Abstract
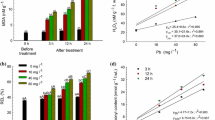
Chemical speciation of metals in soil/solution plays an important role in determining their biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system. The current study evaluated the influence of applied form of Pb (metal speciation) on its toxicity to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. roots. Lead was applied to young V. faba seedlings alone or chelated by organic ligands (citric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). Plants were exposed to all treatments for 1, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h in nutrient solution, and contents of H2O2 and thiobarbituric-acid-reactive substances (TBARS) production were analyzed in V. faba roots. The results showed that Pb toxicity to V. faba roots depended on its applied chemical form and duration of exposure. Lead alone caused two burst of lipid peroxidation and H2O2 induction at 1 h and 12 h. Addition of EDTA dose-dependently inhibited Pb-induced H2O2 and TBARS production, indicating a protective role of this chelator against Pb toxicity during the first 24 h. In contrast, citric acid did not show significant effects on Pb-induced H2O2 and TBARS production, but delayed the induction of these effects. This study suggested that Pb toxicity to V. faba roots varies with Pb speciation in growth medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
citric acid
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric-acidreactive substances
References
Xu, Y., Shi, G.X., Ding, C.X., and Xu, X.Y., Polyamine metabolism and physiological responses of Potamogeton crispus leaves under lead stress, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2011, vol. 58, pp. 460–466.
Shahid, M., Pourrut, B., Dumat, C., Nadeem, M., Aslam, M., and Pinelli, E., Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2014, vol. 232, pp. 1–44.
Shahid, M., Xiong, T., Castrec-Rouelle, M., Leveque, T., and Dumat, C., Water extraction kinetics of metals, arsenic and dissolved organic carbon from industrial contaminated poplar leaves, J. Environ. Sci., 2013, vol. 25, pp. 2451–2459.
Zia, M.H., Codling, E.E., Scheckel, K.G., and Chaney, R.L., In vitro and in vivo approaches for the measurement of oral bioavailability of lead (Pb) in contaminated soils: a review, Environ. Pollut., 2011, vol. 159, pp. 2320–2327.
Foucault, Y., Lévêque, T., Xiong, T., Schreck, E., Austruy, A., Shahid, M., and Dumat, C., Green manure plants for remediation of soils polluted by metals and metalloids: ecotoxicity and human bioavailability assessment, Chemosphere, 2013, vol. 93, pp. 1430–1435.
Austruy, A., Shahid, M., Xiong, T., Castrec, M., Payre, V., Niazi, N.K., Sabir, M., and Dumat, C., Mechanisms of metal-phosphates formation in the rhizosphere soils of pea and tomato: environmental and sanitary consequences, J. Soils Sediments, 2014, vol. 14, pp. 666–678.
Pourrut, B., Jean, S., Silvestre, J., and Pinelli, E., Lead-induced DNA damage in Vicia faba root cells: potential involvement of oxidative stress, Mutat. Res., 2011, vol. 726, pp. 123–128.
Xiong, T., Leveque, T., Shahid, M., Foucault, Y., Mombo, S., and Dumat, C., Lead and cadmium phytoavailability and human bioaccessibility for vegetables exposed to soil or atmospheric pollution by process ultrafine particles, J. Environ. Qual., 2014, vol. 43, pp. 1593–1600.
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Pourrut, B., Sabir, M., and Pinelli, E., Assessing the effect of metal speciation on lead toxicity to Vicia faba pigment contents, J. Geochem. Explor., 2014, vol. 144, pp. 290–297.
Kim, J., Lee, Y., and Yang, M., Environmental exposure to lead (Pb) and variations in its susceptibility, J. Environ. Sci. Health. C. Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev., 2014, vol. 32, pp. 159–185.
Pourrut, B., Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Winterton, P., and Pinelli, E., Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2011, vol. 213, pp. 113–136.
Shahid, M., Pinelli, E., and Dumat, C., Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, vol. 219–220, pp. 1–12.
Mishra, S., Srivastava, S., Tripathi, R.D., Kumar, R., Seth, C.S., and Gupta, D.K., Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation, Chemosphere, 2006, vol. 65, pp. 1027–1039.
