-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
José Antonio Horcajadas, Anne Riesewijk, Jan Polman, Roselinde van Os, Antonio Pellicer, Sietse Mosselman, Carlos Simón, Effect of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in IVF on endometrial gene expression profiles, Molecular Human Reproduction, Volume 11, Issue 3, March 2005, Pages 195–205, https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gah150
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) used in IVF produces lower implantation rates per embryo transferred compared to natural cycles utilized in ovum donation, suggesting a suboptimal endometrial development. Endometrial receptivity has recently been investigated in natural menstrual cycles with the aid of microarray technology. The aim of this study is to investigate the impact of COH using urinary gonadotrophins with a long protocol with GnRH agonists without progesterone supplementation (similar to the natural cycle) on endometrial gene expression profiles during the window of implantation by comparing the profiles at day hCG+7 of COH versus LH+7 of a previous natural cycle in the same women. For this purpose we have used microarray technology by Affymetrix (GeneChip HG_U133A), which allows more than 22 000 genes to be tested simultaneously. Results were validated by semi-quantitative PCR and quantitative PCR experiments. We found that more than 200 genes showed a differential expression of more than 3-fold when COH and normal cycles were compared at hCG+7 versus LH+7. We simultaneously re-analysed the LH+2 versus LH+7 endometrial gene expression profiles in previous natural cycles in the same subject using this specific GeneChip, the results obtained were consistent with our own published results. This is the first time that gene expression profiles of the endometrium during COH are reported. The large degree of gene expression disturbance is surprising and highlights the need for further efforts to optimize COH protocols.
Introduction
Assisted reproduction technologies have provided considerable insight into the human reproductive processes. However, lower implantation rates per transferred embryo than those in natural cycles remain a major problem that is compensated for by increasing the number of transferred embryos (American Society for Reproductive Medicine, 2002) at the cost of increased numbers of twin and triplet pregnancies.
Clinical studies suggest that in patients that display high response to gonadotrophins, supraphysiological levels of estradiol (E2) on the day of hCG administration, are deleterious to embryonic implantation (Simón et al., 1995, 1998, 2003; Pellicer et al., 1996). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that while low doses of E2 maintain the uterus in a receptive state, high doses cause it to become refractory in mice (Ma et al., 2003). Uterine receptivity is diminished during controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) used for IVF compared to natural cycles (Paulson et al., 2000). The endometrium suffers a morphological advancement in the early luteal phase, which is demonstrated by histological techniques (Seif et al., 1992; Psychoyos, 1994; Kolb and Paulson, 1997; Kolibianakis et al., 2003), scanning electron microscopy (Nikas et al., 1999; Giudice, 2003), down-regulation of endometrial estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor (Develioglu et al., 1999) and biochemical changes in the endometrial fluid (Simón et al., 1996). This is not surprising considering that the aim of ovulation induction is to recruit a sufficient number of oocytes, and as a side-effect supraphysiological levels of steroid hormones and paracrine mediators are produced and received by the endometrium.
Following completion of the Human Genome sequence, the principal goal in this field of work has been to enumerate genes involved in the physiological and pathological processes. Genomic analysis of human endometrial receptivity have recently been employed and genome-wide analysis with DNA microarray technology demonstrates that receptivity is an active process involving hundreds of up- and down-regulated genes (Carson et al., 2002; Kao et al., 2002; Borthwick et al., 2003; Riesewijk et al., 2003). One important step forward would be a more operational understanding of the molecular impact of therapeutic interventions in the development of endometrial receptivity. In the present study, we have investigated the genomic impact of COH on the human endometrium during IVF treatment. Our institution's oocyte donation programme allows us the opportunity of obtaining endometrial biopsies in patients undergoing a COH cycle but who did not undergo embryo transfer. Experiments were designed to analyse, using microarray technology, the endometrial gene expression profile in the prereceptive (LH+2, 5 samples) and receptive (LH+7, 14 samples) endometrium in a natural cycle and compare it with that at day hCG+7 (5 samples) during COH in the IVF cycle.
Materials and methods
Experimental subjects
The study population comprised of healthy, fertile women with normal cycles (Caucasians, between the ages of 23 and 39) who served as oocyte donors in our institution. Volunteers signed an informed consent form approved by the Institutional Review Board of our Institution. Patients were followed-up during their natural cycles and during the following cycle, in which COH was performed for IVF.
Endometrial biopsies were obtained from two groups of patients using different experimental designs. In the first group, samples were obtained at days LH+2 (n=5) and LH+7 (n=5) as determined by urinary LH surge during the natural cycle from the same patients to reconfirm previous findings. In the second group, endometrial samples were obtained from the same patients at day LH+7 (n=9) of the natural cycle and at day hCG+7 (n=5) of the next cycle during COH used for IVF treatment (10 women were included in this group, 10 samples were obtained in the natural cycle but one was removed because of the low quality of RNA, only five patients continued the study and samples were obtained at day hCG+7).
In total, 24 endometrial biopsies were obtained, 5 corresponding to LH+2, 14 to LH+7 and 5 to hCG+7. Daily assessment of the urinary LH levels beginning on cycle day 10 was performed by the patients using a commercially available ovulation predictor kit (Donacheck ovulación, Novalab Ibérica, S.A.L, Coslada, Madrid, Spain) and the day of the urinary LH surge was considered as LH = 0. Overall, 24 biopsies were obtained from the uterine fundus using a Pipelle catheter (Genetics, Namont-Achel, Belgium) under sterile conditions.
COH protocol
The protocol for ovarian stimulation used was a long protocol with GnRH agonist without progesterone supplementation. It was initiated by pituitary desensitization via administration of 1 mg/d leuprolide acetate, subcutaneously (Procrin, Abbot S.A., Madrid, Spain), beginning in the luteal phase of the previous cycle. Serum E2 levels <60 pg/ml (220 pmol/l) and negative vaginal ultrasonographic scans were used to define ovarian quiescence. On days 1 and 2 of ovarian stimulation, one ampule/day HMG (Pergonal, Serono Laboratories, Madrid, Spain) was administered together with three ampules of highly purified FSH (FSH HP, Neo-Fertinorm, Serono). On days 3, 4 and 5 of ovarian stimulation, one ampule/day of HMG and one ampule/day of FSH HP were given to each patient. From day 6 onwards, HMG/FSH HP was administered on an individual basis according to the serum E2 levels and transvaginal ovarian ultrasound scans. hCG (10 000 IU, Profasi, Serono) was administered when two or more follicles with a maximum diameter of >19 mm and when serum E2 levels >800 pg/ml (2.94 nmol/l) were observed. Leuprolide acetate and gonadotropin injections were discontinued on the day of hCG administration. Oocyte retrieval was scheduled 36–38 h after hCG injection and no progesterone luteal support was given to the patients, as in a natural cycle.
RNA isolation
Endometrial samples were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −70 °C until further processing. Total RNA was extracted using the ‘TRIzol method’ according to the protocol recommended by the manufacturer (Life Technologies, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD). In short, homogenized biopsies (1 ml TRIzol reagent/75 mg tissue) were incubated at room temperature for 5 min, chloroform (0.2 volumes of TRIzol) was then added and samples incubated for 2.5 min at room temperature. Thereafter, the said samples were centrifuged for 15 min at 12 000 g (4 °C). The aqueous phase was precipitated with an equal volume of 2-propanol, stored in ice for 5 min and centrifuged for 30 min at 12 000 g (4 °C). The pellet was washed with 75% ethanol and dissolved in DEPC-treated water. Approximately, 1–2 μg of total RNA was obtained per microgram of endometrial tissue. RNA quality was confirmed by Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer.
Affymetrix chip hybridization
All samples were hybridized onto the GeneChip HG_U133A (Affymetrix, High Wycombe, UK) encompassing more than 22 000 human DNA fragments (Liu et al., 2003). Details of the chip's content are available at the NetAffx Analysis Centre (www.affymetrix.com/analysis/index.affx).
The protocols for sample preparation and hybridization of the endometrial samples (5×LH+2, 14×LH+7, and 5×hCG+7) were adapted from the Affymetrix Technical Manual. In short, first strand cDNA was transcribed from 5 μg of total RNA (cDNA synthesis kit, Cat. No. 11917-020, Invitrogen, San Diego, CA) using T7-Oligo(dT)24 Promotor Primer (Ambion Cat. No. 5710, Austin, TX), followed by second strand synthesis using DNA polymerase I (Invitrogen, Cat. No. 11917-020). Double stranded cDNA was cleaned with the GeneChip® Sample Clean-up Module Kit (Affymetrix, Cat. No. 900371). Half of the sample was in vitro transcribed and biotin-labelled with the Enzo RNA Transcript Labeling Kit (Enzo Diagnostics, Farmingdale, NY). The cRNA synthesis typically yielded between 30 and 60 μg. Following a further clean-up round (Affymetrix, Cat. No. 900371), cRNA was fragmented into pieces ranging from 35 to 200 bases which was confirmed using Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer technology. Fragmented cRNA samples (15 μg) were hybridized onto chips through 16 h of incubation at 45 °C with constant rotation. Chips were washed and stained using Affymetrix GeneChip Fluidics Station 400. Hybridized chips were scanned and data automigrated into Rosetta Resolver (Rosetta Biosoftware, Kirkland, WA). A chip quality report was evaluated for abnormal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase 3′/5′ ratios, average background and percentage of ‘Present Calls’.
Principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using the ‘analyse experiments using PCA’ option within Spotfire DecisionSite 7.2 (Spotfire, Göteborg, Sweden). A representative set of 500 random genes was selected by K-means clustering. The resulting table of 500 rows (genes) and columns (endometrial samples) was transposed and PCA was ran to detect and reduce the number of variables to three principal components, which represent the majority of the variability in the dataset. A two- or three-dimensional scatterplot was produced in order to visualize the differences in sample sets (LH+2, LH+7 and hCG+7) based on each sample's gene expression profile.
Gene expression analysis
The Rosetta Resolver allows normalization of sample data following selection of the appropriate samples for calculation of one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). A one-way ANOVA with build ratio was calculated (LH+7 samples as baseline) in order to identify significant changes in expression levels between sample sets. The results of ANOVA contain fold change values and P-values per gene.
Three criteria were used to define genes that had altered mRNA abundance among the different sample sets:
An absolute fold change of 2.0 or more.
A corresponding fold change P-value of 0.01 or less.
The number of Present Calls within the high expressing sample group of more than 75%. (Present Calls were calculated using the P-value for significance of expression obtained from the Affymetrix Microarray Suite version 5.0 (MAS5) processed expression signals. A P-value of 0.05 or less was scored as present and higher values as absent. Depending on the sample size at least 4 out of 5, or 11 out of 14 samples in the high expressing group should have a Present Call.
Quantitative-PCR analysis
cDNA synthesis
RNA from patients of each group (LH+2, LH+7 and hCG+7) was pooled. Oligo(dT)12–18 primer (0.5 μg, Invitrogen) and 1.0 μg pd(N)6 (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Inc.) was added to 1 μg of total RNA. The mixture was heated at 65 °C for 5 min and briefly chilled on ice for 2 min. cDNA was synthesized in a total volume of 20 μl containing 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.3), 75 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 10 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5 mM dNTPs and 200 U Superscript II RNase H− Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen). The subsequent incubation process was carried out as follows: 10 min at 25 °C, 50 min at 42 °C and 15 min at 70 °C. The cDNA was diluted to a concentration equivalent to 2 ng/μl RNA.
