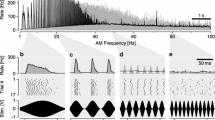
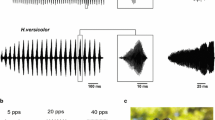
Abstract
Neurophysiological data on the evaluation of neural correlates of the involvement of auditory critical bands in sound localization and recognition are presented. Single unit activity was recorded extracellularly in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus in house mouse females. In the first part, the neuronal sensitivity to acoustic signals simulating spectral localization cues (notch noise with different bandwidths) was studied. Evaluation of neuronal response variability depending on notch bandwidths revealed that the 1/3 octave notch bandwidth was optimal for the analysis of the localization-significant spectral information. This notch bandwidth corresponded to the average critical bandwidth of the auditory midbrain neurons determined previously by the narrow-band masking method. In the second part, the selectivity of neuronal responses to a discomfort-signaling mouse pup wriggling call, its models and frequency components, was evaluated. The data obtained demonstrated that the wriggling call models with frequency components located, like in a natural call, in three non-overlapping critical bands evoked stronger neuronal responses than the other models. These findings support the suggestion of the universal role the critical-band mechanism plays in processing different parameters of acoustic stimuli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fletcher, H., Auditory patterns, Rev. Modern Phys., 1940, vol. 12, pp. 47–65.
Zwicker, E. and Feldtkeller, R., Das Ohr als Nachrichtenempf nger, Stuttgart, 1967.
Greenwood, D.D., Critical bandwidth and the frequency coordinates of the basilar membrane, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1961, vol. 33, pp. 1344–1356.
Vartanian, I., Egorova, M., and Ehret, G., Expression of the main properties of critical bands in the neuronal activity of posterior quadrigemini in mice, Dokl.Biol Sci., 1999, vol. 368, pp. 437–439.
Egorova, M., Vartanian, I., and Ehret, G., Neurophysiological correlates of critical bands in the auditory midbrain, Sens. Systems., 2002, vol. 16, pp. 3–12.
Egorova, M. and Ehret, G., Tonotopy and inhibition in the midbrain inferior colliculus shape spectral resolution of sounds in critical bands, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 28, pp. 675–692.
Egorova, M.A. and Akimov, A.G., Spectral coding in auditory midbrain neurons, J. Integr. Neurosci., 2013, vol. 12, pp. 1–15.
Batteau, D.W., The role of pinna in human localization, Proc. Roy. Soc., 1967, vol. 168, pp. 158–180.
Gardner, M.B. and Gardner, R.S., Problem of localization in the median plan: effect of pinna cavity occlusion, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1973, vol. 53, pp. 400–408.
Shaw, E.A.G., External ear response and sound localization, Localization of Sound: Theory and Applications, Groton, CT: Amphora, 1982. pp. 30–41.
Middlebrooks, J.C. and Green, D.M., Sound localization by human listeners, Ann. Rev. Psychol., 1991, vol. 42, pp. 135–159.
Musicant, A.D., Chan, J.C.K., and Hild, J.E., Direction-dependent spectral properties of cat external ear: New data and cross-species comparisons, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1990, vol. 87, pp. 757–781.
Rice, J.J., May, B.J., Spirou, G.A., and Young, E.D., Pinna-based spectral cues for sound localization in cat, Hear. Res., 1992, vol. 58, pp. 132–152.
Rogers, M.E. and Butler, A., The linkage between stimulus frequency and covert peak areas as it relates to monaural localization, Percept. Psychophys., 1992, vol. 52, pp. 536–546.
Middlebrooks, J.C., Narrow-band sound localization related to external ear acoustics, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1992, vol. 92, pp. 2607–2624.
Neti, C., Young, E.D., and Schneider, M.N., Neural network models of sound localization based on directional filtering by the pinna, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1992, vol. 93, pp. 3140–3156.
Wightman, F. and Kistler, D., Of vulcan ears, human ears and ‘earprints’, Nat. Neurosci., 1998, vol. 1, pp. 337–339.
Zakarouskas, P. and Cynader, M.S., A computational theory of spectral cue localization, J. Acoust. Soc. Amer., 1993, vol. 94, pp. 1323–1331.
Al’tman, Ya.A., Lokalizatsia zvuka. Neirofiziologicheskie mekhanizmy (Sound Localization. Neurophysiological Mechanisms), Leningrad, 1972.
Ehret, G., Frequency resolution, spectral filtering, and integration on the neuronal level, Auditory Function. Neurobiological Bases of Hearing, New York, Wiley, 1988. pp. 363–384.
Ehret, G., Preadaptations in the auditory system of mammals for phoneme perception, The Auditory Processing of Speech. From Sounds to Words, Berlin, de Gruyter, 1992. pp. 99–112.
Ehret, G. and Haak, B., Ultrasound recognition in house mice: key-stimulus configuration and recognition mechanism, J. jomp. Physiol., 1982, vol. 148, pp. 245–251.
Ehret, G. and Riecke, S., Mice and human perceive multiharmonic communication sounds in the same way, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, vol. 99, pp. 479–482.
Egorova, M.A. and Akimov, A.G., Acoustic characteristics of the low-frequency nest call of discomfort of the house mouse (Mus musculus) early ontogenesis, Acoustical Physics, 2010, vol. 56, pp. 364–369.
