Abstract
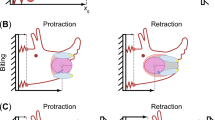
Effect of static load on activity of motor centers controlling motor activity (walking, flight) was studied in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana L. It has been established that under effect of load on the animal body the relative excitability of these centers increases. A suggestion is put forward about the presence of common neuronal elements in the generator networks providing motor acts in the American cockroach; a role of afferent systems in control of excitability of loco-motor centers functioning in the regime of static load is shown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beer, R.D., Chiel, H.J., Quinn, R.D., and Ritzmann, R.E., Biorobotic Approaches to the Study of Motor System, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 1988, vol. 8, pp. 777–782.
Gorelkin, V.S., Kuznetsova, T.V., and Severina, I.Yu., Change of Activity of Locust Locomotor Centers under Effect of Increased Gravitation, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2001, vol. 37, pp. 286–289.
Hooper, S.L. and Dicaprio, R.A., Crustacean Motor Pattern of Generator Networks, Neurosignals, 2004, vol. 13, pp. 50–69.
Delcomyn, F., Insect Walking and Robotics, Ann. Rev. Entomol., 2004, vol. 49, pp. 51–70.
Camhi, J.M. and Tom, W., The Escape Behavior of Cockroach Perplaneta americana, I. Turning Response to Wind Puffs, J. Comp. Physiol., 1978, vol. 128, pp. 193–201.
Zill, S.N., Selective Mechanical Stimulation of an Identified Proprioceptor in Freely Moving Locusts: Role of Resistance reflex in Active Posture, Brain Res., 1987, vol. 417, pp. 195–198.
Laurent, G., Sensory Control in Locomotion of Insect, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 1991, vol. 1, pp. 601–604.
Matsuura, T., Kanou, M., and Yamaguchi, T., Motor Program Initiation and Selection in Crickets with Special Reference to Swimming and Flying Behavior, J. Comp. Physiol., 2002, vol. 187, pp. 987–995.
Ye, S., Leung, V., Khan, A., Baba, Y., and Comer, C.M., The Antennal System and Cockroach Evasive Behavior. I. Roles for Visual and Mechanosnsory Cues in the Response, J. Comp. Physiol., 2003, vol. 189, pp. 89–96.
Svidersky, V.L., Nervous Control of Fast Rhythmical Movements of Insect Muscles, Tr. Vsesoyuzn. entomol. ob-va (Proceed. All-USSR Entomol. Soc.), 1969, vol. 53, pp. 91–131.
Svidersky, V.L., Neirofiziologiya poleta nasekomykh (Neurophysiology of the Insect Flight), Leningrad, 1973.
Svidersky, V.L., Osnovy neirofiziologii nasekomykh (Grounds of Insect neurophysiology), Leningrad, 1980.
Svidersky, V.L., Lokomotsiya nasekomykh. Neirofiziologicheskie aspekty (Insect Locomotion. Neurophysiological aspects), Leningrad, 1988.
Peason, K.G., Common Principles of Motor Control in Vertebrates and Invertebrates, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 1993, vo. 16, pp. 265–297.
Svidersky, V.L., Generation of Motor Rhythms, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1999, vol. 35, pp. 358–367.
Duysens, J., Clarac, F., and Cruse, H., Load-Regulating Mechanisms in Giant and Posture, Comparative Aspects, Physiol. Rev., 2000, vol. 80, pp. 83–133.
Svidersky, V.L. and Plotnikova, S.I., Insects and Vertebrates: Similar Structures in the Higher Integrative Brain Centers, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Physiol., 2002, vol. 38, pp. 492–501.
Fraenkel, G., Untersuchungen über die Koordination von Reflexen und Automatischenervosen bei Insekten, Ztschr. Vergl. Physiol., 1932, vol. 16, pp. 371–392.
Gorelkin, V.L. and Severina, I.Yu., Role of Central and Peripheral Mechanisms in Control of Excitability of Segmental Motor centers in Insects, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2004, vol. 40, pp. 508–513.
Camhi, J.M. and Levy, A., Organization of Complex Movement: Fixed and variable Components of Cockroach Escape Behavior, J. Comp. Phusiol., 1988, vol. 163, pp. 317–328.
Schaeffer, P.L., Kondagunta, V., and Ritzmann, R.E., Motion Analysis of Escape Movements Evoked by Tactile Stimulation on Cockroach Periplaneta americana, J. Exp. Biol., 1994, vol. 190, pp. 287–297.
Levi, R. and Camhi, J.M., Wind Direction Coding in the Cockroach Escape Response: Winner Does not Take All, J. Neurosci., 2000, vol. 20, pp. 3814–3821.
Mc Connel, E. and Richards, A.G., How Fast Can a Cockroach Run? Bull. Brooklyn Entomol. Soc., 1955, vol. 50, pp. 36–43.
Pearson, K.G., Central Programming and Reflex Control of Walking in Cockroach, J. Exp. Biol., 1972, vol. 56, pp. 173–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V. S. Gorelkin, I. Yu. Severina, I. L. Isavnina, V. L. Svidersky, 2008, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2008, Vol. 44, No. 3, pp. 245–249.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorelkin, V.S., Severina, I.Y., Isavnina, I.L. et al. Effect of static load on motor behavior of the cockroach Periplaneta americana . J Evol Biochem Phys 44, 288–293 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093008030046
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093008030046