Abstract
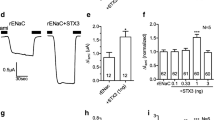
We have recently shown that epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) are regulated by the actin-binding protein cortactin via the Arp2/3 protein complex. It has been also demonstrated that a GTPase dynamin, which is known to regulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis, can as well initiate signaling cascades regulated by cortactin. This study was designed to investigate the involvement of dynamin into cortactin-mediated regulation of ENaC. Initially, a recently described inhibitor of dynamin, dynasore, was used. However, use of this inhibitor seemed to be inappropriate due to discovered side effects. Thus, treatment of mpkCCDc14 cells monolayers with dynasore (in concentrations of 10 and 100 μM) resulted in a decrease in ENaC-mediated transepithelial currents. Besides, dynasore caused reduced amiloride-sensitive currents in CHO cells transfected with ENaC subunits. Therefore, the data demonstrated that dynasore down regulates both native and overexpressed channel’s activity and use of this drug is not appropriate for studies of ENaC endocytosis. We hypothesize that this effect is most likely caused either by dynasore’s toxic actions upon the cells or by enhanced endocytosis of ENaC-activating proteins. In the following experiments plasmids encoding mutant forms of dynamin and cortactin were used. Dominant negative dynamin (K44A) transfected into CHO cells together with ENaC subunits significantly increased amiloride-sensitive current density compared to cells transfected with ENaC only (control); additional transfection of cortactin together with the K44A dynamin resulted in current density restitution back to the control level. Moreover, ENaC overexpression with the SH3 domain of cortactin, which is responsible for dynamin binding, caused a decrease of ENaC current. Thus, we have shown in this study that cortactin can mediate ENaC activity not only via the Arp2/3 complex, but also through the dynamin-mediated processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez de la Rosa, D., Canessa, C.M., Fyfe, G.K., and Zhang, P., Structure and Regulation of Amiloride-sensitive Sodium Channels, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 2000, vol. 62, pp. 573–594.
Bens, M., Vallet, V., Cluzeaud, F., Pascual-Letallec, L., Kahn, A., Rafestin-Oblin, M.E., Rossier, B.C., and Vandewalle, A., Corticosteroid-Dependent Sodium Transport in a Novel Immortalized Mouse Collecting duct Principal Cell Line, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 1999, vol. 10, pp. 923–934.
Blazer-Yost, B.L., Esterman, M.A., and Vlahos, C.J., Insulin-Stimulated Trafficking of ENaC in Renal Cells Requires PI 3-Kinase Activity, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 2003, vol. 284, pp. C1645–C1653.
Campbell, D.H., Sutherland, R.L., and Daly, R.J., Signaling Pathways and Structural Domains Required for Phosphorylation of EMS1/Cortactin, Cancer Res., 1999, vol. 59, pp. 5376–5385.
Cantiello, H.F., Stow, J.L., Prat, A.G., and Ausiello, D.A., Actin Filaments Regulate Epithelial Na+ Channel Activity, Am. J. Physiol., 1991, vol. 261, pp. C882–C888.
Cao, H., Thompson, H.M., Krueger, E.W., and McNiven, M.A., Disruption of Golgi Structure and Function in Mammalian Cells Expressing a Mutant Dynamin, J. Cell Sci., 2000, vol. 113, pp. 1993–2002.
Chang, S.S., Grunder, S., Hanukoglu, A., Rosler, A., Mathew, P.M., Hanukoglu, I., Schild, L., Lu, Y., Shimkets, R.A., Nelson-Williams, C., Rossier, B.C., and Lifton, R.P., Mutations in Subunits of the Epithelial Sodium Channel Cause Salt Wasting with Hyperkalaemic Acidosis, Pseudohypoaldosteronism Type 1, Nat. Genet., 1996, vol. 12, pp. 248–253.
