dominant in the DNA and RNA clone libraries of the enrichment cultures from the production well. Phylotypes of bacteria belonging to Geobacillus, Pseudomonas, Tepidiphilus, and other genera were detected in the DNA and RNA libraries obtained from the culture from the injection well. Phylotypes of bacteria of the genus Geobacillus were predominant in the RNA library and represented the second-largest group (after pseudomonads) in the DNA library. In the RNA libraries of the alkB genes of both enrichments, three homologs close to alkB-geo1, alkB-geo2, and alkB-geo4 of bacteria of the genus Geobacillus were detected. The occurrence pattern of the alkB transcripts, ribosomal RNA, and the 16S rRNA genes of bacteria of the genus Geobacillus indicates the predominance and functional activity of geobacilli in the enrichment cultures of hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria from high-temperature petroleum reservoir.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belyaev, S.S., Laurinavichus, K.S., Obraztsova, A.Ya., Gorlatov, S.N., and Ivanov, M.V., Microbial Processes in Near-Bottom Zones of Oil Field Injection Wells, Mikrobiologiya, 1982, vol. 51, pp. 997–1001 (in Russian).
Nazina, T.N., Rozanova, E.P., and Kuznetsov, S.I., Microbial Oil Transformation Processes Accompanied by Methane and Hydrogen-Sulfide Formation, Geomicrobiol. J., 1985, vol. 4, pp. 103–130.
Nazina, T.N., Grigor’yan, A.A., Shestakova, N.M., Babich, T.L., Pavlova, N.K., Ivoilov, V.S., Belyaev, S.S., Ivanov, M.V., Feng, Q., Ni, F., Wang, J., She, Y., Xiang, T., Mei, B., and Luo, Z., MEOR Study Enhances Production in a High-Temperature Reservoir, World Oil J., 2008, pp. 97–101.
Nazina, T.N., Tourova, T.P., Poltaraus, A.B., Novikova, E.V., Grigoryan, A.A., Ivanova, A.E., Lysenko, A.M., Petrunyaka, V.V., Osipov, G.A., Belyaev, S.S., and Ivanov, M.V., Taxonomic Study of Aerobic Thermophilic Bacilli: Descriptions of Geobacillus subterraneus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Geobacillus uzenensis sp. nov. from Petroleum Reservoirs and Transfer of Bacillus stearothermophilus, Bacillus thermocatenulatus, Bacillus thermoleovorans, Bacillus kaustophilus, Bacillus thermoglucosidasius and Bacillus thermodenitrificans to Geobacillus as the New Combinations G. stearothermophilus, G. thermocatenulatus, G. thermoleovorans, G. kaustophilus, G. thermoglucosidasius and G. thermodenitrificans, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 51, pp. 433–446.
Nazina, T.N., Sokolova, D.Sh., Shestakova, N.M., Grigoryan, A.A., Mikhailova, E.M., Babich, T.L., Lysenko, A.M., Tourova, T.P., and Poltaraus, A.B., Qingxian Feng, Fangtian Ni, and Belyaev, S.S. The Phylogenetic Diversity of Aerobic Organotrophic Bacteria from the Dagang High-Temperature Oil Field, Mikrobiologiya, 2005, vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 401–409 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 343–351].
Nazina, T.N., Sokolova, D.Sh., Grigoryan, A.A., Shestakova, N.M., Mikhailova, E.M., Poltaraus, A.B., Tourova, T.P., Lysenko, A.M., Osipov, G.A., and Belyaev, S.S., Geobacillus jurassicus sp. nov., a New Thermophilic Bacterium Isolated from a High-Temperature Petroleum Reservoir, and the Validation of the Geobacillus Species, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 28, pp. 43–53.
Feng, L., Wang, W., Cheng, J., Ren, Y., Zhao, G., Gao, C., Tang, Y., Liu, X., Han, W., Peng, X., Liu, R., and Wang, L., Genome and Proteome of Long-Chain Alkane Degrading Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 Isolated from a Deep-Subsurface Oil Reservoir, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2007, vol. 104, pp. 5602–5607.
Vomberg, A. and Klinner, U., Distribution of alkB Genes within n-Alkane-Degrading Bacteria, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 89, pp. 339–348.
van Beilen, J.B., Smits, T.H., Whyte, L.G., Schorcht, S., Rothlisberger, M., Plaggemeier, T., Engesser, K.-H., and Witholt, B., Alkane Hydroxylase Homologues in Gram-Positive Strains, Environ. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 4, pp. 676–682.
Van Beilen, J.B., Li, Z., Duetz, W.A., Smits, T.H.M., and Witholt, B., Diversity of Alkane Hydroxylase Systems in the Environment, Oil Gas Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 58, pp. 427–440.
Tourova, T.P., Nazina, T.N., Mikhailova, E.M., Rodionova, T.A., Ekimov, A.N., Mashukova, A.V., and Poltaraus, A.B., alkB Homologs in Thermophilic Bacteria of the Genus Geobacillus, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2008, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 247–257. [Mol. Biol. (Moscow) (Engl. Transl.), vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 217–226].
Orphan, V.J., Goffredi, S.K., Delong, E.F., and Boles, J.R., Geochemical Influence on Diversity and Microbial Processes in High-Temperature Oil Reservoirs, Geomicrobiol. J., 2003, vol. 20, pp. 295–311.
