Abstract
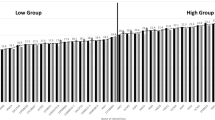
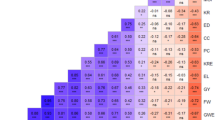
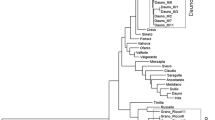
Analysis of genetic diversity in maize populations is a very important step for understanding genetic structure and subsequently for genetic manipulations in maize breeding. Sh2, Bt2, Sh1, Wx1, Ae1 and Su1 involved in starch biosynthesis are important genes associated with yield and quality traits in maize breeding programs. In this study, genetic diversity of these six genes in 67 Chinese elite maize inbred lines was measured using single-nucleotide amplified polymorphisms (SNAPs). The results indicated that the number of haplotypes of each gene and population was far less than theoretically expected 2n (n = the number of the SNAPs). Phenetic clustering analysis showed that the kernel phonetic (semi-) dent and (semi-) flint lines were belong to distinct subclusters based on haplotypes of SNAPs, with a few exceptions. In addition, the genetic origin of these maize inbred lines was associated with the clustered subgroups. Intragenic linkage disequilibrium (LD) was observed in some of the SNAPs in Bt2, Sh1 and Ae1, while intergenic LD was observed in some of the SNAPs in Bt2, Sh1 and Su1. Association study of kernel phenotypes and SNAP haplotypes showed that the (semi-) dent and (semi-) flint lines had the common haplotype of TA and CC at two SNAP sites in Bt2 (Bt2-2 and Bt2-5), respectively. Two haplotypes of ATGT and GTGC at four SNAP sites in Sh1 (Sh1-2, Sh1-3, Sh1-4 and Sh1-5) were associated with temperature and tropical origin of the maize inbred lines, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warbutton M.L., Ribaut J.M., Franco J., Crossa J., Dubreuil P., Betran F.J. 2005. Genetic characterization of 218 elite CIMMYT maize inbred lines using RFLP markers. Euphytica. 142, 97–106.
Li Y., Shi Y.S., Song Y.C., Du J.Y., Tuberosa R., Wang T.Y. 2004. Analysis of genetic diversity in maize inbred lines based on AFLP markers. Maydica. 49, 89–95.
Shieh G.J., Thseng S. 2002. Genetic diversity of Tainan-white maize inbred lines and prediction of single cross hybrid performance using RAPD markers. Euphytica. 124, 307–313.
Yu Y., Wang R., Shi Y., Song Y., Wand T., Li Y. 2007. Genetic diversity and structure of the core collection for maize inbred lines in China. Maydica. 52, 181–194.
Suga H., Gale L.R., Kistler H.C. 2004. Development of VNTR markers for two Fusarium graminearum clade species. Mol. Ecol. Notes. 4, 468–470.
Remington D.L., Thornsberry J.M., Matsuoka Y., Wilson L.M., Whitt S.R., Doebley J., Kresovich S., Goodman M.M., Buckler E.S. 2001. Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic association in the maize genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98, 11479–11484.
Edwards J.D., Janda J., Sweeney M.T., Gaikwad A.B., Liu B., Leung H., Galbraith D.W. 2008. Development and evaluation of a high-throughput, low-cost genotyping platform based on oligonucleotide microarrays in rice. Plant Methods. 4, 1–13.
Braqard C., Verdier V., Maraite H. 1995. Genetic diversity among Xanthomonas campestris strains pathogenic for small grains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 1020–1026.
Cho R.J., Mindrinos M., Richards D.R., Sapolsky R.J., Anderson M., Drenkard E., Dewdney L., Reuber T.L., Stammers M., Federspiel N., et al. 1999. Genome-wide mapping with biallelic markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature Genet. 23, 203–207.
Tenaillon M.I., Sawkins M.C., Anderson L.K., Stack S.M., Doebley J., Gaut B.S. 2001. Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98, 9161–9166.
