Abstract
Adaptive strategies of bacilli involving genetic regulatory mechanisms are reviewed. The role of master regulators and signal transduction systems that coordinate the interaction of the extracellular signals and the genetic programs responsible for the metabolic state of bacteria are discussed. Most of the known regulatory pathways are directly or indirectly regulated by the DegU, Spo0A, AbrB, and CodY global regulators. The main factor affecting the development of cell phenotype is the concentration of the regulatory protein and its ability to bind with varying affinity to promoters of the genes and operons. The effect of the regulatory systems on the bistability of microbial populations is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maamar, H., Raj, A., and Dubnau, D., Noise in gene expression determines cell fate in Bacillus subtilis, Science, 2007, vol. 317, no. 5837, pp. 526–529.
Colledge, V.L., Fogg, M.J., Levdikov, V.M., Leech, A., Dodson, E.J., and Wilkinson, A.J., Structure and organisation of SinR, the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis, J. Mol. Biol., 2011, vol. 411, no. 3, pp. 597–613.
Verhamme, D.T., Kiley, T.B., and Stanley-Wall, N.R., DegU co-ordinates multicellular behaviour exhibited by Bacillus subtilis, Mol. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 554–568.
Fujita, M., Gonzalez-Pastor, J.E., and Losick, R., High- and low-threshold genes in the Spo0a regulon of Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2005, vol. 187, no. 4, pp. 1357–1368.
Heermann, R. and Jung, K., Stimulus perception and signaling in histidine kinases, in Bacterial Signaling, Krämer, R. and Jung, K, Eds., Wiley-VCH, 2009, pp. 135–161.
Utsumi, R. and Igarashi, M., Two-component signal transduction as attractive drug targets in pathogenic bacteria, Yakugaku Zasshi, 2012, vol. 132, no. 1, pp. 51–58.
Stock, A.M., Robinson, V.L., and Goudreau, P.N., Two-component signal transduction, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2000, vol. 69, pp. 183–215.
Shi, X., Wegener-Feldbrügge, S., Huntley, S., Hamann, N., Hedderich, R., and Søgaard-Andersen, L., Bioinformatics and experimental analysis of proteins of two-component systems in Myxococcus xanthus, J. Bacteriol., 2008, vol. 190, no. 1, p. 613–624.
Thevenard, B., Rasoava, N., Fourcassié, P., Monnet, V., Boyaval, P., and Rul, F., Characterization of Streptococcus thermophilus two-component systems: in silico analysis, functional analysis and expression of response regulator genes in pure or mixed culture with its yogurt partner, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2011, vol. 151, no. 2, pp. 171–181.
Gueriri, I., Cyncynatus, C., Dubrac, S., Arana, A.T., Dussurget, O., and Msadek, T., The DegU orphan response regulator of Listeria monocytogenes autorepresses its own synthesis and is required for bacterial motility, virulence and biofilm formation, Microbiology (UK), 2008, vol. 154, no. 8, pp. 2251–2264.
Jung, K., Fried, L., Behr, S., and Heermann, R., Histidine kinases and response regulators in networks, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 118–124.
Mäder, U., Antelmann, H., Buder, T., Dahl, M.K., Hecker, M., and Homuth, G., Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: genome-wide analysis of the DegS-DegU regulon by transcriptomics and proteomics, Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2002, vol. 268, no. 4, pp. 455–467.
Henner, D.J., Yang, M., and Ferrari, E., Localization of Bacillus subtilis sacU(Hy) mutations to two linked genes with similarities to the conserved procaryotic family of two-component signalling systems, J. Bacteriol., 1988, vol. 170, no. 11, pp. 5102–5109.
Borgmeier, C., Biedendieck, R., Hoffmann, K., Jahn, D., and Meinhardt, F., Transcriptome profiling of degU expression reveals unexpected regulatory patterns in Bacillus megaterium and discloses new targets for optimizing expression, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 92, no. 3, pp. 583–596.
