Abstract
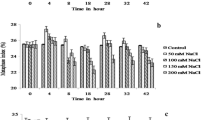
The effects of NaCl stress on the activity of antioxidant enzymes, lipid peroxidation, cell membrane stability, net photosynthetic rate, gas-exchange, and chlorophyll content were investigated in two Jerusalem artichoke cultivars, Dafeng (salt-tolerant) and Wuxi (salt-sensitive), grown under control (nutrient solution) or salt stress (nutrient solution containing 75, 150, and 225 mM NaCl) conditions for 7 days. In leaves of salt-tolerant cv. Dafeng, superoxide dismutase (EC 1.15.1.1), peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7), and catalase (EC 1.11.1.6) activities significantly increased as compared to the controls, whereas no significant change was observed in cv. Wuxi. Lipid peroxidation and cell membrane injury were enhanced in both cultivars. Net photosynthesis and stomatal conductance decreased in response to salt stress, but cv. Dafeng showed a smaller reduction in photosynthesis than cv. Wuxi. The results indicated that stomatal aperture limited leaf photosynthetic capacity in the NaCl-treated plants of both cultivars. However, significant reduction in the leaf chlorophyll content due to NaCl stress was observed only in cv. Wuxi. These results suggested that salt-tolerant Jerusalem artichoke varieties may have a better protection against reactive oxygen species, at least in part, by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes under salt stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
catalase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- NBT:
-
nitroblue tetrazolium
- POD:
-
peroxidase
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Zhu, J.K., Hasegawa, P.M., and Bressan, R.A., Molecular Aspects of Osmotic Stress in Plants, Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 1997, vol. 16, pp. 253–277.
Serrano, R., Mulet, J.M., Rios, G., Marquez, J.A., de Larriona, I.F., Leube, M.P., Mendizabal, I., Pascual-Ahuir, A., Proft, M.R.R., and Montesinos, C., A Glimpse of the Mechanism of Ion Homeostasis during Salt Stress, J. Exp. Bot., 1999, vol. 50, pp. 1023–1036.
Rodriguez-Navarro, A., Potassium Transport in Fungi and Plants, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, vol. 1469, pp. 1–30.
Zhu, J.K., Regulation of Ion Homeostasis under Salt Stress, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2003, vol. 6, pp. 441–445.
Mittler, R., Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Stress Tolerance, Trends Plant Sci., 2002, vol. 7, pp. 405–410.
Neill, S., Desikan, R., and Hancock, J., Hydrogen Peroxide Signaling, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2002, vol. 5, pp. 388–395.
Imlay, J.A., Pathways of Oxidative Damage, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 57, pp. 395–418.
Rout, N.P. and Shaw, B.P., Salt Tolerance in Aquatic Macrophytes: Possible Involvement of the Antioxidative Enzymes, Plant Sci., 2001, vol. 160, pp. 415–423.
Hernández, J.A., Jiménez, A., Mullineaux, P., and Sevilla, F., Tolerance of Pea (Pisum sativum L.) to Long-Term Salt Stress Is Associated with Induction of Antioxidant Defenses, Plant Cell Environ., 2000, vol. 23, pp. 853–862.
Mittova, V., Tal, M., Volokita, M., and Guy, M., Salt Stress Induces Up-Regulation of an Efficient Chloroplast Antioxidant System in the Salt Tolerant Wild Tomato Species Lycopersicon pennellii But Not in the Cultivated Species, Physiol. Plant., 2002, vol. 115, pp. 393–400.
De Azevedi, Neto, A.D., Prisco, J.T., Eněas-Filho, J., de Abreu, C.E.B., and Gomes-Filho, E., Effect of Salt Stress on Antioxidative Enzymes and Lipid Peroxidation in Leaves and Roots of Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Maize Genotypes, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2006, vol. 56, pp. 87–94.
Noctor, G. and Foyer, C.H., Ascorbate and Glutathione: Keeping Active Oxygen under Control, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 1998, vol. 49, pp. 249–279.
Hernández, J.A. and Almansa, M.S., Short-Term Effects of Salt Stress on Antioxidant Systems and Leaf Water Relations of Pea Leaves, Physiol. Plant., 2002, vol. 115, pp. 251–257.
Meloni, D.A., Oliva, M.A., Martinez, C.A., and Cambraia, J., Photosynthesis and Activity of Superoxide Dismutase, Peroxidase and Glutathione Reductase in Cotton under Salt Stress, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2003, vol. 49, pp. 69–76.
Monti, A., Amaducci, M.T., and Venturi, G., Growth Response, Leaf Gas Exchange and Fructans Accumulation of Jerusalem Artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) as Affected by Different Water Regimes, Eur. J. Agron., 2005, vol. 23, pp. 136–145.