Cosen-Binker, L.I. and Kapus, A., Cortactin: The Gray Eminence of the Cytoskeleton, Physiology (Bethesda), 2006, vol. 21, pp. 352–361.
Gallet, C., Rosa, J.P., Habib, A., Lebret, M., Levy-Toledano, S., and Maclouf, J., Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cortactin Associated with Syk Accompanies Thromboxane Analogue-Induced Platelet Shape Change, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, vol. 274, pp. 23610–23616.
Garty, H. and Palmer, L.G., Epithelial Sodium Channels: Function, Structure, and Regulation, Physiol. Rev., 1997, vol. 77, pp. 359–396.
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., and Sigworth, F.J., Improved Patch-Clamp Techniques for High-Resolution Current Recording from Cells and Cell-Free Membrane Patches, Pflügers Archiv, 1981, vol. 391, pp. 85–100.
Hansson, J.H., Nelson-Williams, C., Suzuki, H., Schild, L., Shimkets, R., Lu, Y., Canessa, C., Iwasaki, T., Rossier, B, and Lifton, R.P., Hypertension Caused by a Truncated Epithelial Sodium Channel Gamma Subunit: Genetic Heterogeneity of Liddle Syndrome, Nat. Genet., 1995, vol. 11, pp. 76–82.
Huang, C., Ni, Y., Wang, T., Gao, Y., Haudenschild, C.C., and Zhan, X., Down-Regulation of the Filamentous Actin Cross-Linking Activity of Cortactin by Src-Mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 1997, vol. 272, pp. 13911–13915.
Ilatovskaya, D.V., Levchenko, V., Ryan, R.P., Cowley, A.W., Jr., and Staruschenko, A.A., NSAIDs Acutely Inhibit TRPC Channels in Freshly Isolated Rat Glomeruli, Bichem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2011a, vol. 408, pp. 242–247.
Ilatovskaya, D.V., Pavlov, T.S., Levchenko, V., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Staruschenko, A.A., Cortical Actin Binding Protein Cortactin Mediates ENaC Activity via Arp2/3 Complex, FASEB J., 2011b, vol. 25, pp. 2688–2699.
Kanner, S.B., Reynolds, A.B., Vines, R.R., and Parsons, J.T., Monoclonal Antibodies to Individual Tyrosine-Phosphorylated Protein Substrates of Oncogene-Encoded Tyrosine Kinases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1990, vol. 87, pp. 3328–3332.
Kapus, A., Szaszi, K., Sun, J., Rizoli, S., and Rotstein, O.D., Cell Shrinkage Regulates Src Kinases and Induces Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cortactin, Independent of the Osmotic Regulation of Na+/H+ Exchangers, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, vol. 274, pp. 8093–8102.
Kapus, A., Di, Ciano, C., Sun, J., Zhan, X., Kim, L., Wong, T.W., and Rotstein, O.D., Cell Volume-Dependent Phosphorylation of Proteins of the Cortical Cytoskeleton and Cell-Cell Contact Sites. The Role of Fyn and FER Kinases, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 32289–32298.
Karpushev, A.V., Levchenko, V., Pavlov, T.S., Lam, V.Y., Vinnakota, K.C., Vandewalle, A., Wakatsuki, T., and Staruschenko, A., Regulation of ENaC Expression at the Cell Surface by Rab11, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2008, vol. 377, pp. 521–525.
Karpushev, A.V., Ilatovskaya, D.V., Pavlov, T.S., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Staruschenko, A.A., Intact Cytoskeleton Is Required for Small G Protein Dependent Activation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel, PLoS One, 2010a, vol. 5, p. e8827.
Karpushev, A.V., Ilatovskaya, D.V., and Staruschenko, A.B., The Actin Cytoskeleton and Small G Protein RhoA Are not Involved in Flow-Dependent Activation of ENaC, BMC Res. Notes, 2010b, vol. 3, p. 210.
