Abstract
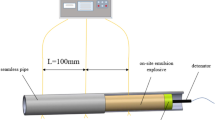
Electrical conductivity of explosion products behind the detonation front of emulsion explosives is measured. The composition of the emulsion matrix and the amount of the additive consisting of sensitizing glass microspheres are varied. The peak value of electrical conductivity for the examined compositions is 0.5–0.05 Ω-1 · cm-1.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
S. A. Bordzilovskii, S. M. Karakhanov, and V. V. Sil’vestrov, “Optical Radiation from Shock-Compressed Epoxy with Glass Microspheres,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 50 (3), 105–112 (2014) [Comb., Expl., Shock Waves 50 (3), 339–345 (2014)].
V. V. Sil’vestrov, S. A. Bordzilovskii, and S. M. Karakhanov, “Temperature of the Detonation Front of an Emulsion Explosive,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 51 (1), 135–142 (2015) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 51 (1), 116–123 (2015)].
L. V. Dubnov N. S. Bakharevich, and A. I. Romanov, Industrial High Explosives (Nedra, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
V. A. Sosnin and E. V. Kolganov, Industrial Emulsion Explosives (GosNII Kristal, Dzerzhinks, 2009, Vol. 1) [in Russian].
J. Lee and P. A. Persson, “Detonation Behavior of Emulsion Explosives,” Propel., Explos., Pyrotech., No. 15, 208–216 (1990).
V. V. Sil’vestrov and A. V. Plastinin, “Investigation of Low Detonation Velocity Emulsion Explosives,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 45 (5), 124–133 (2009) [Comb., Expl., Shock Waves 45 (5), 618–626 (2009)].
V. A. Sosnin and E. V. Kolganov, “Study of the Detonation Process in Industrial Emulsion Explosives,” Khim. Fiz. 22 (8), 100–107 (2003).
G. A. Leiper, I. J. Kirby, and A. Hackett, “Determination of Reaction Rates in Intermolecular Explosives Using the Electromagnetic Particle Velocity Gauge,” in Proc. Eight Symp. on Detonation (1985), pp. 187–195.
A. S. Yunoshev, A. V. Plastinin, and V. V. Sil’vestrov, “Effect of the Density of an Emulsion Explosive on the Reaction Zone Width,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 48 (3), 79–88 (2012) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 48 (3), 319–327 (2012)].
V. V. Sil’vestrov, S. M. Karakhanov, A. V. Plastinin, and A. A. Deribas, “Effect of the Emulsion Explosive Density on the Reaction Zone Width,” in Proc. VII Khariton’s Topical Sci. Readings (Inst. Exp. Phys., Russian Federal Nuclear Center, Sarov, 2005), pp. 132–137.
S. A. Kolesnikov, V. V. Lavrov, V. M. Molchanova, et al., “Experimental Study of the Structure of Detonation Waves in Emulsion Explosives,” in Lavrent’ev’s Readings on Mathematics, Mechanics, and Physics, Proc. Int. Conf. (Lavrent’ev Inst. Hydrodynamics, Novosibirsk, 2010), pp. 216–217.
A. P. Ershov, N. P. Satonkina, and G. M. Ivanov, “Reaction Zones and Conductive Zones in Dense Explosives,” in Proc. of 13th Int. Detonation Symp., Norfolk, VA, 2006, ONR 351-07-01, pp. 79–88.
A. P. Ershov, N. P. Satonkina, and G. M. Ivanov, “Profiles of Electrical Conductivity in Dense Explosives,” Khim. Fiz. 26 (12), 21–33 (2007).
V. M. Titov, E. R. Pruuel, K. A. Ten, et al., “Experience of Using Synchrotron Radiation for Studying Detonation Processes,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 47 (6), 3–15 (2011) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 47 (6), 615–626 (2011)].
S. I. Rafeichik, “Investigation of the Critical Diameter of Emulsion Explosives as a Function of Density in a Steel Shell,” Vest. NGU, Ser. Fiz. 8 (6), 107–110 (2013).
A. C. Mitchell and W. J. Nellis, “Equation of State and Electrical Conductivity ofWater and Ammonia Shocked to the 100 GPa (1 Mbar) Pressure Range,” J. Chem. Phys. 76 (12), 6273–6281 (1982).
A. V. Orlov, “Effect of Temperature on Inelastic Deformation of LK-105 Glass in Shock Waves,” Candidate’s Dissertation in Physics and Mathematics (Moscow Inst. of Physics and Technology, Moscow, 1992).
N. P. Satonkina, E. R. Pruuel, A. P. Ershov, et al., “Electrical Conduction of Emulsion Explosives,” J. Eng. Thermophys. 20 (3), 315–319 (2011).
M. Yoshida, M. Iida, K. Tanaka, and S. Fudjiwara, “Detonation Behavior of Emulsion Explosives Containing Glass Microballoons,” in Proc. 8th Symp. (Int.) on Detonation (1985), pp. 993–1000.
V. V. Yakushev and A. N. Dremin, “Nature of Electrical Conductivity of Detonation Products of Condensed Explosives,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 221 (5), 1143–1144 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text ©N.P. Satonkina, E.R. Pruuel, A.P. Ershov, V.V. Sil’vestrov, D.I. Karpov, A.V. Plastinin.
Published in Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 51, No. 3, pp. 91–97, May–June, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satonkina, N.P., Pruuel, E.R., Ershov, A.P. et al. Evolution of electrical conductivity of emulsion explosives during their detonation conversion. Combust Explos Shock Waves 51, 366–372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508215030132
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508215030132