Wray, L.V., Jr., Zalieckas, J.M., and Fisher, S.H., Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase controls gene expression through a protein-protein interaction with transcription factor TnrA, Cell, 2001, vol. 107, no. 4, p. 427.
Kayumov, A., Heinrich, A., Sharipova, M., Iljinskaya, O., and Forchhammer, K., Inactivation of the general transcription factor TnrA in Bacillus subtilis by proteolysis, Microbiology (UK), 2008, vol. 154, no. 8, pp. 2348–2355.
Abe, S., Yasumura, A., and Tanaka, T., Regulation of Bacillus subtilis aprE expression by glnA through inhibition of scoC and sigma(D)-dependent degR expression, J. Bacteriol., 2009, vol. 191, no. 9, pp. 3050–3058.
Tjalsma, H., Koetje, E.J., Kiewiet, R., Kuipers, O.P., Kolkman, M., van der Laan, J., Daskin, R., Ferrari, E., and Bron, S., Engineering of quorum-sensing systems for improved production of alkaline protease by Bacillus subtilis, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 96, no. 3, pp. 569–578.
Kobayashi, K., Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis, Mol. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 395–409.
Ogura, M. and Tsukahara, K., Autoregulation of the Bacillus subtilis response regulator gene degU is coupled with the proteolysis of DegU-P by ClpCP, Mol. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 75, no. 5, pp. 1244–1259.
Gueriri, I., Bay, S., Dubrac, S., Cyncynatus, C., and Msadek, T., The Pta-AckA pathway controlling acetyl phosphate levels and the phosphorylation state of the DegU orphan response regulator both play a role in regulating Listeria monocytogenes motility and chemotaxis, Mol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 1342–1357.
Tsukahara, K. and Ogura, M., Promoter selectivity of the Bacillus subtilis response regulator DegU, a positive regulator of the fla/che operon and sacB, BMC Microbiol., 2008, vol. 15, no. 8, p. 8.
Tsukahara, K. and Ogura, M., Characterization of DegU-dependent expression of bpr in Bacillus subtilis, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2008, vol. 280, no. 1, pp. 8–13.
Shimane, K. and Ogura, M., Mutational analysis of the helix-turn-helix region of Bacillus subtilis response regulator DegU, and identification of cis-acting sequences for DegU in the aprE and comK promoters, J. Biochem., 2004, vol. 136, no. 3, pp. 387–397.
West, J.T., Estacio, W., and Márquez-Magan~a, L. Relative roles of the fla/che P(A), P(D-3), and P(sigD) promoters in regulating motility and sigD Expression in Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2000, vol. 182, no. 17, pp. 4841–4848.
Cozy, L.M., Phillips, A.M., Calvo, R.A., Bate, A.R., Hsueh, Y.H., Bonneau, R., Eichenberger, P., and Kearns, D.B., SlrA/SinR/SlrR inhibits motility gene expression upstream of a hypersensitive and hysteretic switch at the level of σ(D) in Bacillus subtilis, Mol. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 83, no. 6, pp. 1210–1228.
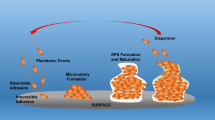
Chai, Y., Chu, F., Kolter, R., and Losick, R., Bistability and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis, Mol. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 254–263.
Diethmaier, C., Pietack, N., Gunka, K., Wrede, C., Lehnik-Habrink, M., Herzberg, C., Hübner, S., and Stülke, J., A novel factor controlling bistability in Bacillus subtilis: the YmdB protein affects flagellin expression and biofilm formation, J. Bacteriol., 2011, vol. 193, no. 21, pp. 5997–6007.
Msadek, T., When the going gets tough: survival strategies and environmental signaling networks in Bacillus subtilis, Trends Microbiol., 1999, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 201–207.
