Abstract
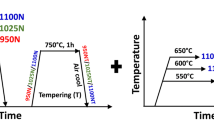
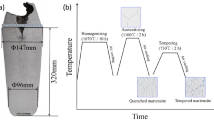
In this work, we have investigated microstructural changes in steel 10Kh9V2MFBR (analog of P02 steel) after long-term creep tests at a temperature of 600°C under an initial stress of 137 MPa. Time to rupture was found to be more than 40000 h. It has been established that, in the zone of grips and in the neck region of the sample, the size of the particles of the M 23C6 carbides increases from 85 nm to 152 nm and 182 nm, respectively. In addition, large particles of the Laves phase with an average size of 295 nm are separated. The particles of these phases are located along high-angle boundaries. During prolonged aging and creep, the transformation of the M(C,N) particles enriched in V into the Z phase occurs. The average size of particles of the Z phase after prolonged ageing was 48 nm; after creep, it reached 97 nm. The size of M(C,N) particles enriched by Nb increases from 26 nm after tempering to 55 nm after prolonged aging and creep. It has been established that, in spite of an increase in the transverse size of the laths of tempered martensite from 0.4 to 0.9 µm in the neck of the sample, the misorientation of the lath boundaries does not increase. No recrystallization processes were found to develop in the steel during creep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creep Resistant Steels, Ed. by F. Abe, T.-U. Kern, and R. Viswanathan (CRC Press, Woodhead Publ., Cambridge, UK, 2008).
J. C. Vaillant, H. B. Vandenberghe, and H. Heuser, “T/P23, 24,911and 92: New grades for advanced coalfired power plants—Properties and experience,” Int. J. Press. Vessel Pip. 85, 38–46 (2008).
K. A. Lanskaya, High-Chromium Refractory Steels (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1976) [in Russian].
R. O. Kaibyshev, V. N. Skorobogatykh, and I. A. Shchenkova, “New martensitic steels for thermal power plant: Creep resistance,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 109, 186–200 (2010).
V. A. Dudko, A. N. Belyakov, V. N. Skorobogatykh, R. O. Kaibyshev, and I. A. Shchenkova, “Structural changes in refractory steel 10Kh9V2MFBR due to creep at 650°C,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 52, 111–117 (2010).
V. Dudko, A. Belyakov, D. Molodov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Microstructure Evolution and Pinning of Boundaries by Precipitates in a9Pct. Cr Heat Resistant Steel During Creep,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 162–172 (2013).
A. Yu. Kipelova, A. N. Belyakov, V. N. Skorobogatykh, I. A. Shchenkova, R. O. Kaibyshev, “Structural changes in steel 10Kh9K3V1M1FBR due to creep,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 52, 118–127 (2010).
A. Kipelova, R. Kaibyshev, A. Belyakov, and D. Molodov, “Microstructure evolution in a 3% Co modified P911 heat resistant steel under tempering and creep condition,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 1280–1286 (2011).
N. Dudova, A. Plotnikova, D. Molodov, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Structural changes of tempered martensitic 9% Cr–2% W–3% Co steel during creep at 650°C,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 534, 632–639 (2012).
K. Kimura, H. Kushima, and K. Sawada, “Long-term creep deformation property of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 510–511, 58–63 (2009).
J. Hald, “Microstructure and long–term creep properties of 9–12% Cr steels,” Int. J. Press. Vess. Pip. 85, 30–37 (2008).
A. Kostka, K.-G. Tak, R. J. Hellmig, Y. Estrin, and G. Eggeler, “On the contribution of carbides and micrograin boundaries to the creep strength of tempered martensite ferritic steels,” Acta Mater. 55, 539–550(2007).
A. Kipelova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Laves phase evolution in a modified P911 heat resistant steel during creep at923K,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 532, 71–77 (2012).
K. Sawada, K. Kubo, and F. Abe, “Creep behavior and stability of MX precipitates at high temperature in 9Cr–0.5Mo–1.8W–VNb Steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 319–321, 784–787 (2001).
R. O. Kaibyshev, V. N. Skorobogatykh, and I. A. Shchenkova, “Formation of the z phase and prospects of martensitic steels with 11% Cr for operation above 590°C,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 52, 90–99 (2010).
I. Fedorova, A. Belyakov, P. Kozlov, V. Skorobogatykh, I. Shenkova, and R. Kaibyshev, “Laves-phase precipitates in a low-carbon 9% Cr martensitic steel during aging and creep at923K,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 615, 153–163 (2014).
M. I. Isik, A. Kostka, and G. Eggeler, “On the nucleation of Laves phase particles during high-temperature exposure and creep of tempered martensite ferritic steels,” Acta Mater. 81, 230–240 (2014).
V. V. Popov and I. I. Gorbachev, “Numerical simulation of carbide and nitride precipitate evolution in steels,” Mat.-Wiss. Werkstofftech. 36, 477–481 (2005).
V. V. Popov, “Simulation of Precipitate Evolution in FeBased Alloys”, Advanctd structured materials, 36, 215–281 (2013).
I. I. Gorbachev, V. V. Popov, and A. Yu. Pasynkov, “Thermodynamic modeling of carbonitride formation in steels with V and Ti,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 113, 974–981 (2012).