Q-PCR
Q-PCR was performed using cDNA equivalent to 10 ng RNA in a total of 25 μl PCR mix. The total mix contained cDNA, 300 nM forward primer, 300 nM reverse primer and 1×SYBRgreen PCR Master Mix. The 2×SYBRgreen PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) is optimized for SYBRgreen reactions and contains SYBRgreen I Dye, AmpliTaq Gold DNA Polymerase, dNTPs with dUTP, passive reference and optimized buffer components. The Q-PCR was performed in a MicroAmp Optical 96-well Reaction Plate (Applied Biosystems) with an ABI Prism Optical Adhesive Cover (Applied Biosystems) in the ABI PRISM 7900HT Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems). The selected program consisted of 10 min at 95 °C, 100% ramp, 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C, 100% ramp and 1 min at 60 °C, 100% ramp, followed by a dissociation curve step of 15 s at 95 °C, 100% ramp, 15 s at 60 °C, 100% ramp and 15 s at 95 °C, 2% ramp. Ramp is the speed with which the thermocycler switches to the next temperature, 100% is fast and 2% is slow. Standard curve material consisted of pooled endometrial RNA from all three groups. All reactions were performed in triplicate. The microarray data set was searched for genes that were not regulated in the three different sample sets, and therefore could be used for normalization in the Q-PCR experiments. Capping protein fulfilled these criteria (data not shown) and was subsequently used for normalization purposes in the Q-PCR. Table I shows the Q-PCR primer sequences, forward (F) and reverse (R).
Results
DNA chip hybridization data analysis
Ten patients started the protocol to obtain an endometrial biopsy at LH+7 in a natural cycle and at hCG+7 during a subsequent COH cycle. From nine of the 10 LH+7 samples, good quality RNA was obtained and five patients failed to deliver the hCG+7 biopsy, and in total from five hCG+7 biopsies good quality RNA was obtained. Together with the previously obtained LH+2 and LH+7 biopsies, in a total of 24 samples (5 LH+2, 14 LH+7 and 5 COH-hCG+7) were hybridized onto the Affymetrix HG_U133A chip. All 24 samples passed quality control.
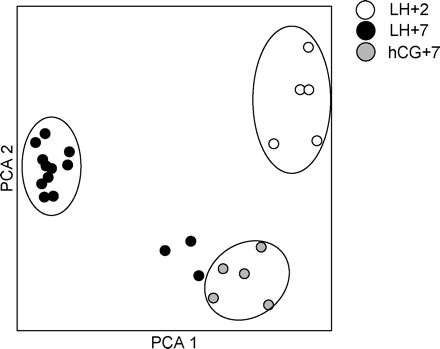
Figure 1 shows a PCA for all the samples, which determines the key variables within the data set that explain the differences between the samples based on the expression profiles of 500 randomly selected genes. LH+2 samples are clearly distinguished from the two other sample sets at a separate position in the PCA analysis. Moreover, the five COH-hCG+7 samples also cluster together, whereas the majority of the LH+7 samples (11/14) cluster together at yet a different position in the PCA analysis. A minority of the LH+7 samples (3/14) seem to cluster in the proximity of the COH-hCG+7 samples. However, these are LH+7 samples and since we have not performed histological analyses on these samples we cannot omit these samples from further analysis.
In order to identify consistent changes in gene expression, the data of the different patients were grouped per category (LH+2;5 samples, LH+7;14 samples and hCG+7;5 samples). Genes that were differentially expressed among the groups were identified according to the procedure described in Materials and methods. As explained previously, the formation of a receptive endometrium is a dynamic process requiring the activation and repression of a large number of genes. Using our criteria, we compared the sets of data for LH+2 and LH+7 and identified 505 genes that were down-regulated in time (at LH+7), and 894 genes that were up-regulated, more than 2-fold during the formation of a receptive endometrium. Many of these genes were regulated over 5-fold (178 up- and 80 down-regulated). For the complete set of data see the supplementary information (Table R1, data sent to the reviewers).
We compared the data of the LH+2 versus LH+7 samples in the present study with our previous work employing an identical experimental design and methodology (Riesewijk et al., 2003). We found that 39 of the 40 most strongly up-regulated and 29 of the 30 most down-regulated genes of the previous study appeared in the results of the present study (Table R2, data sent to the reviewers). This finding is reassuring and indicates the consistency between the HU_95A and the HU_133A microarrays. Surprisingly, one of the new genes that came up in this study was leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (+37-fold up-regulated at LH+7). This gene was also present at the HG_95A chip but was previously scored as not expressed.
In order to identify consistent changes in endometrial gene expression during the receptive phase in a natural cycle versus a COH cycle, data from the different patients were grouped according to category (LH+7 versus hCG+7). Genes differentially expressed in the two groups were identified according to the procedure described in Materials and methods.
COH induces significant differences in endometrial gene expression when compared to the previous natural cycle. In total 558 DNA fragments on the Affymetrix chip were differentially expressed, from which 281 were up-regulated compared to the natural cycle (166 genes between 2- and 3-fold, 74 between 3- and 5-fold and 41 >5-fold). Two hundred and seventy-seven genes were down-regulated (162 between 2- and 3-fold decrease, 72 between 3- and 5-fold and 44 >5-fold decrease). Genes that were up- or down-regulated by more than 3-fold are depicted in Tables II and III, respectively. These results are consistent with the high degree of difference between the three sample sets as observed in the PCA analysis.
Those genes that are differentially expressed in the LH+2 and LH+7 samples in natural cycles are important for the formation of a receptive endometrium [named as window of implantation (WOI) genes]. Therefore, we investigated whether the genes that were differentially expressed in the COH protocol and the natural cycle also belonged to the said group of WOI genes. Of the 558 DNA fragments that were differentially expressed in hCG+7 and LH+7 groups, 351 were also regulated during the formation of a receptive endometrium. Interestingly, genes that were normally down-regulated during the formation of a receptive endometrium tended to be expressed at a higher level during COH, whereas genes that were up-regulated in the WOI tended to be down-regulated during COH (Table IV). There were few genes that were up-regulated during the WOI and showed an increase in the said up-regulation following ovarian hyperstimulation. No genes were down-regulated during the WOI and further down-regulated after COH. The genes that were down-regulated in receptive endometrium and up-regulated in the IVF protocol or up-regulated in receptive endometrium and down-regulated in the IVF protocol are shown in bold in Tables II and III, respectively.
Validation of the microarray data by SQ-PCR and Q-PCR
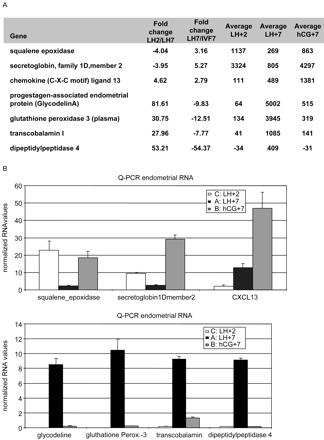
To confirm our microarray data we performed semi-quantitative PCR (SQ-PCR) and Q-PCR analysis. SQ-PCR experiments were performed on pooled patient samples from each group to confirm the differential expression of 40 genes, among which were the progestagen-associated endometrial protein (glycodelin), transcobalamin I, the insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, laminin beta-3 and calpain 6. Differential expression levels could be confirmed by SQ-PCR for most of the selected genes (R3, data sent to the reviewers). However, SQ-PCR is not a quantitative technique. Therefore seven genes (glycodelin, glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPx3), transcobalamin I and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), squalene epoxidase, secretoglobin 1D and CXCL13) were subjected to Q-PCR on the pooled material from LH+2, LH+7 and hCG+7 RNA samples. Capping protein, a non-regualted endometrially expressed gene, was used for normalization purposes. The results of the microarray and Q-PCR for these genes are depicted in Figure 2A and B, respectively. Differential expression was confirmed for all seven genes. In most cases, the fold change obtained with Q-PCR was greater than that calculated from the microarray. However, it was difficult to establish the fold change, for e.g. glycodelin and GPx3, since the LH+2 expression value was hardly detectable.
Discussion
It has long been hypothesized that gonadotrophins and GnRH agonist/antagonists used to induce multifollicular development in COH might also affect endometrial receptivity, either directly or indirectly. In this study we have used a genome-wide approach to compare gene expression patterns during the WOI in patients undergoing first a natural cycle and then a cycle in which COH with gonadotrophins and GnRH analogs is carried out for IVF.
All the women participating in this study were fertile and healthy and participated as oocyte donors in our IVF oocyte donation programme. Since embryos were not transferred back to these women it was possible to obtain an endometrial biopsy during the WOI following COH. The protocol used for COH was similar to protocols used for IVF in many clinics at the time the study was performed, with the difference that no luteal support was given to the oocyte donors in order to accurate comparison with the previous natural cycle without progesterone supplementation. COH was performed with a combination of human menopausal gonadotropin and purified FSH at a relatively high dose. In general, this protocol results in the retrieval of 13–18 oocytes and an average E2 level of 2200±300 pg/ml and progesterone levels below 1.2 ng/ml at the time of hCG administration (Pellicer et al., 1996). At hCG+7 we have previously reported an E2 level of 650 ± 30 pg/ml and a progesterone levels of 70 ng/ml (Pellicer et al., 1996).
Two sets of data were obtained as a result of this study: genes regulated during the formation of a receptive endometrium (LH+2 versus LH+7), called WOI genes and genes dys-regulated at the time of implantation in a COH protocol for IVF (hCG+7 versus LH+7). We have previously published the WOI gene data, generated with the LH+7 versus LH+2 comparison using Affymetrix HG-U95A array. In this study we have used the recently available HG-U133A genechip, which contains almost twice as many gene fragments. A large degree of overlap was identified when we compared our HG-U95A LH+7/LH+2 data with the genes identified in this study. More specifically, of the top 40 up-regulated and top 30 down-regulated genes from the HG-U95A set of data, 68 were also identified as being equally regulated in this study. Differences between the two data sets could be due to the fact that the new genechip (HG-U133A) includes more genes than the previously used genechip (HG-U95A) and that different probe sets were used for several genes. The latter is the case for the LIF gene which is also present in the previously used HG_U95A GeneChip, but which did not yield good hybridization signals when the said genechip was employed. This is in agreement with the results of other endometrial microarray studies, also using the HG_U95A chip (Carson et al., 2002; Kao et al., 2002; Borthwick et al., 2003). Another probe set is present for the LIF gene on the newer HG_U133A chip yielding good expression values and showing differential expression of LIF both in the natural cycle (36-fold up at LH+7) and during COH (23-fold down). LIF is a multifunctional cytokine, considered to be an essential endometrial factor for implantation in the mouse model (Stewart et al., 1992). In both studies we found that, during the formation of a receptive endometrium, more genes were up- than down-regulated in contrast to other authors (Carson et al., 2002; Kao et al., 2002).
When comparing the data of the hCG+7 samples with that of the natural cycle at LH+7 we found to our surprise that the expression of a large number of genes (558) was dys-regulated. We identified equal numbers of up- and down-regulated genes, while more than 200 genes were dys-regulated with a fold change of >3, of which 80 showed a fold change of >5. This unexpected result was confirmed for a number of genes by SQ-PCR and Q-PCR. The consistency of the individual endometrial expression profiles, demonstrated using microarray technology, is surprising. At the microscopical level a large degree of variation in endometrial morphology has been described (Nikas, 2000). Unfortunately, since no histological data are presented, the genomic differences obtained in the endometrium from COH cycle versus the previous natural cycle from the same patient could be due to the advancement of endometrial histology or not.
Why is endometrial gene expression disturbed in such a dramatic way in these patients? We know from previous studies that luteal phase defects are frequently observed during COH. The addition of luteal support, either in the form of progesterone, or as hCG, improves endometrial quality, and consequently, implantation rates. However, the biological mechanism of this luteal support is unclear, since progesterone levels are already supra-physiological in COH cycles, at least during the first 7 days after hCG (Fauser and Devroey, 2003), which is within the time frame in which our biopsies were taken. It would be interesting to analyse whether the dys-regulated genes are indeed transcriptionally regulated by progesterone and/or E2. Probably, the aberrant endometrial receptivity development observed in the COH patients is due, in a large part, to the lack of luteal support.
