Abstract
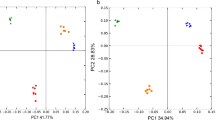
Medicinal plants are the basic materials of traditional Chinese medicine. Soil characteristics and microbial contribution play important roles in the growth and product quality of medicinal plants, but the link between them in the rhizosphere of medicinal plants has been overlooked. Accordingly, Mentha haplocalyx, Perilla frutescens, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and Astragalus membranaceus, four plants used in traditional Chinese medicines, were investigated in this study in order to elucidate bacterial and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal (AMF) diversity in the rhizosphere and its possible association with soil quality. DGGE-based 16S rRNA and 18S rRNA gene sequencing results indicated that the diversity of both bacteria and AMF in Glycyrrhiza uralensis and Astragalus membranaceus was significantly higher than those in Mentha haplocalyx and Perilla frutescens, suggesting that medicinal plants have different preferences even under the same conditions. In addition, enzymatic activities and nutrition were enhanced in the rhizospheric soil of Mentha haplocalyx and Perilla frutescens, and the correlation among AMF diversity, soil enzymatic activities and nutrition was confirmed using RDA analysis. These results suggest the potential to grow medicinal plants with a reasonable rotation or intercrop in order to maintain long-term continuous soil development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alef, K. and Nannipieri, P. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry, Academic, 1995.
Alvarez, M., Huygens, D., Olivares, E., Saavedra, I., Alberdi, M., and Valenzuela, E., Ectomycorrhizal fungi enhance nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition of Nothofagus dombeyi under drought conditions by regulating assimilative enzyme activities, Physiol. Plantarum, 2009, vol. 136, pp. 426–436.
Antoun, H., Beauchamp, C.J., Goussard, N., Chabot, R., and Lalande, R., Potential of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium species as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on non-legumes: effect on radishes (Raphanus sativus L.), Plant Soil, 1998, vol. 204, pp. 57–67.
Benítez, E., Melgar, R., Sainz, H., Gómez, M., and Nogales, R., Enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) grown with olive cake mulches, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2000, vol. 32, pp. 1829–1835.
Bernal, G., Illanes, A., and Ciampi, L., Isolation and partial purification of a metabolite from a mutant strain of Bacillus sp. with antibiotic activity against plant pathogenic agents, Electron. J. Biotechn., 2002, vol. 5, pp. 7–8.
Borcard, D., Legendre, P., and Drapeau, P., Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation, Ecology, 1992, vol. 73, pp. 1045–1055.
Bowles, T.M., Acosta-Martínez, V., Calderón, F., and Jackson, L.E., Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2014, vol. 68, pp. 252–262.
Breidenbach, B., Pump, J., and Dumont, M.G., Microbial community structure in the rhizosphere of rice plants, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 6.
Breuil, C. and Saddler, J.N., Comparison of the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid and Nelson-Somogyi methods of assaying for reducing sugars and determining cellulase activity, Enzyme Microb. Tech., 1985, vol. 7, pp. 327–332.
Burke, C., Steinberg, P., Rusch, D., Kjelleberg, S., and Thomas, T., Bacterial community assembly based on functional genes rather than species, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2011, vol. 108, pp. 14288–14293.
Cassman, N.A., Leite, M.F.A., Pan, Y., Hollander, M.D., Veen, J.A.V., and Kuramae, E.E., Plant and soil fungal but not soil bacterial communities are linked in long-term fertilized grassland, Sci. Rep-UK, 2016, vol. 6.
Chang, Z., The discovery of Qinghaosu (artemisinin) as an effective anti-malaria drug: a unique China story, Science China, Life Sci., 2016, vol. 59, pp. 81–88.
Diedhiou, P.M., Hallmann, J., Oerke, E.C., and Dehne, H.W., Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and a non-pathogenic Fusarium oxysporum on Meloidogyne incognita infestation of tomato, Mycorrhiza, 2003, vol. 13, pp. 199–204.
Evelin, H., Kapoor, R., and Giri, B., Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in alleviation of salt stress: a review, Ann. Bot.-London, 2009, vol. 104, pp. 1263–1280.
Fierer, N., and Jackson, R.B., The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, vol. 103, pp. 626–631.
Gao, J., Wang, Y., Guan, Y.M., and Chen, C.Q., Fusarium cerealis, a new pathogen causing ginseng (Panax ginseng) root rot in China, Plant Dis., 2014, vol. 98, pp. 1433–1433.
