Abstract
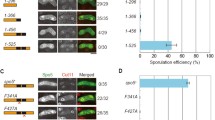
Homologous recombination is initiated in meiotic eukaryotic cells at DNA double-strand breaks, which are generated by several proteins, Spo11p playing a key role. The protein products of SPO11 orthologs are highly conserved, are found in most eukaryotes from plants to human, and are structurally similar to subunit A of archaeal DNA topoisomerase VI. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPO11 is expressed in meiotic prophase I. Spo11p acts as topoisomerase II and is presumably active as a dimer. Experimental data on Spo11p compartmentalization in vegetative yeast cells are unavailable. The SPO11 coding region and its fragments were fused in frame with the egfp reporter and expressed in vegetative yeast cells. The Spo11p-EGFP fusion was localized in the nucleus, while cytoplasmic localization was observed for Spo11Δ-EGFP devoid of the 25 N-terminal residues. N-terminal Spo11p region 7–25 fused with EGFP ensured the nuclear targeting of the reporter protein and was assumed to harbor the nuclear localization signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keeney S., Neale M.J. 2006. Initiation of meiotic recombination by formation of DNA double-strand breaks: Mechanism and regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34, 523–525.
Li J., Hooker G.W., Roeder G.S. 2006. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mer2, Mei4 and Rec114 form a complex required for meiotic double-strand break formation. Genetics. 173, 1969–1981.
Bergerat A., Gadelle D., Forterre P. 1994. Purification of a DNA topoisomerase II from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus shibatae: A thermostable enzyme with both bacterial and eucaryal features. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 27663–27669.
Bergerat A., de Massy B., Gadelle D., Varoutas P.C., Nicolas A., Forterre P. 1997. An atypical topoisomerase II from Archaea with implications for meiotic recombination. Nature. 386, 414–417.
Romanienko P.J., Camerini-Otero R.D. 1999. Cloning, characterization, and localization of mouse and human SPO11. Genomics. 61, 156–169.
Romanienko P.J., Camerini-Otero R.D. 2000. The mouse SPO11 gene is required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Mol. Cell. 6, 975–987.
Hartung F., Puchta H. 2001. Molecular characterization of two paralogous SPO11 homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 271, 81–86.
Stacey N.J., Kuromori T., Azumi Y., Roberts G., Breuer C., Wada T., Maxwell A., Roberts K., Sugimoto-Shirasu K. 2006. Arabidopsis SPO11-2 functions with SPO11-1 in meiotic recombination. Plant J. 48, 206–216.
Nichols M.D., DeAngelis K., Keck J.L., Berger J.M. 1999. Structure and function of an archael topoisomerase VI subunit with homology to the meiotic recombination factor Spo11. EMBO J. 18, 6177–6188.
Wu H., Gao J., Sharif W.D., Davidson M.K., Wahls W.P. 2004. Purification, folding, and characterization of Rec12 (Spo11) meiotic recombinase of fission yeast. Protein Expr. Purif. 38, 136–144.
Sasanuma H., Murakami H., Fukuda T., Shibata T., Nicolas A., Ohta K. 2007. Meiotic association between Spo11 regulated by Rec102, Rec104 and Rec114. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 1119–1133.
Storlazzi A., Tesse S., Gargano S., James F., Kleckner N., Zickler D. 2003. Meiotic double-strand breaks at the interface of chromosome movement, chromosome remodeling, and reductional division. Genes Dev. 17, 2675–2687.
Jain M., Tyagi A.K., Khurana J.P. 2006. Overexpression of putative topoisomerase 6 genes from rice confers stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. FEBS J. 273, 5245–5260.
Champoux J.J. 2001. DNA topoisomerases: Structure, function, and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 369–413.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., Sambrook, J. 1982. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press.
Soni R., Carmichael J.P., Murray J.A. 1993. Parameters affecting lithium acetate-mediated transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and development of a rapid and simplified procedure. Curr. Genet. 24, 455–459.
Komakhin R.A., Komakhina V.V., Zhuchenko A.A. 2007. Production of genetic constructs containing E. coli recA gene for inducing recombination in plants. S-kh. Biol. 3, 25–32.
Bruschi C.V., Esposito M.S. 1983. Enhancement of spontaneous mitotic recombination by the meiotic mutant SPO11-1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 80, 7566–7570.
Klapholz S., Waddell C.S., Esposito R.E. 1985. The role of the SPO11 gene in meiotic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 110, 187–216.
Peciña A., Smith K.N., Mézard C., Murakami H., Ohta K., Nicolas A. 2002. Targeted stimulation of meiotic recombination. Cell. 111, 173–184.
Shulga N., Roberts P., Gu Z., Spitz L., Tabb M.M., Nomura M., Goldfarb D.S. 1996. In vivo nuclear transport kinetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A role for heat shock protein 70 during targeting and translocation. J. Cell. Biol. 135, 329–339.
Alberts B., Bray D., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Watson J.D. 1994. Molecular Biology of the Cell. N.Y.: Garland.
Moreland R.B., Langevin G.L., Singer R.H., Garcea R.L., Hereford L.M. 1987. Amino acid sequences that determine the nuclear localization of yeast histone 2B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 4048–4057.
Park K.J., Kanehisa M. 2003. Prediction of protein subcellular locations by support vector machines using compositions of amino acids and amino acid pairs. Bioinformatics. 19, 1656–1663.
Gadelle D., File J., Buhler C., Forterre P. 2003. Phylogenomics of type II DNA topoisomerases. BioEssays. 25, 232–242.
Hayashi A., Ogawa H., Kohno K., Gasser S.M., Hiraoka Y. 1998. Meiotic behaviors of chromosomes and microtubules in budding yeast: Relocalization of centromeres and telomeres during meiotic prophase. Genes Cells. 3, 587–601.
Hartung F., Puchta H. 2007. Molecular characterization of homologues of both subunits A (SPO11) and B of the archaebacterial topoisomerase 6 in plants. Gene. 271, 81–86.
McKim K.S., Hayashi-Hagihara A. 1998. mei-W68 in Drosophila melanogaster encodes a Spo11 homolog: Evidence that the mechanism for initiating meiotic recombination is conserved. Genes Dev. 12, 2932–2942.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.A. Komakhin, V.V. Komakhina, 2008, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2008, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 494–500.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komakhin, R.A., Komakhina, V.V. Compartmentalization of Spo11p in vegetative cells of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Mol Biol 42, 436–441 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893308030126
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893308030126