The fact that so many genes are dys-regulated suggests a shift in time in the differentiation towards a receptive endometrium caused by COH treatment, rather than the direct dys-regulation of a limited number of genes by the hormones used. Indeed, evidence can be found in the literature that, on the day of oocyte retrieval (36 h after hCG administration) the endometrium appears morphologically advanced (Seif et al., 1992; Psychoyos, 1994; Kolb and Paulson, 1997; Kolibianakis et al., 2003), whereas delayed, advanced and in phase endometrium is described during the WOI following COH. Our study shows that, for many of the genes that are regulated during the formation of the WOI, the expression levels in hCG+7 samples are more comparable with those of LH+2 than with LH+7 patterns (see Figure 2). This observation suggests a delay in the regulation of gene expression necessary for the formation of a receptive endometrium due to COH treatment. The altered gene expression profiles, strongly suggests that a COH endometrium is not optimally prepared for implantation. This could have negative effects on the implantation process and therefore could be one of the main causes of low success rates in COH.
Some of the dys-regulated genes are known to be implicated in endometrial receptivity such as PP-14 (Glycodelin) (Julkunen et al., 1986) or LIF (Stewart et al., 1992) but others have more general functions. From the 151 genes that are dys-regulated more than 3-fold in the COH endometrium we have selected seven of them to analyse their possible implication in endometrial receptivity. Figure 2A shows the fold change expression of these genes in the LH+7 natural cycle endometrium versus hCG+7 endometrium.
Glycodelin appears to be up-regulated in three out of four studies focused on genome-wide analysis of endometrial receptivity (Kao et al., 2002; Borthwick et al., 2003; Riesewijk et al., 2003). First described in 1986 (Julkunen et al., 1986), it belongs to a family of lipocalins that participate in the regulation of the immune response (Akerstrom et al., 2000). The lipocalins typically bind small hydrophobic molecules, like retinol and retinoic acid, although this is not so for glycodelin (Seppala et al., 2001). It appears as different glycoforms that exhibit quantitative physicochemical and functional differences in different sources and individuals (Koistinen et al., 2003). Recently it has been demonstrated that glycodelin gene expression is dys-regulated in patients with endometriosis (Kao et al., 2003) although its specific role in implantation is still uncertain.
Glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPx3) was first described in 1991 (Esworthy et al., 1991). It is a selenoprotein enzyme that protects cells from oxidative damage by catalysing the reduction of hydrogen peroxidase, lipid peroxides and organic hydroxyperoxide by glutathione. In reproductive tissues of female mice, it is regulated by 17β-E2 (Waters et al., 2001) and selenium. Its expression has been demonstrated to increase in ovarian (Hough et al., 2001), uterine and breast cancers (Gorodzanskaya et al., 2001). Several publications have previously reported that its expression increases markedly during the WOI and that it could be implicated in endometrial receptivity (Borthwick et al., 2003; Riesewijk et al., 2003).
Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPPIV) is a serine proteinase that is widely distributed in mammalian tissues, including lymphocytes, where it is identical to the T-cell activation antigen, cluster differentiation antigen-26 (Liu and Hansen, 1995). It has been reported that DPPIV is a membrane-bound peptidase and that it is expressed on human placental cytotrophoblasts. It is considered to be a differentiation marker for glandular cells and surface epithelium (Sato et al., 2002). It also has been demonstrated to be important for the non-invasive phenotype of the extravillous trophoblast and the down-regulation of this enzyme is strongly associated with migration of invasive extravillous trophoblast phenotype (Imai et al., 1992).
Transcobalamin I (TCI) is a vitamin B12-binding protein that transports cobalamin (vitamin B12) into cells. Its expression is significantly increased during the formation of a receptive endometrium (+27.3-fold) but decreased by COH treatment (−7.7-fold). Vitamin B12 deficiency has been associated with infertility and recurrent fetal loss and is associated with folate metabolism (Bennet, 2001). The TCI–vitamin B12 complex can bind to the Megalin receptor, which is involved in the cellular uptake of vitamin B12. Megalin is expressed in the kidney, one of the major organs regulating vitamin B12 levels, and also in the epithelia of other tissues, including the placenta where it plays a role in fetal vitamin B12 supply (Moestrup et al., 1996). Lack of TCI could result in a diminished supply of vitamin B12, which would have negative effects on embryonic implantation and development.
As we have mentioned, LIF is a pleiotropic cytokine of the interleukin-6 family. This means that it has effects on many different cell types and that its activities are not restricted to one lineage. It was first identified by Metcalf and colleagues (Gearing et al., 1987). Other groups have demonstrated that LIF levels are relatively low in the proliferative phase, rise after ovulation and remain high until the end of the menstrual cycle before dropping to baseline levels (Chen et al., 1995; Vogiagis et al., 1996). LIF mRNA is only detected during the mid and late secretory phases of the cycle after day 20 and is maximally present in the human endometrium around the time of implantation suggesting a paracrine and/or autocrine role in endometrial function (Lass et al., 2001). However, until now, there was no evidence of this regulation in microarrays studies. This work incorporates LIF, one of the classic implantation molecules, to the long list of WOI genes described until the moment by means of this technique.
There is a surprisingly high number of genes involved in endometrial receptivity, the WOI genes that are aberrantly expressed in COH endometrium (342 genes), showing expression levels more similar to those in a non-receptive endometrium. This suggests that endometrial development is hampered and delayed under these conditions.
Together, these studies highlight the necessity for continued research in this field and for modifying COH treatments in order to achieve an endometrium that resembles, both morphologically and functionally, the natural cycle endometrium, which will subsequently lead to improved success rates in IVF.
PCA analysis of the 24 endometrial samples using 500 genes randomly selected by K-means clustering. Percentage of variation for the PCA1 and PCA2 axis are 36 and 18%, respectively.
Confirmation of the microarray data by Q-PCR. (A) Microarray gene expression values for each of the seven selected genes and the fold changes between the LH+2/LH+7 and LH+7/hCG+7 samples. (B) Normalized RNA values for the seven selected genes. Patient material was pooled per group. Capping protein was used for normalization purposes.
List of oligonucleotides used for Q-PCR and the size of the amplified product
| Gene name . | . | Sequence 5′–3′ . | Amplicon (bp) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycodelin A | F | GGAGAGAAGACTGAGAATCCAAAGA | 100 |
| R | AGAGAAACAGGAAATTGTCGTAGTCA | ||
| Capping protein | F | GGTCATTCTTCAGAGCTTCTTGTTT | 104 |
| R | GCTGAACGAGATCTACTTTGGAAAA | ||
| Glutathione peroxidase 3 | F | CAGGAACCAGGAGAGAACTCAGA | 63 |
| R | CCTCCACCTGGTCGGACATA | ||
| Transcobalamin I | F | GGGCTCTTACTGTTTTCTTTTATTC | 80 |
| R | TTTAGGCGGATGTAGTTTTCTTCAC | ||
| Squalene epoxidase | F | GGGTGGTTATCATGTTCTCAAAGA | 68 |
| R | CAACCTGGGCATCAAGACCTT | ||
| Secretoglobin 1D member 2 | F | GCTGGCCCTCTGCTGCTA | 54 |
| R | GAAACAAGAGCTGGGCAGAACT | ||
| CXCL13 | F | CCCGTGGGAATGGTTGTC | 73 |
| R | GGGTCCACACACACAATTGACT | ||
| dpp4 | F | TGGTCATATGGAGGGTACGTAACC | 81 |
| R | AGGCGCCACGGCTATTC |
| Gene name . | . | Sequence 5′–3′ . | Amplicon (bp) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycodelin A | F | GGAGAGAAGACTGAGAATCCAAAGA | 100 |
| R | AGAGAAACAGGAAATTGTCGTAGTCA | ||
| Capping protein | F | GGTCATTCTTCAGAGCTTCTTGTTT | 104 |
| R | GCTGAACGAGATCTACTTTGGAAAA | ||
| Glutathione peroxidase 3 | F | CAGGAACCAGGAGAGAACTCAGA | 63 |
| R | CCTCCACCTGGTCGGACATA | ||
| Transcobalamin I | F | GGGCTCTTACTGTTTTCTTTTATTC | 80 |
| R | TTTAGGCGGATGTAGTTTTCTTCAC | ||
| Squalene epoxidase | F | GGGTGGTTATCATGTTCTCAAAGA | 68 |
| R | CAACCTGGGCATCAAGACCTT | ||
| Secretoglobin 1D member 2 | F | GCTGGCCCTCTGCTGCTA | 54 |
| R | GAAACAAGAGCTGGGCAGAACT | ||
| CXCL13 | F | CCCGTGGGAATGGTTGTC | 73 |
| R | GGGTCCACACACACAATTGACT | ||
| dpp4 | F | TGGTCATATGGAGGGTACGTAACC | 81 |
| R | AGGCGCCACGGCTATTC |
List of oligonucleotides used for Q-PCR and the size of the amplified product
| Gene name . | . | Sequence 5′–3′ . | Amplicon (bp) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycodelin A | F | GGAGAGAAGACTGAGAATCCAAAGA | 100 |
| R | AGAGAAACAGGAAATTGTCGTAGTCA | ||
| Capping protein | F | GGTCATTCTTCAGAGCTTCTTGTTT | 104 |
| R | GCTGAACGAGATCTACTTTGGAAAA | ||
| Glutathione peroxidase 3 | F | CAGGAACCAGGAGAGAACTCAGA | 63 |
| R | CCTCCACCTGGTCGGACATA | ||
| Transcobalamin I | F | GGGCTCTTACTGTTTTCTTTTATTC | 80 |
| R | TTTAGGCGGATGTAGTTTTCTTCAC | ||
| Squalene epoxidase | F | GGGTGGTTATCATGTTCTCAAAGA | 68 |
| R | CAACCTGGGCATCAAGACCTT | ||
| Secretoglobin 1D member 2 | F | GCTGGCCCTCTGCTGCTA | 54 |
| R | GAAACAAGAGCTGGGCAGAACT | ||
| CXCL13 | F | CCCGTGGGAATGGTTGTC | 73 |
| R | GGGTCCACACACACAATTGACT | ||
| dpp4 | F | TGGTCATATGGAGGGTACGTAACC | 81 |
| R | AGGCGCCACGGCTATTC |
| Gene name . | . | Sequence 5′–3′ . | Amplicon (bp) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycodelin A | F | GGAGAGAAGACTGAGAATCCAAAGA | 100 |
| R | AGAGAAACAGGAAATTGTCGTAGTCA | ||
| Capping protein | F | GGTCATTCTTCAGAGCTTCTTGTTT | 104 |
| R | GCTGAACGAGATCTACTTTGGAAAA | ||
| Glutathione peroxidase 3 | F | CAGGAACCAGGAGAGAACTCAGA | 63 |
| R | CCTCCACCTGGTCGGACATA | ||
| Transcobalamin I | F | GGGCTCTTACTGTTTTCTTTTATTC | 80 |
| R | TTTAGGCGGATGTAGTTTTCTTCAC | ||
| Squalene epoxidase | F | GGGTGGTTATCATGTTCTCAAAGA | 68 |
| R | CAACCTGGGCATCAAGACCTT | ||
| Secretoglobin 1D member 2 | F | GCTGGCCCTCTGCTGCTA | 54 |
| R | GAAACAAGAGCTGGGCAGAACT | ||
| CXCL13 | F | CCCGTGGGAATGGTTGTC | 73 |
| R | GGGTCCACACACACAATTGACT | ||
| dpp4 | F | TGGTCATATGGAGGGTACGTAACC | 81 |
| R | AGGCGCCACGGCTATTC |
Up-regulated genes in hCG+7
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funtional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 218865_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ22390 | 38.87 | Unknown |
| 209904_at | Troponin C, show | 30.89 | Structural protein |
| 220541_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 26 | 16.96 | Enzyme |
| 201562_s_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 15.79 | Enzyme |
| 202965_s_at | Calpain 6 | 13.56 | Glycoprotein |
| 205671_s_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta | 12.23 | Immune response |
| 212768_s_at | Differentially expressed in hematopoietic lineages | 11.89 | Inhibitor |
| 209443_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5 | 11.88 | Inhibitor |
| 214240_at | Galanin | 11.79 | Neuropeptide |
| 210653_s_at | Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) | 10.32 | Enzyme |
| 221102_s_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 | 10.04 | Receptor |
| 206424_at | Cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | 9.69 | Energy transduction |
| 204560_at | FK506 binding protein 5 | 9.57 | Unknown |
| 204437_s_at | Folate receptor 1 (adult) | 9.30 | Receptor |
| 215800_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 8.91 | Enzyme |
| 205698_s_at | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | 8.65 | Cell cycle |
| 205073_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily J, polypeptide 2 | 7.89 | Energy transduction |
| 204288_s_at | Arg/Abl-interacting protein ArgBP2 | 7.77 | Signal transduction |
| 219597_s_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 7.40 | Enzyme |
| 201563_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 7.32 | Enzyme |
| 205373_at | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 2 | 7.32 | Cell adhesion |
| 205316_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 7.05 | Transporter |
| 202966_at | Calpain 6 | 7.04 | Protease |
| 214324_at | Glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrana) | 6.93 | Glycoprotein |
| 213050_at | KIAA0633 protein | 6.47 | Unknown |
| 205960_at | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | 6.44 | Enzyme |
| 205779_at | Receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying protein 2 | 6.43 | Receptor |
| 220724_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 6.16 | Unknown |
| 209278_s_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 6.13 | Inhibitor |
| 214279_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 6.11 | Development |
| 213562_s_at | Squalene epoxidase | 6.06 | Enzyme |
| 209723_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 | 6.05 | Inhibitor |
| 220994_s_at | Syntaxin binding protein 6 (amisyn) | 5.98 | Unknown |
| 206453_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 5.70 | Development |
| 205379_at | Carbonyl reductase 3 | 5.64 | Enzyme |
| 205413_at | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 8 | 5.53 | Unknown |
| 204394_at | Prostate cancer overexpressed gene 1 | 5.45 | Unknown |
| 214209_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 9 | 5.34 | Transporter |
| 206799_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 2 | 5.27 | Secretory protein |
| 205833_s_at | Prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 | 5.09 | Enzyme |
| 205593_s_at | Phosphodiesterase 9A | 5.04 | Enzyme |
| 209825_s_at | Uridine monophosphate kinase | 4.96 | Enzyme |
| 216248_s_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 4.95 | Receptor |
| 218839_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 4.91 | Unknown |
| 220677_s_at | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 | 4.88 | Unknown |
| 204941_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 4.86 | Enzyme |
| 209277_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 4.72 | Inhibitor |
| 221094_s_at | Likely ortholog of mouse elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | 4.72 | Unknown |