Kayumov, A.R., Balaban, N.P., Mardanova, A.M., Sharipova, M.R., and Kostrov, S.V., Biosynthesis of the subtilisin-like serine proteinase of Bacillus intermedius under salt stress conditions, Microbiology, 2006, vol. 75, no. 5, pp. 557–562.
Shagimardanova, E.I., Chastukhina, I.B., Shamsutdinov, T.R., Balaban, N.P., Mardanova, A.M., Sharipova, M.R., and Kostrov, S.V., Heterologous expression of Bacillus intermedius gene of glutamyl endopeptidase in Bacillus subtilis strains defective in regulatory proteins, Microbiology, 2007, vol. 76, no. 5, pp. 569–574.
Kodgire, P., Dixit, M., and Rao, K.K., ScoC and SinR negatively regulate epr by corepression in Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2006, vol. 188, no. 17, pp. 6425–6428.
Westers, H., Westers, L., Darmon, E., van Dijl, J.M., Quax, W.J., and Zanen, G., The CssRS two-component regulatory system controls a general secretion stress response in Bacillus subtilis, FEBS J., 2006, vol. 273, no. 16, pp. 3816–3827.
Antelmann, H., Darmon, E., Noone, D., Veening, J.W., Westers, H., Bron, S., Kuipers, O.P., Devine, K.M., Hecker, M., and van Dijl, J.M., The extracellular proteome of Bacillus subtilis under secretion stress conditions, Mol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 143–156.
Noone, D., Howell, A., Collery, R., and Devine, K.M., YkdA and YvtA, HtrA-like serine proteases in Bacillus subtilis, engage in negative autoregulation and reciprocal cross-regulation of ykdA and yvtA gene expression, J. Bacteriol., 2001, vol. 183, no. 2, pp. 654–663.
Fujita, M. and Losick, R., Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A, Genes Dev., 2005, vol. 19, no. 18, pp. 2236–2244.
Eswaramoorthy, P., Dinh, J., Duan, D., Igoshin, O.A., and Fujita, M., Single-cell measurement of the levels and distributions of the phosphorelay components in a population of sporulating Bacillus subtilis cells, Microbiology (UK), 2010, vol. 156, no.8, pp. 2294–2304.
Lopez, D., Fischbach, M.A., Chu, F., Losick, R., and Kolter, R., Structurally diverse natural products that cause potassium leakage trigger multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, vol. 106, no. 1, pp. 280–285.
Reder, A., Gerth, U., and Hecker, M., Integration of σB activity into the decision-making process of sporulation initiation in Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2012, vol. 194, no. 5, pp. 1065–1074.
Fujita, M. and Losick, R., The master regulator for entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis becomes a cell-specific transcription factor after asymmetric division, Genes Dev., 2003, vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 1166–1174.
Guberman, J.M., Fay, A., Dworkin, J., Wingreen, N.S., and Gitai, Z., PSICIC: noise and asymmetry in bacterial division revealed by computational image analysis at sub-pixel resolution, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2008, vol. 4, no. 11, p. e1000233.
de Hoon, M.J., Eichenberger, P., and Vitkup, D., Hierarchical evolution of the bacterial sporulation network, Curr. Biol., 2010, vol. 20, no. 17, pp. R735–R745.
Molle, V., Fujita, M., Jensen, S.T., Eichenberger, P., González-Pastor, J.E., Liu, J.S., and Losick, R., The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis, Mol. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 1683–1701.
Chastanet, A. and Losick, R., Just-in-time control of Spo0A synthesis in Bacillus subtilis by multiple regulatory mechanisms, J. Bacteriol., 2011, vol. 193, no. 22, pp. 6366–6374.
Muchová, K., Lewis, R.J., Perecko, D., Brannigan, J.A., Ladds, J.C., Leech, A., Wilkinson, A.J., and Barák, I., Dimer-induced signal propagation in Spo0A, Mol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 829–842.
Banse, A.V., Chastanet, A., Rahn-Lee, L., Hobbs, E.C., and Losick, R., Parallel pathways of repression and antirepression governing the transition to stationary phase in Bacillus subtilis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, vol. 105, no. 40, pp. 15547–15552.
