Abstract
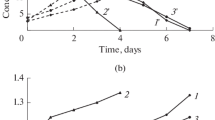
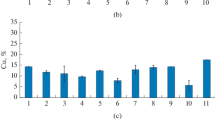
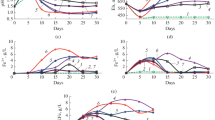
The effect of high ferric sulfate concentrations on the organisms predominating in biohydrometallurgical processes (bacteria of genus Sulfobaсillus and archaea of the genus Acidiplasma) was studied. Ability of the studied strains to grow and oxidize ferrous iron in the media with 125 to 500 mM ferric sulfate was determined. High concentrations of ferric sulfate significantly inhibited the oxidative activity and growth of the studied microorganisms. Bacteria of the genus Sulfobaсillus were found to be incapable of active iron oxidation in the presence of ferric iron sulfate at concentrations exceeding 250 mM. Archaea of the genus Acidiplasma oxidized ferrous iron completely in the presence of 500 mM Fe3+. Microbial growth was suppressed by relatively low ferric sulfate concentrations. Almost no growth occurred at ferric sulfate concentrations exceeding 199 mM, while lysis of the cells of all studied strains was observed at higher Fe3+ concentrations. Archaea (genus Acidiplasma, family Ferroplasmaceae) were shown to be more tolerant to high ferric sulfate concentrations than bacteria of the genus Sulfobaсillus. The results obtained may be used for improvement of biohydrometallurgical technologies and are also important for the understanding of the patterns of formation of microbial communities carrying out the technological processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond, P.L., Druschel, G.K., and Banfield, J.F., Comparison of acid mine drainage microbial communities in physically and geochemically distinct ecosystems, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, pp. 4962–4971.
Braun, V. and Hantke, K., Acquisition of iron by bacteria, in Molecular Microbiology of Heavy Metals, Nies, D.H. and Silver, S., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2007, pp. 189–219.
Bryan, C.G., Watkin, E.L., McCredden, T.J., Wong, Z.R., Harrison, S.T.L., and Kaksonen, A.H., The use of pyrite as a source of lixiviant in the bioleaching of electronic waste, Hydrometallurgy, 2015, vol. 152, pp. 33–43.
Bulaev, A.G., Ferrous iron oxidation in packed-bed reactors at elevated temperatures, Adv. Mater. Res., 2015, vol. 1130, pp. 226–229.
Bulaev, A.G., Muravyov, M.I., Pivovarova, T.A., Fomchenko, N.V., and Kondrat’eva, T.F., The treatment of mining and metallurgical wastes containing nonferrous and precious metals, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 825, pp. 301–304.
Cardenas, J.P., Moya, F., Covarrubias, P., Shmaryahu, A., Levicán, G., Holmes, D.S., and Quatrini, R., Comparative genomics of the oxidative stress response in bioleaching microorganisms, Hydrometallurgy, 2012, vol. 127–128, pp. 162–167.
Clark, D.A. and Norris, P.R., Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov.: mixed-culture ferrous iron oxidation with Sulfobacillus species, Microbiology (UK), 1996, vol. 142, pp. 785–790.
Dopson, M. and Holmes, D.S., Metal resistance in acidophilic microorganisms and its significance for biotechnologies, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 98. pp. 8133–8144.
Dopson, M., Baker-Austin, C., Koppineedi, P.R., and Bond, P.L., Growth in sulfidic mineral environments: metal resistance mechanisms in acidophilic microorganisms, Microbiology (UK), 2003, vol. 149, pp. 1959–1970.
Golyshina, O.V. and Timmis, K.N., Ferroplasma and relatives, recently discovered cell wall-lacking archaea making a living in extremely acid, heavy metal-rich environments, Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 1277–1288.
Guezennec, A.-G., Bru, K., Jacob, J., and d’Hugues P., Co-processing of sulfidic mining wastes and metal-rich post-consumer wastes by biohydrometallurgy, Minerals Eng., 2015, vol. 75, pp. 45–53.