| 214040_s_at | Gelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type) | 4.68 | Calcium-related |
| 205317_s_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 4.65 | Transporter |
| 213033_s_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 4.52 | Unknown |
| 47553_at | DKFZP434N014 protein | 4.45 | Unknown |
| 207910_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 1 | 4.41 | Signal transduction |
| 204794_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 2 | 4.31 | Enzyme |
| 218816_at | LAP (leucine-rich repeats and PDZ) and no PDZ protein | 4.28 | Unknown |
| 203779_s_at | Epithelial V-like antigen 1 | 4.27 | Enzyme |
| 214307_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 4.23 | Enzyme |
| 218692_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20366 | 4.21 | Unknown |
| 204130_at | Hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 | 4.18 | Enzyme |
| 206723_s_at | Endothelial differentiation, lysophosphatidic acid G-protein-coupled receptor, 4 | 3.91 | Receptor |
| 204622_x_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 3.85 | Nuclear receptor |
| 208004_at | Proline rich 1 | 3.81 | Secretory protein |
| 209781_s_at | KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 210538_s_at | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 213587_s_at | Chromosome 7 open reading frame 32 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 205081_at | Cysteine-rich protein 1 (intestinal) | 3.74 | Unknown |
| 212686_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 218292_s_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 205221_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.71 | Enzyme |
| 203932_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta | 3.70 | Immune response |
| 213032_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 3.70 | Unknown |
| 204942_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 3.69 | Enzyme |
| 219667_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20706 | 3.69 | Unknown |
| 219786_at | Metallothionein-like 5, testis-specific (tesmin) | 3.66 | Enzyme |
| 220723_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 3.65 | Unknown |
| 212110_at | KIAA0062 protein | 3.63 | Unknown |
| 211470_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.56 | Enzyme |
| 221887_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.54 | Enzyme |
| 205864_at | Solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 4 | 3.50 | Transporter |
| 206385_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.50 | Membrane protein |
| 217284_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.50 | Enzyme |
| 209442_x_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.49 | Membrane protein |
| 217973_at | Dicarbonyl/l-xylulose reductase | 3.49 | Enzyme |
| 213498_at | Old astrocyte specifically induced substance | 3.40 | Transcription factor |
| 44783_s_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 3.38 | Unknown |
| 207030_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 211126_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 217080_s_at | Homer homolog 2 (Drosophila) | 3.35 | Unknown |
| 210657_s_at | Peanut-like 2 (Drosophila) | 3.33 | Unknown |
| 202150_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.31 | Unknown |
| 218963_s_at | Keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) | 3.30 | Structural protein |
| 207367_at | ATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide | 3.29 | Transporter |
| 210372_s_at | Tumour protein D52-like 1 | 3.29 | Oncogene |
| 214308_s_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.28 | Enzyme |
| 205348_s_at | Dynein, cytoplasmic, intermediate polypeptide 1 | 3.24 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 219735_s_at | LBP protein; likely ortholog of mouse CRTR-1 | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 211676_s_at | Interferon gamma receptor 1 | 3.22 | Immune response |
| 205345_at | BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 | 3.20 | Apoptosis |
| 219968_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 210145_at | Phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) | 3.18 | Enzyme |
| 206299_at | TED protein | 3.17 | Unknown |
| 209218_at | Squalene epoxidase | 3.16 | Enzyme |
| 207950_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.14 | Membrane protein |
| 217276_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.13 | Enzyme |
| 201467_s_at | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 | 3.12 | Enzyme |
| 208286_x_at | POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 | 3.12 | Transcription factor |
| 211113_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 | 3.12 | Transporter |
| 204187_at | Guanosine monophosphate reductase | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 215783_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 221648_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203892_at | CGI-146 protein | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 204698_at | WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 202149_at | Interferon stimulated gene 20kDa | 3.04 | Immune response |
| 210062_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.04 | Transcription factor |
| 213029_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.04 | Unknown |
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funtional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 218865_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ22390 | 38.87 | Unknown |
| 209904_at | Troponin C, show | 30.89 | Structural protein |
| 220541_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 26 | 16.96 | Enzyme |
| 201562_s_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 15.79 | Enzyme |
| 202965_s_at | Calpain 6 | 13.56 | Glycoprotein |
| 205671_s_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta | 12.23 | Immune response |
| 212768_s_at | Differentially expressed in hematopoietic lineages | 11.89 | Inhibitor |
| 209443_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5 | 11.88 | Inhibitor |
| 214240_at | Galanin | 11.79 | Neuropeptide |
| 210653_s_at | Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) | 10.32 | Enzyme |
| 221102_s_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 | 10.04 | Receptor |
| 206424_at | Cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | 9.69 | Energy transduction |
| 204560_at | FK506 binding protein 5 | 9.57 | Unknown |
| 204437_s_at | Folate receptor 1 (adult) | 9.30 | Receptor |
| 215800_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 8.91 | Enzyme |
| 205698_s_at | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | 8.65 | Cell cycle |
| 205073_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily J, polypeptide 2 | 7.89 | Energy transduction |
| 204288_s_at | Arg/Abl-interacting protein ArgBP2 | 7.77 | Signal transduction |
| 219597_s_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 7.40 | Enzyme |
| 201563_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 7.32 | Enzyme |
| 205373_at | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 2 | 7.32 | Cell adhesion |
| 205316_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 7.05 | Transporter |
| 202966_at | Calpain 6 | 7.04 | Protease |
| 214324_at | Glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrana) | 6.93 | Glycoprotein |
| 213050_at | KIAA0633 protein | 6.47 | Unknown |
| 205960_at | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | 6.44 | Enzyme |
| 205779_at | Receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying protein 2 | 6.43 | Receptor |
| 220724_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 6.16 | Unknown |
| 209278_s_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 6.13 | Inhibitor |
| 214279_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 6.11 | Development |
| 213562_s_at | Squalene epoxidase | 6.06 | Enzyme |
| 209723_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 | 6.05 | Inhibitor |
| 220994_s_at | Syntaxin binding protein 6 (amisyn) | 5.98 | Unknown |
| 206453_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 5.70 | Development |
| 205379_at | Carbonyl reductase 3 | 5.64 | Enzyme |
| 205413_at | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 8 | 5.53 | Unknown |
| 204394_at | Prostate cancer overexpressed gene 1 | 5.45 | Unknown |
| 214209_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 9 | 5.34 | Transporter |
| 206799_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 2 | 5.27 | Secretory protein |
| 205833_s_at | Prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 | 5.09 | Enzyme |
| 205593_s_at | Phosphodiesterase 9A | 5.04 | Enzyme |
| 209825_s_at | Uridine monophosphate kinase | 4.96 | Enzyme |
| 216248_s_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 4.95 | Receptor |
| 218839_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 4.91 | Unknown |
| 220677_s_at | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 | 4.88 | Unknown |
| 204941_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 4.86 | Enzyme |
| 209277_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 4.72 | Inhibitor |
| 221094_s_at | Likely ortholog of mouse elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | 4.72 | Unknown |
| 214040_s_at | Gelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type) | 4.68 | Calcium-related |
| 205317_s_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 4.65 | Transporter |
| 213033_s_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 4.52 | Unknown |
| 47553_at | DKFZP434N014 protein | 4.45 | Unknown |
| 207910_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 1 | 4.41 | Signal transduction |
| 204794_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 2 | 4.31 | Enzyme |
| 218816_at | LAP (leucine-rich repeats and PDZ) and no PDZ protein | 4.28 | Unknown |
| 203779_s_at | Epithelial V-like antigen 1 | 4.27 | Enzyme |
| 214307_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 4.23 | Enzyme |
| 218692_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20366 | 4.21 | Unknown |
| 204130_at | Hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 | 4.18 | Enzyme |
| 206723_s_at | Endothelial differentiation, lysophosphatidic acid G-protein-coupled receptor, 4 | 3.91 | Receptor |
| 204622_x_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 3.85 | Nuclear receptor |
| 208004_at | Proline rich 1 | 3.81 | Secretory protein |
| 209781_s_at | KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 210538_s_at | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 213587_s_at | Chromosome 7 open reading frame 32 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 205081_at | Cysteine-rich protein 1 (intestinal) | 3.74 | Unknown |
| 212686_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 218292_s_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 205221_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.71 | Enzyme |
| 203932_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta | 3.70 | Immune response |
| 213032_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 3.70 | Unknown |
| 204942_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 3.69 | Enzyme |
| 219667_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20706 | 3.69 | Unknown |
| 219786_at | Metallothionein-like 5, testis-specific (tesmin) | 3.66 | Enzyme |
| 220723_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 3.65 | Unknown |
| 212110_at | KIAA0062 protein | 3.63 | Unknown |
| 211470_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.56 | Enzyme |
| 221887_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.54 | Enzyme |
| 205864_at | Solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 4 | 3.50 | Transporter |
| 206385_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.50 | Membrane protein |
| 217284_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.50 | Enzyme |
| 209442_x_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.49 | Membrane protein |
| 217973_at | Dicarbonyl/l-xylulose reductase | 3.49 | Enzyme |
| 213498_at | Old astrocyte specifically induced substance | 3.40 | Transcription factor |
| 44783_s_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 3.38 | Unknown |
| 207030_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 211126_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 217080_s_at | Homer homolog 2 (Drosophila) | 3.35 | Unknown |
| 210657_s_at | Peanut-like 2 (Drosophila) | 3.33 | Unknown |
| 202150_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.31 | Unknown |
| 218963_s_at | Keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) | 3.30 | Structural protein |
| 207367_at | ATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide | 3.29 | Transporter |
| 210372_s_at | Tumour protein D52-like 1 | 3.29 | Oncogene |
| 214308_s_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.28 | Enzyme |
| 205348_s_at | Dynein, cytoplasmic, intermediate polypeptide 1 | 3.24 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 219735_s_at | LBP protein; likely ortholog of mouse CRTR-1 | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 211676_s_at | Interferon gamma receptor 1 | 3.22 | Immune response |
| 205345_at | BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 | 3.20 | Apoptosis |
| 219968_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 210145_at | Phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) | 3.18 | Enzyme |
| 206299_at | TED protein | 3.17 | Unknown |
| 209218_at | Squalene epoxidase | 3.16 | Enzyme |
| 207950_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.14 | Membrane protein |
| 217276_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.13 | Enzyme |
| 201467_s_at | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 | 3.12 | Enzyme |
| 208286_x_at | POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 | 3.12 | Transcription factor |
| 211113_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 | 3.12 | Transporter |
| 204187_at | Guanosine monophosphate reductase | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 215783_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 221648_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203892_at | CGI-146 protein | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 204698_at | WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 202149_at | Interferon stimulated gene 20kDa | 3.04 | Immune response |
| 210062_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.04 | Transcription factor |