Bobay, B.G., Andreeva, A., Mueller, G.A., Cavanagh, J., and Murzin, A.G., Revised structure of the AbrB N-terminal domain unifies a diverse superfamily of putative DNA-binding proteins, FEBS Lett., 2005, vol. 579, no. 25, pp. 5669–5674.
Lieman-Hurwitz, J., Haimovich, M., Shalev-Malul, G., Ishii, A., Hihara, Y., Gaathon, A., Lebendiker, M., and Kaplan, A., A cyanobacterial AbrB-like protein affects the apparent photosynthetic affinity for CO2 by modulating low-CO2-induced gene expression, Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 927–936.
Chumsakul, O., Takahashi, H., Oshima, T., Hishimoto, T., Kanaya, S., Ogasawara, N., and Ishikawa, S., Genome-wide binding profiles of the Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB and its homolog Abh reveals their interactive role in transcriptional regulation, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 414–428.
Shivers, R.P. and Sonenshein, A.L., Activation of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY by direct interaction with branched-chain amino acids, Mol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 599–611.
Handke, L.D., Shivers, R.P., and Sonenshein, A.L., Interaction of Bacillus subtilis CodY with GTP, J. Bacteriol., 2008, vol. 190, no. 3, pp. 798–806.
Wolz, C., Geiger, T., and Goerke, C., The synthesis and function of the alarmone (p)ppGpp in firmicutes, Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 300, nos. 2–3, pp. 142–147.
Belitsky, B.R. and Sonenshein, A.L., Contributions of multiple binding sites and effector-independent binding to CodY-mediated regulation in Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2011, vol. 193, no. 2, pp. 473–484.
Mirouze, N., Desai, Y., Raj, A., and Dubnau, D., Spo0A∼P imposes a temporal gate for the bimodal expression of competence in Bacillus subtilis, PLoS Genet., 2012, vol. 8, no. 3, p. e1002586.
Smits, W.K. and Grossman, A.D., The transcriptional regulator Rok binds A+T rich DNA and is involved in repression of a mobile genetic element in Bacillus subtilis, PLoS Genet., 2010, vol. 6, p. e1001207.
González-Pastor, J.E., Hobbs, E.C., and Losick, R., Cannibalism by sporulating bacteria, Science, 2003, vol. 301, no. 5632, pp. 510–513.
Suntharalingam, P., Senadheera, M.D., Mair, R.W., Lévesque, C.M., and Cvitkovitch, D.G., The LiaFSR system regulates the cell envelope stress response in Streptococcus mutans, J. Bacteriol., 2009, vol. 191, no. 9, pp. 2973–2984.
Jordan, S., Rietkötter, E., Strauch, M.A., Kalamorz, F., Butcher, B.G., Helmann, J.D., and Mascher, T., LiaRS-dependent gene expression is embedded in transition state regulation in Bacillus subtilis, Microbiology (UK), 2007, vol. 153, no. 8, pp. 2530–2540.
Wolf, D., Kalamorz, F., Wecke, T., Juszczak, A., Mäder, U., Homuth, G., Jordan, S., Kirstein, J., Hoppert, M., Voigt, B., Hecker, M., and Mascher, T., Indepth profiling of the LiaR Response of Bacillus subtilis, J. Bacteriol., 2010, vol. 192, no. 18, pp. 4680–4693.
Levine, J.H., Fontes, M.E., Dworkin, J., and Elowitz, M.B., Pulsed feedback defers cellular differentiation, PLoS Biol., 2012, vol. 10, no. 1. e1001252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Toymentseva, M.R. Sharipova, 2013, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2013, Vol. 82, No. 3, pp. 259–273.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toymentseva, A.A., Sharipova, M.R. Genetic mechanisms of bacilli adaptation. Microbiology 82, 257–270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261713030119
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261713030119