Nazina, T.N., Shestakova, N.M., Grigor’yan, A.A., Mikhailova, E.M., Tourova, T.P., Poltaraus, A.B., Cingxian Feng, Fangtian Ni, and Belyaev, S.S. Phylogenetic Diversity and Activity of Anaerobic Microorganisms of High-Temperature Horizons of the Dagang Oil Field (P. R. China), Mikrobiologiya, 2006, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 70–81 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 75 no. 1, pp. 55–65].
Li, H., Yang, S.Z., Mu, B.Z., Rong, Z.F., and Zhang, J., Molecular Phylogenetic Diversity of the Microbial Community Associated with a High-Temperature Petroleum Reservoir at an Offshore Oilfield, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2007, vol. 60, pp. 74–84.
Marchant, R., Sharkey, F.H., Banat, I.M., Rahman, T.J., and Perfumo, A., The Degradation of N-Hexadecane in Soil by Thermophilic Geobacilli, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2006, vol. 56, pp. 44–54.
Nogales, B., Moore, E.R., Llobet-Brossa, E., Rossello-Mora, R., Amann, R., and Timmis, K.N., Combined Use of 16S Ribosomal DNA and 16S rRNA To Study the Bacterial Community of Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Polluted Soil, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 67, pp. 1874–1884.
Mills, H.J., Martinez, R.J., Story, S., and Sobecky, P.A., Characterization of Microbial Community Structure in Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrates: Comparative Analysis of DNA- and RNA-Derived Clone Libraries, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 71, pp. 3235–3247.
Miskin, I.P., Farrimond, P., and Head, I.M., Identification of Novel Bacterial Lineages as Active Members of Microbial Populations in a Freshwater Sediment Using a Rapid RNA Extraction Procedure and RT-PCR, Microbiology (UK), 1999, vol. 145, pp. 1977–1987.
Borzenkov, I.A., Milekhina, E.I., Gotoeva, M.T., Rozanova, E.P., and Belyaev, S.S., The Properties of Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Bacteria Isolated from the Oilfields of Tatarstan, Western Siberia, and Vietnam, Mikrobiologiya, 2006, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 82–89 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 75 no. 1, pp. 66–72].
Yamamoto, S. and Harayama, S., PCR Amplification and Direct Sequencing of gyrB Genes with Universal Primers and Their Application to the Detection and Taxonomic Analysis of Pseudomonas putida Strains, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1995, vol. 61, pp. 1104–1109.
Tourova, T.P., Korshunova, A.V., Mikhailova, E.M., Sokolova, D.Sh., Poltaraus, A.B., and Nazina, T.N., Application of gyrB and pare Sequence Similarity Analyses for Differentiation of Species within the Genus Geobacillus, Mikrobiologiya, 2010, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 376–389 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 79 no. 3, pp. 356–369].
Brunk, C.F., Avaniss-Aghajani, E., and Brunk, C.A., A Computer Analysis of Primer and Probe Hybridization Potential with Bacterial Small-Subunit rRNA Sequences, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 61, pp. 872–879.
Weisburg, W.G., Barns, S.M., Pelletier, D.A., and Lane, D.J., 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplification for Phylogenetic Study, J. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 173, pp. 697–703.
Kolganova, T.V., Kuznetsov, B.B., and Tourova, T.P., Designing and Testing Oligonucleotide Primers for Amplification and Sequencing of Archaeal 16S rRNA Genes, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 283–285 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71 no. 2, pp. 243–246].
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G., and Gibson, T.J., CLUSTAL W: Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment Through Sequence Weighting, Positions-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice, Nucleic Acids Res., 1994, vol. 9, pp. 3251–3270.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M., The Neighbour-Joining Method: a New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1987, vol. 4, pp. 406–425.
Van de Peer, Y. and De Wachter, R., TREECON for Windows: a Software Package for the Construction and Drawing of Evolutionary Trees for the Microsoft Windows Environment, Comput. Appl. Biosci., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 569–570.
Kato, T., Haruki, M., Imanaka, T., Morikawa, M., and Kanaya, S., Isolation and Characterization of Psychotrophic Bacteria from Oil-Reservoir Water and Oil Sands, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2001, vol. 55, pp. 794–800.
Gerdes, B., Brinkmeyer, R., Dieckmann, G., and Helmke, E., Influence of Crude Oil on Changes of Bacterial Communities in Arctic Sea-Ice, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 129–139.
Manaia, C.M., Nogales, B., and Nunes, O.C., Tepidiphilus margaritifer gen. nov., sp. nov., Isolated from a Thermophilic Aerobic Digester, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 1405–1410.
Van Beilen, J.B., Panke, S., Lucchini, S., Franchini, A.G., Röthlisberger, M., and Witholt, B., Analysis of Pseudomonas putida Alkane Degradation Gene Clusters and Flanking Insertion Sequences: Evolution and Regulation of the alk-Genes, Microbiology (UK), 2001, vol. 147, pp. 1621–1630.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.M. Shestakova, A.V. Korshunova, E.M. Mikhailova, D.Sh. Sokolova, T. P. Tourova, S.S. Belyaev, A.B. Poltaraus, T.N. Nazina, 2011, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2011, Vol. 80, No. 1, pp. 63–73.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shestakova, N.M., Korshunova, A.V., Mikhailova, E.M. et al. Characterization of the aerobic hydrocarbon-oxidizing enrichments from a high-temperature petroleum reservoir by comparative analysis of DNA- and RNA-derived clone libraries. Microbiology 80, 60–69 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261711010140
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261711010140