Abstract
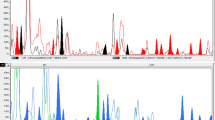
Bamboo is an important member of the giant grass subfamily Bambusoideae of Poaceae. In this study, 13 bamboo accessions belonging to 5 different genera were subjected to morphological evaluation and sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) analysis. Unweighted pair-group method of arithmetic averages (UPGMA) cluster analysis was used to construct a dendrogram and to estimate the genetic distances among accessions. On the basis of morphological characteristics, the 13 accessions were distinctly classified into 2 major clusters; 3 varieties, PPYX, PGNK, and PLYY were grouped as cluster A, and 10 accessions were categorized under cluster B. Similarity coefficients ranging from 0.23 to 0.96 indicated abundant genetic variation among bamboo varieties. Approximately 38 SRAP primer combinations generated 186 bands, with 150 bands (80.65%) showing polymorphisms among the 13 accessions. Based on SRAP analysis, 13 bamboo accessions were grouped into 3 major clusters. Five species comprised Cluster I (PASL, PLYY, PTSC, SCNK, and BMAK), which belongs to genus Phyllostachys. Cluster II consisted of 5 varieties, PASL, PLYY, PTSC, SCNK, and BMAK; Cluster III included 3 varieties, PGNK, PLSY, and BMRS. Comparison of the results generated by morphological and SRAP analyses showed that the classification based on SRAP markers was more concordant to the taxonomic results of Gamble than that performed using morphological characters, thus suggesting that SRAP analysis is more efficient in evaluating genetic diversity in bamboos compared to morphological analysis. The SRAP technique serves as an alternative method in assessing genetic diversity within bamboo collections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kochhar, S., Prasad, R.N., Mal, B., et al., Bamboo germplasm diversity and conservation in North East India, Ind. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 1990, vol. 3, pp. 21–36.
Wang, D.J., Shen, S.J. and San, C.U., Guatemala Bamboos of China, Portland: Timber Press, 1987.
Friar, E. and Kochert, G., Bamboo germplasm screening with nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1991, vol. 82, pp. 697–703.
Janzen, D.H., Why bamboos wait so long to flower, Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 1976, vol. 7, pp. 347–391.
Wu, C.Y., The classification of Bambuseae based on leaf anatomy, Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin., 1962, vol. 3, pp. 83–108.
Friar, E. and Kochert, G., A study of genetic variation and evolution of Phyllostachys (Bambusoideae: Poaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1994, vol. 89, pp. 265–270.
Lai, C.C. and Hsiao, J.Y., Genetic variation of Phyllostachys pubescens (Bambusoideae, Poaceae) in Taiwan based on DNA polymorphisms, Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin., 1997, vol. 38, pp. 145–152.
Trevor, R.H., Stephen, A.R., Grainne, N.C., et al., A Comparison of ITS nuclear rDNA sequence data and AFLP markers for phylogenetic studies in Phyllostachys (Bambusoideae, Poaceae), J. Plant Res., 2000, vol. 113, pp. 259–269.
Barkley, N.A., Newman, M.L., Wang, M.L., et al., Assessment of the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of a temperate bamboo collection by using transferred EST-SSR markers, Genome, 2005, vol. 48, pp. 731–737.
Sharma, R.K., Gupta, P., Sharma, V., et al., Evaluation of rice and sugarcane SSR markers for phylogenetic and genetic diversity analyses in bamboo, Genome, 2008, vol. 51, pp. 91–103.
Li, G. and Quiros, C.F., Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2001, vol. 103, pp. 455–461.
Hao, Q., Liu, Z.A., Shu, Q.Y., et al., Studies on Paeonia cultivars and hybrids identification based on SRAP analysis, Hereditas, 2008, vol. 145, pp. 38–47.
Muhammad, Y., James., A.C., Rivera-Madrid, R., et al., Musa genetic diversity revealed by SRAP and AFLP, Mol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 47, pp. 189–199.
Osman, G., Suleyman, K., and Kazim, A., Diversity and relationships among Turkish okra germplasm by SRAP and phenotypic marker polymorphism, Biologia (Bratislava), 2007, vol. 62, pp. 41–45.
Zhang, F., Ge, Y., Wang, W., et al., Genetic diversity and population structure of cultivated Bromeliad accessions assessed by SRAP markers, Sci. Hortic., 2012, vol. 141, pp. 1–6.
Ferriol, M., Pico, B., Pascual, F.C., et al., Molecular diversity of a germplasm collection of squash (Cucurbita moschata) determined by SRAP and AFLP markers, Crop Sci., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 653–664.
Zhang, F., Chen, S., Chen, F., et al., SRAP-based mapping and QTL detection for inflorescence-related traits in chrysanthemum (Dendranthema morifolium), Mol. Breed., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 11–23.
