Abstract
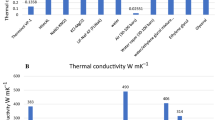
Aluminum-5 wt % manganese alloy heat pipe with a nano-fluid of n-butanol and 0.2 wt % carbon nano-tubes was prepared by deep-drawing, and its mechanical and corrosion properties were determined to improve thermal conductivity performance. The heat pipe was designed to have micro-sized inner fins working at temperature higher than 200°C and simultaneously retaining a similar thermal conductivity to that of pure aluminum. The heat pipe formed by aluminum-5 wt % manganese alloys had improved mechanical properties such as 38% micro-hardness, 45.8% yield strength, and 53.5 wt % ultimate tensile strength due to grain size refinement and work hardening effects. The corrosion rate of the aluminum alloy in artificial sea water at room temperature decreased from 0.110 mpy to 0.102 mpy. The nano-fluid of n-butanol and 0.2 wt % carbon nano-tubes improved the thermal conductivity of the heat-pipe by about 250%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. U. S. Choi, “Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles,” in Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, Ed. by D. A. Siginer and H. P. Wang (ASME, New York, 1995), vol. 231.
H. B. Ma, C. Wilson, B. Borgmeyer, K. Park, Q. Yu, S. U. S. Choi, and M. Tirumala, “Effect of nano-fluid on the heat transport capability in an oscillating heat pipe,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 14316–14319 (2006).
R. Senthilkumar, S. Vaidyanathan, B. Sivaraman, “Performance analysis of heat pipe using copper nanofluids with aqueous solution of n-butanol,” Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 5, 251–256 (2010).
S. Lee, S. U. S. Choi, J. A. Eastman, and S. Lee, “Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles,” Trans. ASME 121, 280–289 (1999).
S. U. S. Choi, X. Wang and W. Xu, “Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture,” J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 13, 474–480 (1999).
H. Xie, J. Wang, and T. Xi, “Thermal conductivity of suspensions containing nanosized SiC particles,” Int. J. Thermophys. 23, 30–35 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.R., Choi, Y. Performance tests of Mn-added aluminum heat pipe with micro-sized inner fins and thermal fluid for cooling electronic device. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 115, 1362–1365 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14130109
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14130109