Latha R., Rubia L., Bennet J., Swaminathan M.S. 2004. Allele mining for stress tolerance genes in Oryza species and related germplasm. Mol. Biotechnol. 27, 101–108.
Whitt S.R, Wilson L.M., Tenaillon M.I., Gaut B.S., Buckler E.S. 2002. Genetic diversity and selection in the maize starch pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 12959–12962.
Wilson L.M., Whitt S.R., Ibanez A.M., Rocheford T.R., Goodman M.M. 2004. Dissection of maize kernel composition and starch production by candidate gene association. Plant Cell. 16, 2719–2733.
Chourey P.S., Nelson O.E. 1976. The enzymatic deficiency conditioned by the shrunken-1 mutations in maize. Biochem. Genet. 14, 1041–1055.
Hannah L.C., Shaw J.R., Giroux M.J., Reyss A., Prioul J.L., Bae J., Lee J.Y. 2001. Maize genes encoding the small subunit of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 127, 173–183.
Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. 1983. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 35, 225–233.
Kim K.N., Fisher D.K., Gao M., Guiltinan M.J. 1998. Molecular cloning and characterization of the amyloseextender gene encoding starch branching enzyme IIB in maize. Plant Mol. Biol. 38, 945–956.
James M.G., Robertson D.S., Myers A.M. 1995. Characterization of the maize gene sugaryl, a determinant of starch composition in kernels. Plant Cell. 7, 417–429.
Shin J.H., Kwon S.J., Lee J.K., Min H.K., Kim N.S. 2006. Genetic diversity of maize kernel starch-synthesis gene with SNAPs. Genome. 49, 1287–1296.
Greene B., Walko R., Hake S. 1994. Mutator insertions in an intron of maize knotted1 gene result in dominant suppressible mutations. Genetics. 138, 1275–1285.
Rohlf F.J. 2000. NTSYS-pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1. N.Y.: Exeter.
Nei M., Li W. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 76, 5269–5273.
Rozas J., Rozas R. 1999. DnaSP version3: An integrated program for molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics. 15, 174–175.
Nelson O., Pan D. 1995. Starch synthesis in maize endosperms. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 46, 475–496.
Myers A.M., Morell M.K., James M.G., Ball S.G. 2000. Recent progress toward understanding biosynthesis of the arnylopectin crystal. Plant Physiol. 122, 989–997.
Matsuoka Y., Vigouroux Y., Goodman M.M., Jesus S.G., Buckle E., Doebley J. 2002. A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 6080–6084.
Wright S.I., Bi I.V., Schroeder S.G., Yamasaki M., Doebley J.F., McMullen M.D., Gaut B.S. 2005. The effects of artificial selection on the maize genome. Science. 308, 1310–1314.
Gupta P.K., Rustgi S., Kulwal P.L. 2005. Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: Recent status and future prospects. Plant Mol. Biol. 57, 461–485.
Reif J.C., Hallauer A.R., Melchinger A.E. 2005. Heterosis and heterotic patterns in maize. Maydica. 50, 215–223.
Wan Y.S., Watanabe J.A., Yi S.S., Htaik T., Win K., Yamanaka S., Nakamura I., Watanabe K.N. 2005. Assessment of genetic diversity among the major Myanmar banana landraces. Breeding Sci. 55, 365–369.
Ohm M.S., Kazuyuki D., Khin A., Kenji I., Atsushi Y. 2006. Genetic diversity of Myanmar rice cultivars detected by DNA markers. J. Fac. Agr. Kyushu Univ. 51, 181–187.
Melani M.D., Carena M.J. 2005. Alternative maize heterotic patterns for the Northern Corn Belt. Crop Sci. 45, 2186–2194.
Liu J.L. 2002. Maize Breeding Science, 2nd ed. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, W.B., Zheng, L.L., Zhang, Z.F. et al. Genetic diversity of starch synthesis genes of Chinese maize (Zea mays L.) with SNAPs. Mol Biol 43, 937–945 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309060041
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893309060041