Karpushev, A.V., Levchenko, V., Ilatovskaya, D.V., Pavlov, T.S., and Staruschenko, A., Novel Role of Rac1/WAVE Signaling Mechanism in Regulation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel, Hypertension, 2011, vol. 57, pp. 996–1002.
Kellenberger, S. and Schild, L., Epithelial Sodium Channel/Degenerin Family of Ion Channels: A Variety of Functions for a Shared Structure, Physiol. Rev., 2002, vol. 82, pp. 735–767.
Kirchhausen, T., Macia, E., and Pelish, H.E., Use of Dynasore, the Small Molecule Inhibitor of Dynamin, in the Regulation of Endocytosis, Methods Enzymol., 2008, vol. 438, pp. 77–93.
Levchenko, V., Zheleznova, N.N., Pavlov, T.S., Vandewalle, A., Wilson, P.D., and Staruschenko, A., EGF and Its Related Growth Factors Mediate Sodium Transport in MpkCCD(c14) Cells via ErbB2 (neu/HER-2) Receptor, J. Cell. Physiol., 2010, vol. 223, pp. 252–259.
Lifton, R.P., Genetic Determinants of Human Hypertension, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1995, vol. 92, pp. 8545–8551.
Martinez-Quiles, N., Ho, H.Y., Kirschner, M.W., Ramesh, N., and Geha, R.S., Erk/Src Phosphorylation of Cortactin Acts as a Switch On/Switch Off Mechanism That Controls Its Ability to Activate N-WASP, Mol. Cell Biol., 2004, vol. 24, pp. 5269–5280.
Mazzochi, C., Benos, D.J., and Smith, P.R., Interaction of Epithelial Ion Channels with the Actin-Based Cytoskeleton, Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol., 2006a, vol. 291, pp. F1113–F1122.
Mazzochi, C., Bubien, J.K., Smith, P.R., and Benos, D.J., The Carboxyl Terminus of the Alpha-Subunit of the Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Sodium Channel Binds to F-Actin, J. Biol. Chem., 2006b, vol. 281, pp. 6528–6538.
Meighan, S.E., Meighan, P.C., Choudhury, P., Davis, C.J., Olson, M.L., Zornes, P.A., Wright, J.W., and Harding, J.W., Effects of Extracellular Matrix-Degrading Proteases Matrix Metalloproteinases 3 and 9 on Spatial Learning and Synaptic Plasticity, J. Neurochem., 2006, vol. 96, pp. 1227–1241.
Mettlen, M., Pucaduil, T., Ramachandran, R., and Schmid, S.L., Dissecting Dynamin’s Role in Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2009, vol. 37, pp. 1022–1026.
Mizutani, K., Miki, H., He, H., Maruta, H., and Takenawa, T., Essential Role of Neural Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein in Podosome Formation and Degradation of Extracellular Matrix in Src-Transformed Fibroblasts, Cancer Res., 2002, vol. 62, pp. 669–674.
Mooren, O.L., Kotova, T.I., Moore, A.J., and Schafer, D.A., Dynamin2 GTPase and Cortactin Remodel Actin Filaments, J. Biol. Chem., 2009, vol. 284, pp. 23995–24005.
Rossier, B.C. and Shield, R., Epithelial Sodium Channel: Mendelian versus Essential Hypertension, Hypertension, 2008, vol. 52, pp. 595–600.
Schafer, D.A., Weed, S.A., Binns, D., Karginov, A.V., Parsons, J.T., and Cooper, J.A., Dynamin2 and Cortactin Regulate Actin Assembly and Filament Organization, Curr. Biol., 2002, vol. 12, pp. 1852–1857.
Schild, L., The Epithelial Sodium Channel: From Molecule to Disease, Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 2004, vol. 151, pp. 93–107.
Shimkets, R.A., Lifton, R.P., and Canessa, C.M., The Activity of the Epithelial Sodium Channel Is Regulated by Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis, J. Biol. Chem., 1997, vol. 272, pp. 25537–25541.