| 213029_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.04 | Unknown |
Up-regulated genes in hCG+7
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funtional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 218865_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ22390 | 38.87 | Unknown |
| 209904_at | Troponin C, show | 30.89 | Structural protein |
| 220541_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 26 | 16.96 | Enzyme |
| 201562_s_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 15.79 | Enzyme |
| 202965_s_at | Calpain 6 | 13.56 | Glycoprotein |
| 205671_s_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta | 12.23 | Immune response |
| 212768_s_at | Differentially expressed in hematopoietic lineages | 11.89 | Inhibitor |
| 209443_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5 | 11.88 | Inhibitor |
| 214240_at | Galanin | 11.79 | Neuropeptide |
| 210653_s_at | Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) | 10.32 | Enzyme |
| 221102_s_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 | 10.04 | Receptor |
| 206424_at | Cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | 9.69 | Energy transduction |
| 204560_at | FK506 binding protein 5 | 9.57 | Unknown |
| 204437_s_at | Folate receptor 1 (adult) | 9.30 | Receptor |
| 215800_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 8.91 | Enzyme |
| 205698_s_at | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | 8.65 | Cell cycle |
| 205073_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily J, polypeptide 2 | 7.89 | Energy transduction |
| 204288_s_at | Arg/Abl-interacting protein ArgBP2 | 7.77 | Signal transduction |
| 219597_s_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 7.40 | Enzyme |
| 201563_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 7.32 | Enzyme |
| 205373_at | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 2 | 7.32 | Cell adhesion |
| 205316_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 7.05 | Transporter |
| 202966_at | Calpain 6 | 7.04 | Protease |
| 214324_at | Glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrana) | 6.93 | Glycoprotein |
| 213050_at | KIAA0633 protein | 6.47 | Unknown |
| 205960_at | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | 6.44 | Enzyme |
| 205779_at | Receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying protein 2 | 6.43 | Receptor |
| 220724_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 6.16 | Unknown |
| 209278_s_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 6.13 | Inhibitor |
| 214279_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 6.11 | Development |
| 213562_s_at | Squalene epoxidase | 6.06 | Enzyme |
| 209723_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 | 6.05 | Inhibitor |
| 220994_s_at | Syntaxin binding protein 6 (amisyn) | 5.98 | Unknown |
| 206453_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 5.70 | Development |
| 205379_at | Carbonyl reductase 3 | 5.64 | Enzyme |
| 205413_at | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 8 | 5.53 | Unknown |
| 204394_at | Prostate cancer overexpressed gene 1 | 5.45 | Unknown |
| 214209_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 9 | 5.34 | Transporter |
| 206799_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 2 | 5.27 | Secretory protein |
| 205833_s_at | Prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 | 5.09 | Enzyme |
| 205593_s_at | Phosphodiesterase 9A | 5.04 | Enzyme |
| 209825_s_at | Uridine monophosphate kinase | 4.96 | Enzyme |
| 216248_s_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 4.95 | Receptor |
| 218839_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 4.91 | Unknown |
| 220677_s_at | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 | 4.88 | Unknown |
| 204941_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 4.86 | Enzyme |
| 209277_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 4.72 | Inhibitor |
| 221094_s_at | Likely ortholog of mouse elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | 4.72 | Unknown |
| 214040_s_at | Gelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type) | 4.68 | Calcium-related |
| 205317_s_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 4.65 | Transporter |
| 213033_s_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 4.52 | Unknown |
| 47553_at | DKFZP434N014 protein | 4.45 | Unknown |
| 207910_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 1 | 4.41 | Signal transduction |
| 204794_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 2 | 4.31 | Enzyme |
| 218816_at | LAP (leucine-rich repeats and PDZ) and no PDZ protein | 4.28 | Unknown |
| 203779_s_at | Epithelial V-like antigen 1 | 4.27 | Enzyme |
| 214307_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 4.23 | Enzyme |
| 218692_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20366 | 4.21 | Unknown |
| 204130_at | Hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 | 4.18 | Enzyme |
| 206723_s_at | Endothelial differentiation, lysophosphatidic acid G-protein-coupled receptor, 4 | 3.91 | Receptor |
| 204622_x_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 3.85 | Nuclear receptor |
| 208004_at | Proline rich 1 | 3.81 | Secretory protein |
| 209781_s_at | KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 210538_s_at | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 213587_s_at | Chromosome 7 open reading frame 32 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 205081_at | Cysteine-rich protein 1 (intestinal) | 3.74 | Unknown |
| 212686_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 218292_s_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 205221_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.71 | Enzyme |
| 203932_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta | 3.70 | Immune response |
| 213032_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 3.70 | Unknown |
| 204942_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 3.69 | Enzyme |
| 219667_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20706 | 3.69 | Unknown |
| 219786_at | Metallothionein-like 5, testis-specific (tesmin) | 3.66 | Enzyme |
| 220723_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 3.65 | Unknown |
| 212110_at | KIAA0062 protein | 3.63 | Unknown |
| 211470_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.56 | Enzyme |
| 221887_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.54 | Enzyme |
| 205864_at | Solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 4 | 3.50 | Transporter |
| 206385_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.50 | Membrane protein |
| 217284_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.50 | Enzyme |
| 209442_x_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.49 | Membrane protein |
| 217973_at | Dicarbonyl/l-xylulose reductase | 3.49 | Enzyme |
| 213498_at | Old astrocyte specifically induced substance | 3.40 | Transcription factor |
| 44783_s_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 3.38 | Unknown |
| 207030_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 211126_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 217080_s_at | Homer homolog 2 (Drosophila) | 3.35 | Unknown |
| 210657_s_at | Peanut-like 2 (Drosophila) | 3.33 | Unknown |
| 202150_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.31 | Unknown |
| 218963_s_at | Keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) | 3.30 | Structural protein |
| 207367_at | ATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide | 3.29 | Transporter |
| 210372_s_at | Tumour protein D52-like 1 | 3.29 | Oncogene |
| 214308_s_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.28 | Enzyme |
| 205348_s_at | Dynein, cytoplasmic, intermediate polypeptide 1 | 3.24 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 219735_s_at | LBP protein; likely ortholog of mouse CRTR-1 | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 211676_s_at | Interferon gamma receptor 1 | 3.22 | Immune response |
| 205345_at | BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 | 3.20 | Apoptosis |
| 219968_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 210145_at | Phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) | 3.18 | Enzyme |
| 206299_at | TED protein | 3.17 | Unknown |
| 209218_at | Squalene epoxidase | 3.16 | Enzyme |
| 207950_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.14 | Membrane protein |
| 217276_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.13 | Enzyme |
| 201467_s_at | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 | 3.12 | Enzyme |
| 208286_x_at | POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 | 3.12 | Transcription factor |
| 211113_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 | 3.12 | Transporter |
| 204187_at | Guanosine monophosphate reductase | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 215783_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 221648_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203892_at | CGI-146 protein | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 204698_at | WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 202149_at | Interferon stimulated gene 20kDa | 3.04 | Immune response |
| 210062_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.04 | Transcription factor |
| 213029_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.04 | Unknown |
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funtional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 218865_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ22390 | 38.87 | Unknown |
| 209904_at | Troponin C, show | 30.89 | Structural protein |
| 220541_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 26 | 16.96 | Enzyme |
| 201562_s_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 15.79 | Enzyme |
| 202965_s_at | Calpain 6 | 13.56 | Glycoprotein |
| 205671_s_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta | 12.23 | Immune response |
| 212768_s_at | Differentially expressed in hematopoietic lineages | 11.89 | Inhibitor |
| 209443_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5 | 11.88 | Inhibitor |
| 214240_at | Galanin | 11.79 | Neuropeptide |
| 210653_s_at | Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) | 10.32 | Enzyme |
| 221102_s_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 | 10.04 | Receptor |
| 206424_at | Cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | 9.69 | Energy transduction |
| 204560_at | FK506 binding protein 5 | 9.57 | Unknown |
| 204437_s_at | Folate receptor 1 (adult) | 9.30 | Receptor |
| 215800_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 8.91 | Enzyme |
| 205698_s_at | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | 8.65 | Cell cycle |
| 205073_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily J, polypeptide 2 | 7.89 | Energy transduction |
| 204288_s_at | Arg/Abl-interacting protein ArgBP2 | 7.77 | Signal transduction |
| 219597_s_at | Dual oxidase 1 | 7.40 | Enzyme |
| 201563_at | Sorbitol dehydrogenase | 7.32 | Enzyme |
| 205373_at | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 2 | 7.32 | Cell adhesion |
| 205316_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 7.05 | Transporter |
| 202966_at | Calpain 6 | 7.04 | Protease |
| 214324_at | Glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrana) | 6.93 | Glycoprotein |
| 213050_at | KIAA0633 protein | 6.47 | Unknown |
| 205960_at | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | 6.44 | Enzyme |
| 205779_at | Receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying protein 2 | 6.43 | Receptor |
| 220724_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 6.16 | Unknown |
| 209278_s_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 6.13 | Inhibitor |
| 214279_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 6.11 | Development |
| 213562_s_at | Squalene epoxidase | 6.06 | Enzyme |
| 209723_at | Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 | 6.05 | Inhibitor |
| 220994_s_at | Syntaxin binding protein 6 (amisyn) | 5.98 | Unknown |
| 206453_s_at | NDRG family member 2 | 5.70 | Development |
| 205379_at | Carbonyl reductase 3 | 5.64 | Enzyme |
| 205413_at | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 8 | 5.53 | Unknown |
| 204394_at | Prostate cancer overexpressed gene 1 | 5.45 | Unknown |
| 214209_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 9 | 5.34 | Transporter |
| 206799_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 2 | 5.27 | Secretory protein |
| 205833_s_at | Prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 | 5.09 | Enzyme |
| 205593_s_at | Phosphodiesterase 9A | 5.04 | Enzyme |
| 209825_s_at | Uridine monophosphate kinase | 4.96 | Enzyme |
| 216248_s_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 4.95 | Receptor |
| 218839_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 4.91 | Unknown |
| 220677_s_at | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 | 4.88 | Unknown |
| 204941_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 4.86 | Enzyme |
| 209277_at | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | 4.72 | Inhibitor |
| 221094_s_at | Likely ortholog of mouse elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | 4.72 | Unknown |
| 214040_s_at | Gelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type) | 4.68 | Calcium-related |
| 205317_s_at | Solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 | 4.65 | Transporter |
| 213033_s_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 4.52 | Unknown |
| 47553_at | DKFZP434N014 protein | 4.45 | Unknown |
| 207910_at | Secretoglobin, family 1D, member 1 | 4.41 | Signal transduction |
| 204794_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 2 | 4.31 | Enzyme |
| 218816_at | LAP (leucine-rich repeats and PDZ) and no PDZ protein | 4.28 | Unknown |
| 203779_s_at | Epithelial V-like antigen 1 | 4.27 | Enzyme |
| 214307_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 4.23 | Enzyme |
| 218692_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20366 | 4.21 | Unknown |
| 204130_at | Hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 | 4.18 | Enzyme |
| 206723_s_at | Endothelial differentiation, lysophosphatidic acid G-protein-coupled receptor, 4 | 3.91 | Receptor |
| 204622_x_at | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | 3.85 | Nuclear receptor |
| 208004_at | Proline rich 1 | 3.81 | Secretory protein |