Malinina, E.S., Auditory neurons receptive fields and spectral notches processing in the mouse middle brain, Sensornye Systemy, 2002, vol. 16, pp. 13–22.
Holmstrom, L.A., Eeuwes, L.B.M., Roberts, P.D., and Portfors, C.V., Efficient encoding of vocalizations in the auditory midbrain, J. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 30, pp. 802–819.
Imig, T.J., Poirier, P., Irons, W.A., and Samson, F.K., Monaural spectral contrast mechanism for neural sensitivity to sound direction in medial geniculate body of the cat, J. Neurophysiol., 1997, vol. 78, pp. 2754–2771.
Malinina, E.S. and Vartanyan, I.A., Activity of neurons in the mouse Inferior Colliculus in relation to the position and direction of displacement of spectral contrast, Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 2004, vol. 34, pp. 961–974.
Imig, T.J., Bibikov, N.G., Poirier, P., and Samson, F.K., Directionality derived from pinna-cue spectral notches in cat dorsal cochlear nucleus, J. Neurophysiol., 2000, vol. 83, pp. 907–995.
Poirier, P., Samson, F.K., and Imig, T.J., Spectral shape sensitivity contributes to the azimuth tuning of neurons in the cat’s inferior colliculus, J. Neurophysiol., 2003, vol. 89, pp. 2760–2777.
Barone, P., Clarey, J.C., Irons, W.A., and Imig, T.J., Single unit responses in the primary auditory cortex and medial geniculate body of the cat: evidence for cortical synthesis of azimuth receptive fields with nonmonotonic level tuning, J. Neurophysiol., 1996, vol. 75, pp. 1206–1220.
Samson, F.K., Barone, W.P., Irons, W.A., Clarey, J.C., Poirier, P., and Imig, T.J., Directionality derived from differential sensitivity to monaural and binaural cues in cat’s medial geniculate body, J. Neurophysiol., 2000, vol. 84, pp. 1330–1345.
Malmierca, M.S., The inferior colliculus: a center for convergence of ascending and descending auditory information, Neuroembryol. Aging, 2004, vol. 3, pp. 215–229.
Fuzessery, Z.M. and Hall, J.C., Role of GABA in shaping frequency tuning and creating FM sweep selectivity in the inferior colliculus, J. Neurophysiol., 1996, vol. 76, pp. 1059–1073.
Le Beau, F.F.N., Malmierca, M.S., and Rees, A., The role of inhibition in determining neuronal response properties in the inferior colliculus, Advances in Hearing Research, Singapore, Words Scientific Publ., 1995. pp. 300–311.
Palombi, P.S. and Caspary, D.M., GABA inputs control discharge rate primarily within frequency receptive fields of inferior colliculus neurons, J. Neurophysiol., 1996, vol. 75, pp. 2211–2219.
Le Beau, F.F.N., Malmierca, M.S., and Rees, A., Contribution of GABA-and glicin-mediated inhibition to monaural temporal response properties of neurons in inferior colliculus, J. Neurophysiol., 1996, vol. 75, pp. 902–919.
Kulkarni, A. and Colburn, H.S., Role of spectral detail in sound-source localization, Nature, 1998, vol. 396, pp. 747–749.
Rauschecker, J.P., Parallel processing in the auditory cortex of primates, Audiol. Neurootol., 1998, vol. 3, pp. 86–103.
Kaas, J.H. and Hackett, T.A., Subdivisions of auditory cortex and processing streams in primates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, vol. 97, pp. 11793–11799.
Rauschecker, J.P. and Tian, B., Mechanisms and streams for processing of “what” and “where” in auditory cortex, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, vol. 97, pp. 11800–11806.
Ungerlieder, L.G. and Mishkin, M., Two cortical visual systems, Analysis of Visual Behavior, Boston, MIT Press, 1982. pp. 549–586.
Recanzone, G.H. and Cohen, Y.E., Serial and parallel processing in the primate auditory cortex revisited, Behav. Brain. Res., 2010, vol. 206, pp. 1–7.
Kuwada, S., Bishop, B., and Kim, D.O., Approaches to the study of neural coding of sound source location and sound envelope in real environments, Front. Neural Circuits., 2012, vol. 6, pp. 1–12.
Kuwada, S., Bishop, B., and Kim, D.O., Azimuth and envelope coding in the inferior colliculus of the unanesthetized rabbit: effect of reverberation and distance, J. Neurophysiol., 2014, vol. 112, pp. 1340–1355.
Lewald, J. and Getzmann, S., When and where of auditory spatial processing in cortex: a novel approach using electrotomography, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, pp. 1–17.
Tian, B., Reser, D., Durham, A., Kustov, A., and Rauschecker, J.P., Functional specialization in rhesus monkey auditory cortex, Science, 2001, vol. 292, pp. 290–293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.S. Malinina, M.A. Egorova, A.G. Akimov, 2015, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2015, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 352—361.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malinina, E.S., Egorova, M.A. & Akimov, A.G. Neurophysiological approaches to studying the functional role of auditory critical bands. J Evol Biochem Phys 51, 401–411 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093015050063
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093015050063