Hawkes, R.B., Franzmann, P.D., O’Hara, G., and Plumb, J.J., Ferroplasma cupricumulans sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, acidophilic archaea isolated from an industrial-scale chalcocite bioleach heap, Extremophiles, 2006, vol. 10, pp. 525–530.
Kondrat’eva, T.F., Bulaev, A.G., and Muravyov, M.I., Mikroorganizmy v biogeotekhnologiyakh pererabotki sulfidnykh rud (Microorganisms in Biotechnologies of Sulfide Ores Processing), Moscow: Nauka, 2015.
Li, Q., Tian, Y., Fu, X., Yin, H., Zhou, Z., Liang, Y., Qiu, G., Liu, J., Liu, H., Liang, Y., Shen, L., Cong, J., and Liu, X., The community dynamics of major bioleaching microorganisms during chalcopyrite leaching under the effect of organics, Curr. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 63, pp. 164–172.
Melamud, V.S. and Pivovarova, T.A., Specific features of the growth of the type strain of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans in medium 9K, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 1998, vol. 34, pp. 314–315.
Muravyov, M.I. and Bulaev, A.G., Two-step oxidation of a refractory gold-bearing sulfidic concentrate and the effect of organic nutrients on its biooxidation, Minerals Eng., 2013, vol. 45, pp. 108–114.
Muravyov, M.I., Bulaev, A.G., and Kondrat’eva, T.F., Complex treatment of mining and metallurgical wastes for recovery of base metals, Minerals Eng., 2014, vol. 64, pp. 63–66.
Rawlings, D.E., Tributsch, H., and Hansford, G., Reasons why “Leptospirillum”-like species rather than Thiobacillus ferrooxidans are the dominant iron-oxidizing bacteria in many commercial processes for the biooxidation of pyrite and related ores, Microbiology (UK), 1999, vol. 145, pp. 5–13.
Rea, S.M., McSweeney, N.J., Degens, B.P., Morrisa, C., Siebert, H.M., and Kaksonen, A.H., Salt-tolerant microorganisms potentially useful for bioleaching operations where fresh water is scarce, Minerals Eng., 2015, vol. 75, pp. 126–132.
Reznikov, A.A., Mulikovskaya, E.P., and Sokolov I.Yu., Metody analiza prirodnykh vod (Methods for Analysis of Natural Waters), Moscow: Nedra, 1970.
Romero, R., Mazuelos, A., Palencia, I., and Carranza, F., Copper recovery from chalcopyrite concentrates by BRISA process, Hydrometallurgy, 2003, vol. 70, pp. 205–215.
Sand, W., Gehrke, T., Jozsa, P.-G., and Schippers, A. (Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching—direct vs. indirect bioleaching, Hydrometallurgy, 2001, vol. 59, pp. 159–175.
Schippers, A., Microorganisms involved in bioleaching and nucleic acid-based molecular methods for their identification and quantification, in Microbial Processing of Metal Sulfides, Donati, E.R. and Sand, W., Eds., New York: Springer, 2007, pp. 3–33.
Suzuki, I., Lee, D., Mackay, B., Harahuc, L., and Oh, J.K., Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 65, pp. 5163–5168.
van Hille, R.P., van Wyk, N., Froneman, T., and Harrison, S.T.L., Dynamic evolution of the microbial community in BIOX leaching tanks, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 825, pp. 331–334.
Watling, H.R., Watkin, E.J.L., and Ralph, D.E., The resilience and versatility of acidophiles that contribute to the bio-assisted extraction of metals from mineral sulfides, Environ. Technol., 2010, vol. 31, nos. 8–9, pp. 915–933.
Zhou, H., Zhang, R., Hu, P., Zeng, W., Xie, Y., Wu, C., and Qiu, G., Isolation and characterization of Ferroplasma thermophilum sp. nov., a novel extremely acidophilic, moderately thermophilic archaeon and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 105, pp. 591–601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.G. Bulaev, 2017, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2017, Vol. 86, No. 4, pp. 455–462.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulaev, A.G. Effect of ferric sulfate on activity of moderately thermophilic acidophilic iron-oxidizing microorganisms. Microbiology 86, 469–475 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002626171704004X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002626171704004X