| 209781_s_at | KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 210538_s_at | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 213587_s_at | Chromosome 7 open reading frame 32 | 3.80 | Unknown |
| 205081_at | Cysteine-rich protein 1 (intestinal) | 3.74 | Unknown |
| 212686_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 218292_s_at | KIAA1157 protein | 3.73 | Unknown |
| 205221_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.71 | Enzyme |
| 203932_at | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta | 3.70 | Immune response |
| 213032_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564H1916 (from clone DKFZp564H1916) | 3.70 | Unknown |
| 204942_s_at | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B2 | 3.69 | Enzyme |
| 219667_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ20706 | 3.69 | Unknown |
| 219786_at | Metallothionein-like 5, testis-specific (tesmin) | 3.66 | Enzyme |
| 220723_s_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ21511 | 3.65 | Unknown |
| 212110_at | KIAA0062 protein | 3.63 | Unknown |
| 211470_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.56 | Enzyme |
| 221887_s_at | Sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 1 | 3.54 | Enzyme |
| 205864_at | Solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 4 | 3.50 | Transporter |
| 206385_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.50 | Membrane protein |
| 217284_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.50 | Enzyme |
| 209442_x_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.49 | Membrane protein |
| 217973_at | Dicarbonyl/l-xylulose reductase | 3.49 | Enzyme |
| 213498_at | Old astrocyte specifically induced substance | 3.40 | Transcription factor |
| 44783_s_at | Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 | 3.38 | Unknown |
| 207030_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 211126_s_at | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 | 3.35 | Development |
| 217080_s_at | Homer homolog 2 (Drosophila) | 3.35 | Unknown |
| 210657_s_at | Peanut-like 2 (Drosophila) | 3.33 | Unknown |
| 202150_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.31 | Unknown |
| 218963_s_at | Keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) | 3.30 | Structural protein |
| 207367_at | ATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide | 3.29 | Transporter |
| 210372_s_at | Tumour protein D52-like 1 | 3.29 | Oncogene |
| 214308_s_at | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase) | 3.28 | Enzyme |
| 205348_s_at | Dynein, cytoplasmic, intermediate polypeptide 1 | 3.24 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 219735_s_at | LBP protein; likely ortholog of mouse CRTR-1 | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 211676_s_at | Interferon gamma receptor 1 | 3.22 | Immune response |
| 205345_at | BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 | 3.20 | Apoptosis |
| 219968_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 210145_at | Phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) | 3.18 | Enzyme |
| 206299_at | TED protein | 3.17 | Unknown |
| 209218_at | Squalene epoxidase | 3.16 | Enzyme |
| 207950_s_at | Ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) | 3.14 | Membrane protein |
| 217276_x_at | Kraken-like | 3.13 | Enzyme |
| 201467_s_at | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 | 3.12 | Enzyme |
| 208286_x_at | POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 | 3.12 | Transcription factor |
| 211113_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 | 3.12 | Transporter |
| 204187_at | Guanosine monophosphate reductase | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 215783_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.11 | Enzyme |
| 221648_s_at | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203892_at | CGI-146 protein | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 204698_at | WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 | 3.05 | Unknown |
| 202149_at | Interferon stimulated gene 20kDa | 3.04 | Immune response |
| 210062_s_at | Enhancer of filamentation 1 | 3.04 | Transcription factor |
| 213029_at | KRAB-zinc finger protein SZF1-1 | 3.04 | Unknown |
Down-regulated genes in hCG+7
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funcional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 205713_s_at | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple) | 58.55 | Structural protein |
| 203716_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 54.37 | Immune response |
| 211478_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 43.48 | Immune response |
| 203888_at | Thrombomodulin | 24.38 | Coagulation factor |
| 205266_at | Leukaemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) | 23.02 | Cytokine |
| 220196_at | Mucin 16 | 13.61 | Membrane protein |
| 203717_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 13.58 | Immune response |
| 205765_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 12.96 | Energy transduction |
| 201348_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 12.51 | Enzyme |
| 205302_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 | 11.99 | Regulatory protein |
| 209641_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 11.12 | Transporter |
| 214091_s_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 11.12 | Enzyme |
| 207254_at | Solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 | 10.62 | Transporter |
| 208791_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 10.04 | Apoptosis |
| 206859_s_at | Progestagen-associated endometrial protein (placental protein 14, pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, alpha uterine protein) | 9.83 | Secreted protein |
| 214234_s_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 9.32 | Energy transduction |
| 203951_at | Calponin 1, basic, smooth muscle | 9.26 | Muscle protein |
| 208335_s_at | Duffy blood group | 9.24 | Receptor |
| 218002_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 | 8.95 | Chemokine |
| 206396_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 8.18 | Transporter |
| 208161_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 8.04 | Transporter |
| 205513_at | Transcobalamin I (vitamin B12 binding protein, R binder family) | 7.77 | Transporter |
| 207961_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 7.71 | Muscle protein |
| 204863_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 7.42 | Immune response |
| 212531_at | Lipocalin 2 (oncogene 24p3) | 7.35 | Protection factor |
| 209260_at | Stratifin | 7.04 | Epithelial marker |
| 209201_x_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 6.83 | Chemokine |
| 209173_at | Anterior gradient 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) | 6.73 | Unknown |
| 206010_at | Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | 6.41 | Enzyme |
| 205083_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 6.24 | Enzyme |
| 203559_s_at | Amiloride binding protein 1 [amine oxidase (copper-containing)] | 6.01 | Enzyme |
| 219369_s_at | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 137 | 5.92 | Unknown |
| 203126_at | Inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 | 5.88 | Enzyme |
| 214235_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 5.86 | Energy transduction |
| 203824_at | Transmembrane 4 superfamily member 3 | 5.84 | Transmembrane protein |
| 202481_at | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 1 | 5.80 | Enzyme |
| 209270_at | laminin, beta 3 | 5.68 | Cell adhesion |
| 208893_s_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 6 | 5.66 | Signal transduction |
| 220293_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ14298 | 5.62 | Unknown |
| 206392_s_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 5.39 | Receptor |
| 205082_s_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 5.27 | Enzyme |
| 210652_s_at | Chromosome 1 open reading frame 34 | 5.26 | Unknown |
| 204304_s_at | Prominin 1 | 5.03 | Membrana protein |
| 206043_s_at | KIAA0703 gene product | 5.02 | Unknown |
| 213524_s_at | Putative lymphocyte G0/G1 switch gene | 4.95 | Regulatory protein |
| 206391_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.79 | Receptor |
| 203887_s_at | Thrombomodulin | 4.75 | Coagulation factor |
| 209114_at | Tetraspan 1 | 4.75 | Cell adhesion |
| 205844_at | Vanin 1 | 4.74 | Membrana protein |
| 217521_at | Histidine ammonia-lyase | 4.74 | Enzyme |
| 213664_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 4.73 | Transporter |
| 212143_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (3′ region) (human, tuberous sclerosis cells, mRNA Partial, 704 nt) | 4.67 | Regulatory protein |
| 204720_s_at | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 6 | 4.66 | Unknown |
| 220017_x_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 | 4.66 | Energy transduction |
| 39249_at | Aquaporin 3 | 4.61 | Channel |
| 205674_x_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.60 | Transmembrane protein |
| 212196_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564F053 (from clone DKFZp564F053) | 4.55 | Unknown |
| 201497_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 4.47 | Muscle protein |
| 211919_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 4.47 | Chemokine |
| 207434_s_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.46 | Transmembrane protein |
| 221872_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.46 | Receptor |
| 205627_at | Cytidine deaminase | 4.45 | Enzyme |
| 209687_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) | 4.40 | Chemokine |
| 205141_at | Ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 | 4.36 | Enzyme |
| 206643_at | Histidina ammonia-lyase | 4.35 | Enzyme |
| 208792_s_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 4.22 | Apoptosis |
| 204259_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 206303_s_at | Nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 4 | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 204726_at | Cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) | 4.09 | Cell adhesion |
| 203766_s_at | Leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) | 4.08 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 205730_s_at | KIAA0843 protein | 4.06 | Unknown |
| 203662_s_at | Tropomodulin 1 | 4.05 | Muscle protein |
| 219195_at | Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 | 4.05 | Receptor |
| 205681_at | BCL2-related protein A1 | 3.97 | Apoptosis |
| 211000_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 3.97 | Immune response |
| 212942_s_at | KIAA1199 protein | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 219313_at | Hypothetical protein DKFZp434C0328 | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 206631_at | Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53 kDa | 3.88 | Receptor |
| 210095_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 | 3.85 | Regulatory protein |
| 205547_s_at | Transgelin | 3.72 | Muscle protein |
| 202357_s_at | B-factor, properdin | 3.66 | Immune response |
| 208138_at | Gastrin | 3.64 | Regulatory protein |
| 218404_at | Sorting nexin 10 | 3.64 | Unknown |
| 202541_at | Small inducible cytokine subfamily E, member 1 (endothelial monocyte-activating) | 3.61 | Chemotaxis |
| 208102_s_at | Pleckstrin and Sec7 domain protein | 3.58 | Secretion involved |
| 206488_s_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.55 | Channel |
| 39248_at | CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor) | 3.55 | Receptor |
| 204363_at | Coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) | 3.52 | Coagulation factor |
| 201998_at | Sialyltransferase 1 (beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase) | 3.41 | Enzyme |
| 209869_at | Adrenergic, alpha-2A- receptor | 3.37 | Receptor |
| 212326_at | KIAA0453 protein | 3.34 | Unknown |
| 220112_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ11795 | 3.32 | Unknown |
| 219630_at | Epithelial protein up-regulated in carcinoma, membrane associated protein 17 | 3.30 | Membrane protein |
| 205074_at | Solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 5 | 3.28 | Transporter |
| 203144_s_at | KIAA0040 gene product | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 205597_at | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 29 | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 206528_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 | 3.25 | Channel |
| 201110_s_at | Thrombospondin 1 | 3.24 | Cell adhesion |
| 203878_s_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 11 (stromelysin 3) | 3.24 | Enzyme |
| 201510_at | E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific) | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 201843_s_at | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 | 3.22 | Extracellular matrix protein |
| 206785_s_at | Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 1 | 3.22 | Receptor |
| 204273_at | Endothelin receptor type B | 3.20 | Receptor |
| 219432_at | Ellis van Creveld síndrome | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 209373_at | BENE protein | 3.13 | Unknown |
| 209552_at | Paired box gene 8 | 3.13 | Regulatory protein |
| 209955_s_at | Fibroblast activation protein, alpha | 3.10 | Receptor |
| 203060_s_at | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 2 | 3.08 | Enzyme |
| 212741_at | Monoamine oxidase A | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203725_at | Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha | 3.03 | Neuromodulator |
| 205190_at | Plastin 1 (I isoform) | 3.03 | Signal transduction |
| 219010_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ10901 | 3.03 | Unknown |
| 203747_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.02 | Channel |
| 205654_at | Complement component 4 binding protein, alpha | 3.02 | Immune response |
| 203083_at | Thrombospondin 2 | 3.01 | Cell adhesion |
| 205355_at | Acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, short/branched chain | 3.00 | Enzyme |
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funcional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 205713_s_at | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple) | 58.55 | Structural protein |
| 203716_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 54.37 | Immune response |
| 211478_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 43.48 | Immune response |
| 203888_at | Thrombomodulin | 24.38 | Coagulation factor |