Govindarajulu, M., Pfeffer, P.E., Jin, H., Abubaker, J., Douds, D.D., Allen, J.W., Bucking, H., Lammers, P.J., and Shachar-Hill, Y., Nitrogen transfer in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis, Nature, 2005, vol. 435, pp. 819–823.
Jian, S., Li, J., Chen, J., Wang, G., Mayes, M.A., Dzantor, K.E., Hui, D., and Luo, Y., Soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil carbon and nitrogen storage under nitrogen fertilization: a meta-analysis, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2016, vol. 101, pp. 32–43.
Kandeler, E. and Gerber, H., Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium, Biol. Fert. Soils, 1988, vol. 6, pp. 68–72.
Kang, R., Helms, R., Stout, M.J., Jaber, H., Chen, Z., and Nakatsu, T., Antimicrobial activity of the volatile constituents of Perilla frutescens and its synergistic effects with polygodial, J. Agr. Food Chem., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 2328–2330.
Kim, H. and Kang, H., The impacts of excessive nitrogen additions on enzyme activities and nutrient leaching in two contrasting forest soils, J. Microbiol. (Seoul, Korea), 2011, vol. 49, pp. 369–375.
Kong, L.Y. and Tan, R.X., Artemisinin, a miracle of traditional Chinese medicine, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2015, vol. 32, pp. 1617–1621.
Li, Y., Liu, Z., Hou, H., Lei, H., Zhu, X., Li, X., He, X., and Tian, C., Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-enhanced resistance against Phytophthora sojae infection on soybean leaves is mediated by a network involving hydrogen peroxide, jasmonic acid, and the metabolism of carbon and nitrogen, Acta Physiol. Plant., 2013, vol. 35, pp. 3465–3475.
Liu, Z., Li, Y., Ma, L., Wei, H., Zhang, J., He, X., and Tian, C., Coordinated regulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soybean MAPK pathway genes improved mycorrhizal soybean drought tolerance, Mol. Plant Microbe In., 2015, vol. 48, pp. 408–419.
Liu, Z., Ma, L., He, X., and Tian, C., Water strategy of mycorrhizal rice at low temperature through the regulation of PIP aquaporins with the involvement of trehalose, Appl. Soil Ecol., 2014b, vol. 84, pp. 185–191.
Luo, H.F., Qi, H.Y., and Zhang, H.X., Assessment of the bacterial diversity in fenvalerate-treated soil, World J. Microb. Biot., 2004, vol. 20, pp. 509–515.
McArdle, B.H. and Anderson, M.J., Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance-based redundancy analysis, Ecology, 2001, vol. 82, pp. 290–297.
McGowan, S., Leavitt, P.R., Hall, R.I., Anderson, N.J., Jeppesen, E., and Odgaard, B.V., Controls of algal abundance and community composition during ecosystem state change, Ecology, 2005, vol. 86, pp. 2200–2211.
Meng L.J., Geng Z.C., Wang H.T., Yin J.Y., and Ji P.F., Soil chemical properties and enzyme activities of three traditional Chinese herbal drugs in the rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere on the east section of Qilian mountain, J. Northwest For. U., 2013, vol. 28, pp. 26–32. (in Chinese)
Moonseong, H., and Ruben Gabriel, K., A permutation test of association between configurations by means of the rv coefficient, Communications in Statistics—Simulation and Computation, 1998, vol. 27, pp. 843–856.
Normile, D., Asian medicine. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine, Science, 2003, vol. 299, pp. 188–190.
Nuccio, E.E., Hodge, A., Pett-Ridge, J., Herman, D.J., Weber, P.K., and Firestone, M.K., An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus significantly modifies the soil bacterial community and nitrogen cycling during litter decomposition, Environ. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 15, pp. 1870–1881.
Oksanen, J., Kindt, R., and O’Hara, B., Vegan: R functions for vegetation ecologists, 2005, vol. 12, p. 2014.
Phillips, R.P., Brzostek, E., and Midgley, M.G., The mycorrhizal-associated nutrient economy: a new framework for predicting carbon-nutrient couplings in temperate forests, New Phytol., 2013, vol. 199, pp. 41–51.
Pukall, R., Buntefuss, D., Frühling, A., Rohde, M., Kroppenstedt, R.M., Burghardt, J., Lebaron, P., Bernard, L., and Stackebrandt, E., Sulfitobacter mediterraneus sp. nov., a new sulfite-oxidizing member of the alpha-Proteobacteria, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1999, vol. 49, pp. 513–519.
Punja, Z.K., Wan, A., Rahman, M., Goswami, R.S., Barasubiye, T., Seifert, K.A., and Lévesque, C.A., Growth, population dynamics, and diversity of Fusarium equiseti in ginseng fields, Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2008, vol. 121, pp. 173–184.