Saengthongpinit, W. and Sajjaanantakul, T., Influence of Harvest Time and Storage Temperature on Characteristics of Inulin from Jerusalem Artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) Tubers, Postharvest Biol. Technol., 2005, vol. 37, pp. 93–100.
Liu, Z.P., Deng, L.Q., Liu, L., Qi, C.H., Chen, M.D., and Xia, T.X., Physiological Characteristics of Helianthus tuberosus L. Irrigated by Seawater, Laizhou, Shandong Province, J. Plant Ecol., 2005, vol. 29, pp. 474–478.
Wellburn, A.R., The Spectral Determination of Chlorophylls a and b, as Well as Total Carotenoids Using Various Solvents with Spectrophotometers of Different Resolution, J. Plant Physiol., 1994, vol. 144, pp. 307–313.
Zhao, H.J. and Tan, J.F., Role of Calcium Ion in Protection against Heat and High Irradiance Stress-Induced Oxidative Damage to Photosynthesis of Wheat Leaves, Photosynthetica, 2005, vol. 43, pp. 473–476.
Lutts, S., Kiner, J.M., and Bouharmont, J., NaCl-Induced Senescence in Leaves of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars Differing in Salinity Resistance, Ann. Bot., 1996, vol. 78, pp. 389–398.
Chen, L.Z., Wang, W.Q., and Lin, P., Photosynthetic and Physiological Responses of Kandelia candel L. Druce Seedlings to Duration of Tidal Immersion in Artificial Seawater, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2005, vol. 54, pp. 256–266.
Ghazi, H.B., Yasuo, Y., Emi, S., Ryozo, S., Naoyoshi, K., Kunisuke, T., and Kiyoshi, T., Enhanced Tolerance to Salt Stress and Water Deficit by Overexpressing Superoxide Dismutase in Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Chloroplasts, Plant Sci., 2004, vol. 166, pp. 919–928.
Bradford, M.M., A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Using the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Polle, A., Dissecting the Superoxide Dismutase-Ascorbate Peroxidase-Glutathione Pathway in Chloroplasts by Metabolic Modeling. Computer Simulation as a Step towards Flux Analysis, Plant Physiol., 2001, vol. 126, pp. 445–462.
Meneguzzo, S., Navarri-Izzo, F., and Izzo, R., Antioxidative Responses of Shoots and Roots of Wheat to Increasing NaCl Concentrations, J. Plant Physiol., 1999, vol. 155, pp. 274–280.
Yu, Q. and Rengel, Z., Drought and Salinity Differentially Influence Activities of Superoxide Dismutases in Narrow-Leafed Lupins, Plant Sci., 1999, vol. 142, pp. 1–11.
Jahnke, L.S. and White, A.L., Long-Term Hyposaline and Hypersaline Stresses Produce Distinct Antioxidant Responses in the Marine Alga Dunaliella tertiolecta, J. Plant Physiol., 2003, vol. 160, pp. 1193–1202.
Sudhakar, C., Lakshmi, A., and Giridarakumar, S., Changes in the Antioxidant Enzyme Efficacy in Two High Yielding Genotypes of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl Salinity, Plant Sci., 2001, vol. 161, pp. 613–619.
Liang, Y., Chen, Q., Liu, Q., Zhang, W., and Ding, R., Exogenous Silicon (Si) Increases Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Reduces Lipid Peroxidation in Roots of Salt-Stressed Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), J. Plant Physiol., 2003, vol. 160, pp. 1157–1164.
Steduto, P., Albrizio, R., Giorio, P., and Sorrentino, G., Gas Exchange Response and Stomatal and Non-Stomatal Limitations to Carbon Assimilation of Sunflower under Salinity, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2000, vol. 44, pp. 243–255.
Sultana, N., Ikeda, T., and Itoh, R., Effect of NaCl Salinity on Photosynthesis and Dry Matter Accumulation in Developing Rice Grains, Environ. Exp. Bot., 1999, vol. 42, pp. 211–220.
Delfine, S., Alvino, A., Villani, M.C., and Loreto, F., Restrictions to Carbon Dioxide Conductance and Photosynthesis in Spinach Leaves Recovering from Salt Stress, Plant Physiol., 1999, vol. 119, pp. 1101–1106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Y.F. Xue, Zh.P. Liu, 2008, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2008, Vol. 55, No. 6, pp. 863–858.
This text was submitted by the authors in English.
An erratum to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1021443709010221.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y.F., Liu, Z.P. Antioxidant enzymes and physiological characteristics in two Jerusalem artichoke cultivars under salt stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 55, 776–781 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102144370806006X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102144370806006X