| 205266_at | Leukaemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) | 23.02 | Cytokine |
| 220196_at | Mucin 16 | 13.61 | Membrane protein |
| 203717_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 13.58 | Immune response |
| 205765_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 12.96 | Energy transduction |
| 201348_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 12.51 | Enzyme |
| 205302_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 | 11.99 | Regulatory protein |
| 209641_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 11.12 | Transporter |
| 214091_s_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 11.12 | Enzyme |
| 207254_at | Solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 | 10.62 | Transporter |
| 208791_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 10.04 | Apoptosis |
| 206859_s_at | Progestagen-associated endometrial protein (placental protein 14, pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, alpha uterine protein) | 9.83 | Secreted protein |
| 214234_s_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 9.32 | Energy transduction |
| 203951_at | Calponin 1, basic, smooth muscle | 9.26 | Muscle protein |
| 208335_s_at | Duffy blood group | 9.24 | Receptor |
| 218002_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 | 8.95 | Chemokine |
| 206396_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 8.18 | Transporter |
| 208161_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 8.04 | Transporter |
| 205513_at | Transcobalamin I (vitamin B12 binding protein, R binder family) | 7.77 | Transporter |
| 207961_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 7.71 | Muscle protein |
| 204863_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 7.42 | Immune response |
| 212531_at | Lipocalin 2 (oncogene 24p3) | 7.35 | Protection factor |
| 209260_at | Stratifin | 7.04 | Epithelial marker |
| 209201_x_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 6.83 | Chemokine |
| 209173_at | Anterior gradient 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) | 6.73 | Unknown |
| 206010_at | Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | 6.41 | Enzyme |
| 205083_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 6.24 | Enzyme |
| 203559_s_at | Amiloride binding protein 1 [amine oxidase (copper-containing)] | 6.01 | Enzyme |
| 219369_s_at | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 137 | 5.92 | Unknown |
| 203126_at | Inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 | 5.88 | Enzyme |
| 214235_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 5.86 | Energy transduction |
| 203824_at | Transmembrane 4 superfamily member 3 | 5.84 | Transmembrane protein |
| 202481_at | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 1 | 5.80 | Enzyme |
| 209270_at | laminin, beta 3 | 5.68 | Cell adhesion |
| 208893_s_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 6 | 5.66 | Signal transduction |
| 220293_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ14298 | 5.62 | Unknown |
| 206392_s_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 5.39 | Receptor |
| 205082_s_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 5.27 | Enzyme |
| 210652_s_at | Chromosome 1 open reading frame 34 | 5.26 | Unknown |
| 204304_s_at | Prominin 1 | 5.03 | Membrana protein |
| 206043_s_at | KIAA0703 gene product | 5.02 | Unknown |
| 213524_s_at | Putative lymphocyte G0/G1 switch gene | 4.95 | Regulatory protein |
| 206391_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.79 | Receptor |
| 203887_s_at | Thrombomodulin | 4.75 | Coagulation factor |
| 209114_at | Tetraspan 1 | 4.75 | Cell adhesion |
| 205844_at | Vanin 1 | 4.74 | Membrana protein |
| 217521_at | Histidine ammonia-lyase | 4.74 | Enzyme |
| 213664_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 4.73 | Transporter |
| 212143_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (3′ region) (human, tuberous sclerosis cells, mRNA Partial, 704 nt) | 4.67 | Regulatory protein |
| 204720_s_at | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 6 | 4.66 | Unknown |
| 220017_x_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 | 4.66 | Energy transduction |
| 39249_at | Aquaporin 3 | 4.61 | Channel |
| 205674_x_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.60 | Transmembrane protein |
| 212196_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564F053 (from clone DKFZp564F053) | 4.55 | Unknown |
| 201497_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 4.47 | Muscle protein |
| 211919_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 4.47 | Chemokine |
| 207434_s_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.46 | Transmembrane protein |
| 221872_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.46 | Receptor |
| 205627_at | Cytidine deaminase | 4.45 | Enzyme |
| 209687_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) | 4.40 | Chemokine |
| 205141_at | Ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 | 4.36 | Enzyme |
| 206643_at | Histidina ammonia-lyase | 4.35 | Enzyme |
| 208792_s_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 4.22 | Apoptosis |
| 204259_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 206303_s_at | Nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 4 | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 204726_at | Cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) | 4.09 | Cell adhesion |
| 203766_s_at | Leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) | 4.08 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 205730_s_at | KIAA0843 protein | 4.06 | Unknown |
| 203662_s_at | Tropomodulin 1 | 4.05 | Muscle protein |
| 219195_at | Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 | 4.05 | Receptor |
| 205681_at | BCL2-related protein A1 | 3.97 | Apoptosis |
| 211000_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 3.97 | Immune response |
| 212942_s_at | KIAA1199 protein | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 219313_at | Hypothetical protein DKFZp434C0328 | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 206631_at | Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53 kDa | 3.88 | Receptor |
| 210095_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 | 3.85 | Regulatory protein |
| 205547_s_at | Transgelin | 3.72 | Muscle protein |
| 202357_s_at | B-factor, properdin | 3.66 | Immune response |
| 208138_at | Gastrin | 3.64 | Regulatory protein |
| 218404_at | Sorting nexin 10 | 3.64 | Unknown |
| 202541_at | Small inducible cytokine subfamily E, member 1 (endothelial monocyte-activating) | 3.61 | Chemotaxis |
| 208102_s_at | Pleckstrin and Sec7 domain protein | 3.58 | Secretion involved |
| 206488_s_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.55 | Channel |
| 39248_at | CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor) | 3.55 | Receptor |
| 204363_at | Coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) | 3.52 | Coagulation factor |
| 201998_at | Sialyltransferase 1 (beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase) | 3.41 | Enzyme |
| 209869_at | Adrenergic, alpha-2A- receptor | 3.37 | Receptor |
| 212326_at | KIAA0453 protein | 3.34 | Unknown |
| 220112_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ11795 | 3.32 | Unknown |
| 219630_at | Epithelial protein up-regulated in carcinoma, membrane associated protein 17 | 3.30 | Membrane protein |
| 205074_at | Solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 5 | 3.28 | Transporter |
| 203144_s_at | KIAA0040 gene product | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 205597_at | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 29 | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 206528_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 | 3.25 | Channel |
| 201110_s_at | Thrombospondin 1 | 3.24 | Cell adhesion |
| 203878_s_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 11 (stromelysin 3) | 3.24 | Enzyme |
| 201510_at | E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific) | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 201843_s_at | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 | 3.22 | Extracellular matrix protein |
| 206785_s_at | Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 1 | 3.22 | Receptor |
| 204273_at | Endothelin receptor type B | 3.20 | Receptor |
| 219432_at | Ellis van Creveld síndrome | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 209373_at | BENE protein | 3.13 | Unknown |
| 209552_at | Paired box gene 8 | 3.13 | Regulatory protein |
| 209955_s_at | Fibroblast activation protein, alpha | 3.10 | Receptor |
| 203060_s_at | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 2 | 3.08 | Enzyme |
| 212741_at | Monoamine oxidase A | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203725_at | Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha | 3.03 | Neuromodulator |
| 205190_at | Plastin 1 (I isoform) | 3.03 | Signal transduction |
| 219010_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ10901 | 3.03 | Unknown |
| 203747_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.02 | Channel |
| 205654_at | Complement component 4 binding protein, alpha | 3.02 | Immune response |
| 203083_at | Thrombospondin 2 | 3.01 | Cell adhesion |
| 205355_at | Acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, short/branched chain | 3.00 | Enzyme |
Down-regulated genes in hCG+7
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funcional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 205713_s_at | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple) | 58.55 | Structural protein |
| 203716_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 54.37 | Immune response |
| 211478_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 43.48 | Immune response |
| 203888_at | Thrombomodulin | 24.38 | Coagulation factor |
| 205266_at | Leukaemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) | 23.02 | Cytokine |
| 220196_at | Mucin 16 | 13.61 | Membrane protein |
| 203717_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 13.58 | Immune response |
| 205765_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 12.96 | Energy transduction |
| 201348_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 12.51 | Enzyme |
| 205302_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 | 11.99 | Regulatory protein |
| 209641_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 11.12 | Transporter |
| 214091_s_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 11.12 | Enzyme |
| 207254_at | Solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 | 10.62 | Transporter |
| 208791_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 10.04 | Apoptosis |
| 206859_s_at | Progestagen-associated endometrial protein (placental protein 14, pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, alpha uterine protein) | 9.83 | Secreted protein |
| 214234_s_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 9.32 | Energy transduction |
| 203951_at | Calponin 1, basic, smooth muscle | 9.26 | Muscle protein |
| 208335_s_at | Duffy blood group | 9.24 | Receptor |
| 218002_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 | 8.95 | Chemokine |
| 206396_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 8.18 | Transporter |
| 208161_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 8.04 | Transporter |
| 205513_at | Transcobalamin I (vitamin B12 binding protein, R binder family) | 7.77 | Transporter |
| 207961_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 7.71 | Muscle protein |
| 204863_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 7.42 | Immune response |
| 212531_at | Lipocalin 2 (oncogene 24p3) | 7.35 | Protection factor |
| 209260_at | Stratifin | 7.04 | Epithelial marker |
| 209201_x_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 6.83 | Chemokine |
| 209173_at | Anterior gradient 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) | 6.73 | Unknown |
| 206010_at | Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | 6.41 | Enzyme |
| 205083_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 6.24 | Enzyme |
| 203559_s_at | Amiloride binding protein 1 [amine oxidase (copper-containing)] | 6.01 | Enzyme |
| 219369_s_at | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 137 | 5.92 | Unknown |
| 203126_at | Inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 | 5.88 | Enzyme |
| 214235_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 5.86 | Energy transduction |
| 203824_at | Transmembrane 4 superfamily member 3 | 5.84 | Transmembrane protein |
| 202481_at | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 1 | 5.80 | Enzyme |
| 209270_at | laminin, beta 3 | 5.68 | Cell adhesion |
| 208893_s_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 6 | 5.66 | Signal transduction |
| 220293_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ14298 | 5.62 | Unknown |
| 206392_s_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 5.39 | Receptor |
| 205082_s_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 5.27 | Enzyme |
| 210652_s_at | Chromosome 1 open reading frame 34 | 5.26 | Unknown |
| 204304_s_at | Prominin 1 | 5.03 | Membrana protein |
| 206043_s_at | KIAA0703 gene product | 5.02 | Unknown |
| 213524_s_at | Putative lymphocyte G0/G1 switch gene | 4.95 | Regulatory protein |
| 206391_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.79 | Receptor |
| 203887_s_at | Thrombomodulin | 4.75 | Coagulation factor |
| 209114_at | Tetraspan 1 | 4.75 | Cell adhesion |
| 205844_at | Vanin 1 | 4.74 | Membrana protein |
| 217521_at | Histidine ammonia-lyase | 4.74 | Enzyme |
| 213664_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 4.73 | Transporter |
| 212143_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (3′ region) (human, tuberous sclerosis cells, mRNA Partial, 704 nt) | 4.67 | Regulatory protein |
| 204720_s_at | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 6 | 4.66 | Unknown |
| 220017_x_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 | 4.66 | Energy transduction |
| 39249_at | Aquaporin 3 | 4.61 | Channel |
| 205674_x_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.60 | Transmembrane protein |
| 212196_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564F053 (from clone DKFZp564F053) | 4.55 | Unknown |
| 201497_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 4.47 | Muscle protein |
| 211919_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 4.47 | Chemokine |
| 207434_s_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.46 | Transmembrane protein |