Staruschenko, A., Medina, J.L., Patel, P., Shapiro, M.S., Booth, R.E., and Stockand, J.D., Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Analysis of Subunit Stoichiometry of the Epithelial Na+ Channel, J. Biol. Chem., 2004a, vol. 279, pp. 27729–27734.
Staruschenko, A., Patel, P., Tong, Q., Medina, J.L., and Stockand, J.D., Ras Activates the Epithelial Na(+) Channel through Phosphoinositide 3-OH Kinase Signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 2004b, vol. 279, pp. 37771–37778.
Staruschenko, A., Pochynyuk, O.M., and Stockand, J.D., Regulation of Epithelial Na+ Channel Activity by Conserved Serine/Threonine Switches within Sorting Signals, J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, pp. 39161–39167.
Takai, Y., Sasaki, T., and Maozaki, T., Small GTP-Binding Proteins, Physiol. Rev., 2001, vol. 81, pp. 153–208.
Tian, L., Chen, L., McClafferty, H., Sailer, C.A., Ruth, P., Knaus, H.G., and Shipston, M.J., A Noncanonical SH3 Domain Binding Motif Links BK Channels to the Actin Cytoskeleton via the SH3 Adapter Cortactin, FASEB J., 2006, vol. 20, pp. 2588–2590.
Tian, L., McClafferty, H., Chen, L., and Shipston, M.J., Reversible Tyrosine Protein Phosphorylation Regulates Large Conductance Voltage- and Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels via Cortactin, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, pp. 3067–3076.
Uruno, T., Liu, J., Zhang, P., Fan, Y., Egile, C., Li, R., Mueller, S.C., and Zhan, X., Activation of Arp2/3 Complex-Mediated Actin Polymerization by Cortactin, Nat. Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 3, pp. 259–266.
Vachugova, D.V. and Morachevskaya, E.A., Mechanosensitivity of Cationic Channels of DEG/ENaC Family, Tsitologiia, 2009, vol. 51, no. 10, pp. 806–814.
Vidal, C., Geny, B., Melle, J., Jandrot-Perrus, M., and Fontenay-Roupie, M., Cdc42/Rac1-Dependent Activation of the P21-Activated Kinase (PAK) Regulates Human Platelet Lamellipodia Spreading: Implication of the Cortical-Actin Binding Protein Cortactin, Blood, 2002, vol. 100, pp. 4462–4469.
Wang, H., Traub, L.M., Weixel, K.M., Hawryluk, M.J., Shah, N., Edinger, R.S., Perry, C.J., Kester, L., Butterworth, M.B., Peters, K.W., Kleyman, T.R., Frizzell, R.A., and Johnson, J.P., Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis of the Epithelial Sodium Channel. Role of Epsin, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, vol. 281, pp. 14129–14135.
Weed, S.A. and Parsons, J.T., Cortactin: Coupling Membrane Dynamics to Cortical Actin Assembly, Oncogene, 2001, vol. 20, pp. 6418–6434.
Williams, M.R., Markey, J.C., Doczi, M.A., and Morielli, A.D., An Essential Role for Cortactin in the Modulation of the Potassium Channel Kv1–2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, vol. 104, pp. 17412–17417.
Wu, H. and Parsons, J.T., Cortactin, an 80/85-Kilodalton Pp60src Substrate, Is a Filamentous Actin-Binding Protein Enriched in the Cell Cortex, J. Cell Biol., 1993, vol. 120, pp. 1417–1426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.V. Ilatovskaya, T.S. Pavlov, Y.A. Negulyaev, A. Staruschenko, 2011, published in Tsitologiya, 2011, Vol. 53, No. 11, pp. 903–910.
The article was translated by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilatovskaya, D.V., Pavlov, T.S., Negulyaev, Y.A. et al. Mechanisms of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) regulation by cortactin: Involvement of dynamin. Cell Tiss. Biol. 6, 52–59 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X1201004X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X1201004X