Qian, X., Gu, J., Pan, H.-J., Zhang, K.-Y., Sun, W., Wang, X.-J., and Gao, H., Effects of living mulches on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and bacterial community diversities of apple orchard soils, Eur. J. Soil Biol., 2015, vol. 70, pp. 23–30.
Qiao, X., Bei, S., Li, C., Dong, Y., Li, H., Christie, P., Zhang, F., and Zhang, J., Enhancement of faba bean competitive ability by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is highly correlated with dynamic nutrient acquisition by competing wheat, Sci. Rep-UK, 2015, vol. 5.
Qin, S., Chen, H.H., Zhao, G.Z., Li, J., Zhu, W.Y., Xu, L.H., Jiang, J.H., and Li, W.J., Abundant and diverse endophytic actinobacteria associated with medicinal plant Maytenus austroyunnanensis in Xishuangbanna tropical rainforest revealed by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods, Env. Microbiol. Rep., 2012, vol. 4, pp. 522–531.
Redecker, D., and Raab, P., Phylogeny of the glomeromycota (arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi): recent developments and new gene markers, Mycologia, 2006, vol. 98, pp. 885–895.
Ren, C., Kang, D., Wu, J.P., Zhao, F., Yang, G., Han, X., Feng, Y., and Ren, G., Temporal variation in soil enzyme activities after afforestation in the Loess Plateau, China, Geoderma, 2016, vol. 282, pp. 103–111.
Rosenberg, E. and Zilber-Rosenberg, I., Role of microorganisms in adaptation, development, and evolution of animals and plants: the hologenome concept, in The Prokaryotes: Prokaryotic Biology and Symbiotic Associations, Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., and Thompson, F., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2013.
Söderberg, K.H., Olsson, P.A., and Bååth, E., Structure and activity of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of different plant species and the effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2002, vol. 40, pp. 223–231.
Schinner, F., Öhlinger, R., Kandeler, E., and Margesin, R., Methods in Soil Biology, Berlin: Springer, 1996.
Schlatter, D.C., Bakker, M.G., Bradeen, J.M., and Kinkel, L.L., Plant community richness and microbial interactions structure bacterial communities in soil, Ecology, 2015, vol. 96, pp. 134–142.
Sun, S., Li, H., Zhou, W., Liu, A., and Zhu, H., Bacterial quorum sensing inhibition activity of the traditional Chinese herbs, Ficus carica L. and Perilla frutescens, Chemotherapy, 2015, vol. 60, pp. 379–383.
Tabatabai, M.A. and Bremner, J.M., Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity, Soil Biol. Biochem., 1969, vol. 1, pp. 301–307.
Tian, L., Zhou, X., Ma, L., Xu, S., Nasir, F., and Tian, C., Root-associated bacterial diversities of Oryza rufipogon and Oryza sativa and their influencing environmental factors, Arch. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 199, pp. 563–571.
Verbruggen, E., Veresoglou, S.D., Anderson, I.C., Caruso, T., Hammer, E.C., Kohler, J., and Rillig, M.C., Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi–short-term liability but longterm benefits for soil carbon storage?, New Phytol., 2013, vol. 197, pp. 366–368.
Wang, G., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Liang, B., Chen, K., Li, S., and Jiang, J., Co-metabolism of DDT by the newly isolated bacterium, Pseudoxanthomonas sp. wax, Braz. J. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 41, pp. 431–438.
Wang, L., Zheng, C.D., Li, X.J., Gao, J.M., Zhang, X.C., and Wei, G.H., Cyclo(PRO-TYR) from an endophytic rhizobium isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Chem. Nat. Compd+, 2012, vol. 47, pp. 1040–1042.
Wang, W., Wu, N., Fu, Y., and Zu, Y., Antimicrobial activities of Mentha haplocalyx Briq. essential oil, Bull. Bot. Res., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 626–629.
Weiss, J.V., Emerson, D., and Megonigal, J.P., Geochemical control of microbial Fe(III) reduction potential in wetlands: comparison of the rhizosphere to non-rhizosphere soil, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2004, vol. 48, pp. 89–100.
Zhang, G.Z. and Zhang, H.W., First report of root rot of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) caused by Ditylenchus destructor in China, Plant Dis., 2007, vol. 91, pp. 459–459.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, S., Tian, L., Ma, L. et al. Community Structure of Rhizomicrobiomes in Four Medicinal Herbs and Its Implication on Growth Management. Microbiology 87, 425–436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261718030098
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261718030098