I. I. Gorbachev, V. V. Popov, and A. Yu. Pasynkov, “Simulation of evolution of precipitates of two carbonitride phases in Nband Ti-containing steels during isothermal annealing,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 741–751 (2013).
A. Kipelova, M. Odnobokova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Effect of Co on creep behavior of a P911 steel,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 577–583 (2012).
I. Fedorova, A. Kipelova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Microstructure evolution in an advanced9Pct Cr martensitic steel during creep at923K (650°C),” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 128–135 (2013).
K. Sawada, H. Kushima, and K. Kimura, “Z-phase formation during creep and aging in 9–12% Cr heat resistant steels,” ISIJ Int. 46, 769–775 (2006).
A. Golpayegani, H. -O. Andren, H. Danielsen, and J. Hald, “A study on Z-phase nucleation in martensitic chromium steels,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 489, 310–318 (2008).
F.-S. Yin, L.-Q. Tian, B. Xue, X.-B. Jiang, and L. Zhou, “Effect of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of9to12Pct Cr ferritic/martensitic heat-resistant steels,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43, 2203–2209 (2012).
L. Cipolla, H. K. Danielsen, D. Venditti, E. D. Nunzio, J. Hald, and M. A. J. Somers, “Conversion of MX nitrides to Z-phase in a martensitic 12% Cr steel,” Acta Mater. 58, 669–679 (2010).
C. Panait, W. Bendick, A. Fuchsmann, A.-F. Gourgues-Lorenzon, and J. Besson, “Study of the microstructure of the grade91steel after more than100000h of creep exposure at 600°C,” Int. J. Press. Vessel Pip. 87, 326–335 (2010).
R. P. Chena, H. G. Armaki, K. Maruyamaa, and M. Igarashi, “Long-term microstructural degradation and creep strength in grade91steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 4390–4394 (2011).
K. Kimura, Y. Toda, H. Kushima, and K. Sawada, “Creep strength of high chromium steel with ferrite matrix,” Int. J. Press. Vessel Pip. 87, 282–288 (2010).
A. Aghajani, C. Somsen, and G. Eggeler, “On the effect of long-term creep on the microstructure of a 12% chromium tempered martensite ferritic steel,” Acta Mater. 57, 5093–5106 (2009).
S. Zaefferer, “Computer-aided crystallographic analysis in the TEM,” Adv. Imag. Electron Phys. 125, 355–415 (2002).
M. Yoshizawa, M. Igarashi, K. Moriguchi, A. Iseda, H. Armaki, and K. Maruyama, “Effect of precipitates on long-term creep deformation properties of P92 and P122 type advanced ferritic steels for USC power plants,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 510–511, 162–168 (2009).
A. Kipelova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “The crystallography of M23C6 carbides in a martensitic 9% Cr steel after tempering, aging and creep,” Philos. Mag. 93, 2259–2268 (2013).
D. A. Porter, K. E. Esterling, and M. Sherif, Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys 3rd ed. (CRS Press, Roca Baton, Fl., 2009).
K. Suzuki, S. Kumai, Y. Toda, H. Kushima, and K. Kimura, “Two-hase separation of primary MX carbonitride during tempering in creep resistant 9Cr1MoVNb steel,” ISIJ Int. 43, 1089–1094 (2003).
A. Yu. Kipelova, A. N. Belyakov, V. N. Skorobogatykh, I. A. Shchenkova, R. O. Kaibyshev, “Tempering-induced structural changes in steel 10Kh9K3V1M1FBR and their effect on the mechanical properties,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 52, 100–110 (2010).
O. Prat, J. Garcia, D. Rojas, C. Carrasco, and G. Inden, “Investigations on the growth kinetics of Laves phase precipitates in 12% Cr creep-resistant steels: Experimental and DICTRA calculations,” Acta Mater. 58, 6142–6153 (2010).
H. Cui, F. Sun, K. Chen, L. Zhang, R. Wan, A. Shan, and J. Wu, “Precipitation behavior of Laves phase in 10% Cr steel X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 during short–erm creep exposure,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 7505–7509(2010).
Q. Li, “Precipitation of Fe2W Laves phase and modeling of its direct influence on the strength of a 12Cr–2W steel,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 89–97 (2006).
K. Sawada, K. Suzuki, H. Kushima, M. Tabuchi, and K. Kimura, “Effect of tempering temperature on Z-phase formation and creep strength in 9Cr–1Mo–V–Nb–N steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 480, 558–563 (2008).
F. J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed. (Elsevier, Atlanta, GA, 2004), pp. 91–112.
E. Hornbogen and U. Koster, in Recrystallization of Metallic Materials, Ed. by F. Haessner (Verlag, Stuttgart, 1978), pp. 159–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.E. Fedoseeva, P.A. Kozlov, V.A. Dudko, V.N. Skorobogatykh, I.A. Shchenkova, R.O. Kaibyshev, 2015, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2015, Vol. 116, No. 10, pp. 1102–1111.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedoseeva, A.E., Kozlov, P.A., Dudko, V.A. et al. Microstructural changes in steel 10Kh9V2MFBR during creep for 40000 hours at 600°C. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 116, 1047–1056 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15080049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15080049