Li, G., Gao, M., Yang, B., et al., Gene for gene alignment between the Brassica and Arabidopsis genomes by direct transcriptome mapping, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2003, vol. 107, pp. 168–180.
Guo, D.L. and Luo, Z.R., Genetic relationships of some PCNA persimmons (Diospyros kaki Thumb.) from China and Japan revealed by SRAP analysis, Genet. Resour. Crop Evol., 2006, vol. 53, pp. 1597–1603.
Das, M., Bhattacharya, S., Basak, J., et al., Phylogenetic relationships among the bamboo species as revealed by morphological characters and polymorphism analyses, Biol. Plant., 2007, vol. 51, pp. 667–672.
Sneath, P.H.A. and Sokal, R.R., Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification, San-Francisco: Freeman, 1973.
Rohlf, F.J., NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System: Version 2.1, Setauket: Exeter Software, 2000.
Murray, M.G. and Thompson, W.F., Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 1980, vol. 8, pp. 4321–4326.
Wu, G.Y., Pan, H.Z., and Wu, Y., Protocols of Common Experimental Data for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Beijing: Science Press, 1999.
Nei, M. and Li, W.H., Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1979, vol. 76, pp. 5269–5273.
Raizada, M.B. and Chatterjee, R.N., World distribution of bamboos with special reference to the Indian species and their more important uses, Indian For., 1956, vol. 82, pp. 215–218.
He, D.H., Lin, Z.X., Zhang, X.L., et al., Mapping QTLs of traits contributing to yield and analysis of genetic effects in tetraploid cotton, Euphytica, 2005, vol. 144, pp. 141–149.
Wang, G., Pan, J.S., Li, X.Z., et al., Construction of a cucumber genetic linkage map with SRAP markers and location of the genes for lateral branch traits, Sci. China: Life Sci., 2005, vol. 48, pp. 213–220.
Ferriol, M., Pico, B., and Nuez, F., Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2003, vol. 107, pp. 271–282.
Zeng, B., Zhang, X.G., Lan, Y., et al., Evaluation of genetic diversity and relationships in orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.) germplasm based on SRAP markers, Can. J. Plant Sci., 2008, vol. 88, pp. 53–60.
Budak, H., Shearman, R.C., Parmaksiz, I., et al., Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, and SRAPs, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2004, vol. 109, pp. 280–288.
Lin, Z.X., Zhang, X.L., Nie, Y.C., et al., Construction of a genetic linkage map for cotton based on SRAP, Chin. Sci. Bull., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 2064–2068.
Mutlu, N., Boyaci, F.H., Göçmen, M., and Abak, K., Development of SRAP, SRAP-RGA, RAPD and SCAR markers linked with a Fusarium wilt resistance gene in eggplant, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2008, vol. 117, pp. 1303–1312.
Zhang, F., Chen, S., Chen, F., et al., Genetic analysis and associated SRAP markers for flowering traits of chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium), Euphytica, 2011, vol. 177, pp. 15–24.
Uzun, A., Yesiloglu, T., Tuzcu, O., et al., Genetic diversity and relationships within Citrus and related genera based on sequence related amplified polymorphism markers (SRAPs), Sci. Hortic., 2009, vol. 121, pp. 306–312.
Song, Z.Q., Li, X.F., Wang, H.G., et al., Genetic diversity and population structure of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge in China revealed by ISSR and SRAP, Genetica, 2010, vol. 138, pp. 241–249.
Ariss, J.J. and Vandemark, G.J., Assessment of genetic diversity among nondormant and semidormant alfalfa populations using sequence-related amplified polymorphisms, Crop Sci., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 2274–2284.
Chang, D., Yang, F.Y., Yan, J.J., et al., SRAP analysis of genetic diversity of nine native populations of wild sugarcane, Saccharum spontaneum, from Sichuan, China, Genet. Mol. Res., 2012, vol. 11, pp. 1245–1253.
Gamble, J.S., The Bambuseae of British India, Bengal Secretariat Press, 1896.
Gielis, J., Everaert, I., and De, L.M., Analysis of genetic variability and relationships in Phyllostachys using random amplified polymorphic DNA, The Bamboos, Chapman, G., Ed., London: Academic, 1997, pp. 107–124.
Nayak, S., Rout, G.R., and Das, P., Evaluation of the genetic variability in bamboo using RAPD markers, Plant Soil Environ., 2003, vol. 49, pp. 24–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Liu, T., Tang, Q. et al. Evaluation of bamboo genetic diversity using morphological and SRAP analyses. Russ J Genet 50, 267–273 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414030132
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414030132