Bhattacharjee, S., Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: roles in stress, senescence and signal transduction in plants, Curr. Sci., 2005, vol. 89, pp. 1113–1121.
Shahid, M., Austruy, A., Echevarria, G., Arshad, M., Sanaullah, M., Aslam, M., Nadeem, M., Nasim, W., and Dumat, C., EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review, Soil Sediment. Contam., 2014, vol. 23, pp. 389–416.
Zalaghi, R. and Safari-Sinegani, A.-A., The importance of different forms of Pb on diminishing biological activities in a calcareous soil, Chem. Ecol., 2014, vol. 30, pp. 446–462.
Shahid, M., Pinelli, E., Pourrut, B., Silvestre, J., and Dumat, C., Lead-induced genotoxicity to Vicia faba L. roots in relation with metal cell uptake and initial speciation, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2011, vol. 74, pp. 78–84.
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Silvestre, J., and Pinelli, E., Effect of fulvic acids on lead-induced oxidative stress to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. plant, Biol. Fertil. Soils, 2012, vol. 48, pp. 689–697.
Ruley, A.T., Sharma, N.C., Sahi, S.V., Singh, S.R., and Sajwan, K.S., Effects of lead and chelators on growth, photosynthetic activity and Pb uptake in Sesbania drummondii grown in soil, Environ. Pollut., 2006, vol. 144, pp. 11–18.
Marcato-Romain, C.-E., Guiresse, M., Cecchi, M., Cotelle, S., and Pinelli, E., New direct contact approach to evaluate soil genotoxicity using the Vicia faba micronucleus test, Chemosphere, 2009, vol. 77, pp. 345–350.
Pourrut, B., Perchet, G., Silvestre, J., Cecchi, M., Guiresse, M., and Pinelli, E., Potential role of NADPH-oxidase in early steps of lead-induced oxidative burst in Vicia faba roots, J. Plant Physiol., 2008, vol. 165, pp. 571–579.
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Pourrut, B., Silvestre, J., Laplanche, C., and Pinelli, E., Influence of EDTA and citric acid on lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots, J. Soils Sediments, 2014, vol. 14, pp. 835–843.
Blaylock, M.J., Salt, D.E., Dushenkov, S., Zakharova, O., Gussman, C., Kapulnik, Y., Ensley, B.D., and Raskin, I., Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 31, pp. 860–865.
Huang, J.W., Chen, J., Berti, W.R., and Cunningham, S.D., Phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 31, pp. 800–805.
Liu, D., Li, T.Q., Jin, X.F., Yang, X.E., Islam, E., and Mahmood, Q., Lead induced changes in the growth and antioxidant metabolism of the lead accumulating and non-accumulating ecotypes of Sedum alfredii, J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2008, vol. 50, pp. 129–140.
Huang, H., Li, T., Tian, S., Gupta, D.K., Zhang, X., and Yang, X.E., Role of EDTA in alleviating lead toxicity in accumulator species of Sedum alfredii H., Bioresour. Technol., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 6088–6096.
Markovska, Y., Geneva, M., Petrov, P., Boychinova, M., Lazarova, I., Todorov, I., and Stancheva, I., EDTA reduces heavy metal impacts on Tribulus terrestris photosynthesis and antioxidants, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2013, vol. 60, pp. 623–632.
Abbas, G., Saqib, M., Akhtar, J., Murtaza, G., Shahid, M., and Hussain, A., Relationship between rhizosphere acidification and phytoremediation in two acacia species, J. Soils Sediments, 2014, doi 10.1007/s11368-014-1051-9
Duarte, B., Delgado, M., and Caçador, I., The role of citric acid in cadmium and nickel uptake and translocation in Halimione portulacoides, Chemosphere, 2007, vol. 69, pp. 836–840.
Evangelou, M.W.H., Ebel, M., and Schaeffer, A., Evaluation of the effect of small organic acids on phytoextraction of Cu and Pb from soil with tobacco, Nicotiana tabacum, Chemosphere, 2006, vol. 63, pp. 996–1004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Pourrut, B. et al. Role of metal speciation in lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. Russ J Plant Physiol 62, 448–454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715040159
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715040159