| 221872_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.46 | Receptor |
| 205627_at | Cytidine deaminase | 4.45 | Enzyme |
| 209687_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) | 4.40 | Chemokine |
| 205141_at | Ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 | 4.36 | Enzyme |
| 206643_at | Histidina ammonia-lyase | 4.35 | Enzyme |
| 208792_s_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 4.22 | Apoptosis |
| 204259_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 206303_s_at | Nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 4 | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 204726_at | Cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) | 4.09 | Cell adhesion |
| 203766_s_at | Leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) | 4.08 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 205730_s_at | KIAA0843 protein | 4.06 | Unknown |
| 203662_s_at | Tropomodulin 1 | 4.05 | Muscle protein |
| 219195_at | Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 | 4.05 | Receptor |
| 205681_at | BCL2-related protein A1 | 3.97 | Apoptosis |
| 211000_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 3.97 | Immune response |
| 212942_s_at | KIAA1199 protein | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 219313_at | Hypothetical protein DKFZp434C0328 | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 206631_at | Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53 kDa | 3.88 | Receptor |
| 210095_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 | 3.85 | Regulatory protein |
| 205547_s_at | Transgelin | 3.72 | Muscle protein |
| 202357_s_at | B-factor, properdin | 3.66 | Immune response |
| 208138_at | Gastrin | 3.64 | Regulatory protein |
| 218404_at | Sorting nexin 10 | 3.64 | Unknown |
| 202541_at | Small inducible cytokine subfamily E, member 1 (endothelial monocyte-activating) | 3.61 | Chemotaxis |
| 208102_s_at | Pleckstrin and Sec7 domain protein | 3.58 | Secretion involved |
| 206488_s_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.55 | Channel |
| 39248_at | CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor) | 3.55 | Receptor |
| 204363_at | Coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) | 3.52 | Coagulation factor |
| 201998_at | Sialyltransferase 1 (beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase) | 3.41 | Enzyme |
| 209869_at | Adrenergic, alpha-2A- receptor | 3.37 | Receptor |
| 212326_at | KIAA0453 protein | 3.34 | Unknown |
| 220112_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ11795 | 3.32 | Unknown |
| 219630_at | Epithelial protein up-regulated in carcinoma, membrane associated protein 17 | 3.30 | Membrane protein |
| 205074_at | Solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 5 | 3.28 | Transporter |
| 203144_s_at | KIAA0040 gene product | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 205597_at | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 29 | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 206528_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 | 3.25 | Channel |
| 201110_s_at | Thrombospondin 1 | 3.24 | Cell adhesion |
| 203878_s_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 11 (stromelysin 3) | 3.24 | Enzyme |
| 201510_at | E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific) | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 201843_s_at | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 | 3.22 | Extracellular matrix protein |
| 206785_s_at | Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 1 | 3.22 | Receptor |
| 204273_at | Endothelin receptor type B | 3.20 | Receptor |
| 219432_at | Ellis van Creveld síndrome | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 209373_at | BENE protein | 3.13 | Unknown |
| 209552_at | Paired box gene 8 | 3.13 | Regulatory protein |
| 209955_s_at | Fibroblast activation protein, alpha | 3.10 | Receptor |
| 203060_s_at | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 2 | 3.08 | Enzyme |
| 212741_at | Monoamine oxidase A | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203725_at | Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha | 3.03 | Neuromodulator |
| 205190_at | Plastin 1 (I isoform) | 3.03 | Signal transduction |
| 219010_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ10901 | 3.03 | Unknown |
| 203747_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.02 | Channel |
| 205654_at | Complement component 4 binding protein, alpha | 3.02 | Immune response |
| 203083_at | Thrombospondin 2 | 3.01 | Cell adhesion |
| 205355_at | Acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, short/branched chain | 3.00 | Enzyme |
| Sequence code . | Name . | Fold change . | Funcional category . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 205713_s_at | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple) | 58.55 | Structural protein |
| 203716_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 54.37 | Immune response |
| 211478_s_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 43.48 | Immune response |
| 203888_at | Thrombomodulin | 24.38 | Coagulation factor |
| 205266_at | Leukaemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) | 23.02 | Cytokine |
| 220196_at | Mucin 16 | 13.61 | Membrane protein |
| 203717_at | Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (CD26, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2) | 13.58 | Immune response |
| 205765_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 12.96 | Energy transduction |
| 201348_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 12.51 | Enzyme |
| 205302_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 | 11.99 | Regulatory protein |
| 209641_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 11.12 | Transporter |
| 214091_s_at | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | 11.12 | Enzyme |
| 207254_at | Solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 | 10.62 | Transporter |
| 208791_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 10.04 | Apoptosis |
| 206859_s_at | Progestagen-associated endometrial protein (placental protein 14, pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, alpha uterine protein) | 9.83 | Secreted protein |
| 214234_s_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 9.32 | Energy transduction |
| 203951_at | Calponin 1, basic, smooth muscle | 9.26 | Muscle protein |
| 208335_s_at | Duffy blood group | 9.24 | Receptor |
| 218002_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 | 8.95 | Chemokine |
| 206396_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 8.18 | Transporter |
| 208161_s_at | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 3 | 8.04 | Transporter |
| 205513_at | Transcobalamin I (vitamin B12 binding protein, R binder family) | 7.77 | Transporter |
| 207961_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 7.71 | Muscle protein |
| 204863_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 7.42 | Immune response |
| 212531_at | Lipocalin 2 (oncogene 24p3) | 7.35 | Protection factor |
| 209260_at | Stratifin | 7.04 | Epithelial marker |
| 209201_x_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 6.83 | Chemokine |
| 209173_at | Anterior gradient 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) | 6.73 | Unknown |
| 206010_at | Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | 6.41 | Enzyme |
| 205083_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 6.24 | Enzyme |
| 203559_s_at | Amiloride binding protein 1 [amine oxidase (copper-containing)] | 6.01 | Enzyme |
| 219369_s_at | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 137 | 5.92 | Unknown |
| 203126_at | Inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 | 5.88 | Enzyme |
| 214235_at | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 5 | 5.86 | Energy transduction |
| 203824_at | Transmembrane 4 superfamily member 3 | 5.84 | Transmembrane protein |
| 202481_at | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 1 | 5.80 | Enzyme |
| 209270_at | laminin, beta 3 | 5.68 | Cell adhesion |
| 208893_s_at | Dual specificity phosphatase 6 | 5.66 | Signal transduction |
| 220293_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ14298 | 5.62 | Unknown |
| 206392_s_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 5.39 | Receptor |
| 205082_s_at | Aldehyde oxidase 1 | 5.27 | Enzyme |
| 210652_s_at | Chromosome 1 open reading frame 34 | 5.26 | Unknown |
| 204304_s_at | Prominin 1 | 5.03 | Membrana protein |
| 206043_s_at | KIAA0703 gene product | 5.02 | Unknown |
| 213524_s_at | Putative lymphocyte G0/G1 switch gene | 4.95 | Regulatory protein |
| 206391_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.79 | Receptor |
| 203887_s_at | Thrombomodulin | 4.75 | Coagulation factor |
| 209114_at | Tetraspan 1 | 4.75 | Cell adhesion |
| 205844_at | Vanin 1 | 4.74 | Membrana protein |
| 217521_at | Histidine ammonia-lyase | 4.74 | Enzyme |
| 213664_at | Solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 | 4.73 | Transporter |
| 212143_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (3′ region) (human, tuberous sclerosis cells, mRNA Partial, 704 nt) | 4.67 | Regulatory protein |
| 204720_s_at | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 6 | 4.66 | Unknown |
| 220017_x_at | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 | 4.66 | Energy transduction |
| 39249_at | Aquaporin 3 | 4.61 | Channel |
| 205674_x_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.60 | Transmembrane protein |
| 212196_at | Homo sapiens mRNA; cDNA DKFZp564F053 (from clone DKFZp564F053) | 4.55 | Unknown |
| 201497_x_at | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | 4.47 | Muscle protein |
| 211919_s_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 4.47 | Chemokine |
| 207434_s_at | FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 | 4.46 | Transmembrane protein |
| 221872_at | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 4.46 | Receptor |
| 205627_at | Cytidine deaminase | 4.45 | Enzyme |
| 209687_at | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) | 4.40 | Chemokine |
| 205141_at | Ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 | 4.36 | Enzyme |
| 206643_at | Histidina ammonia-lyase | 4.35 | Enzyme |
| 208792_s_at | Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor, SP-40,40, sulfated glycoprotein 2, testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, apolipoprotein J) | 4.22 | Apoptosis |
| 204259_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 206303_s_at | Nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 4 | 4.20 | Enzyme |
| 204726_at | Cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) | 4.09 | Cell adhesion |
| 203766_s_at | Leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) | 4.08 | Cytoskeletal protein |
| 205730_s_at | KIAA0843 protein | 4.06 | Unknown |
| 203662_s_at | Tropomodulin 1 | 4.05 | Muscle protein |
| 219195_at | Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 | 4.05 | Receptor |
| 205681_at | BCL2-related protein A1 | 3.97 | Apoptosis |
| 211000_s_at | Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) | 3.97 | Immune response |
| 212942_s_at | KIAA1199 protein | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 219313_at | Hypothetical protein DKFZp434C0328 | 3.96 | Unknown |
| 206631_at | Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53 kDa | 3.88 | Receptor |
| 210095_s_at | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 | 3.85 | Regulatory protein |
| 205547_s_at | Transgelin | 3.72 | Muscle protein |
| 202357_s_at | B-factor, properdin | 3.66 | Immune response |
| 208138_at | Gastrin | 3.64 | Regulatory protein |
| 218404_at | Sorting nexin 10 | 3.64 | Unknown |
| 202541_at | Small inducible cytokine subfamily E, member 1 (endothelial monocyte-activating) | 3.61 | Chemotaxis |
| 208102_s_at | Pleckstrin and Sec7 domain protein | 3.58 | Secretion involved |
| 206488_s_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.55 | Channel |
| 39248_at | CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor) | 3.55 | Receptor |
| 204363_at | Coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) | 3.52 | Coagulation factor |
| 201998_at | Sialyltransferase 1 (beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase) | 3.41 | Enzyme |
| 209869_at | Adrenergic, alpha-2A- receptor | 3.37 | Receptor |
| 212326_at | KIAA0453 protein | 3.34 | Unknown |
| 220112_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ11795 | 3.32 | Unknown |
| 219630_at | Epithelial protein up-regulated in carcinoma, membrane associated protein 17 | 3.30 | Membrane protein |
| 205074_at | Solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 5 | 3.28 | Transporter |
| 203144_s_at | KIAA0040 gene product | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 205597_at | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 29 | 3.26 | Unknown |
| 206528_at | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 | 3.25 | Channel |
| 201110_s_at | Thrombospondin 1 | 3.24 | Cell adhesion |
| 203878_s_at | Matrix metalloproteinase 11 (stromelysin 3) | 3.24 | Enzyme |
| 201510_at | E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific) | 3.23 | Unknown |
| 201843_s_at | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 | 3.22 | Extracellular matrix protein |
| 206785_s_at | Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 1 | 3.22 | Receptor |
| 204273_at | Endothelin receptor type B | 3.20 | Receptor |
| 219432_at | Ellis van Creveld síndrome | 3.19 | Unknown |
| 209373_at | BENE protein | 3.13 | Unknown |
| 209552_at | Paired box gene 8 | 3.13 | Regulatory protein |
| 209955_s_at | Fibroblast activation protein, alpha | 3.10 | Receptor |
| 203060_s_at | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 2 | 3.08 | Enzyme |
| 212741_at | Monoamine oxidase A | 3.07 | Enzyme |
| 203725_at | Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha | 3.03 | Neuromodulator |
| 205190_at | Plastin 1 (I isoform) | 3.03 | Signal transduction |
| 219010_at | Hypothetical protein FLJ10901 | 3.03 | Unknown |
| 203747_at | Aquaporin 3 | 3.02 | Channel |
| 205654_at | Complement component 4 binding protein, alpha | 3.02 | Immune response |
| 203083_at | Thrombospondin 2 | 3.01 | Cell adhesion |
| 205355_at | Acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, short/branched chain | 3.00 | Enzyme |
Number of genes up- and down-regulated in the different comparison performed
| Comparison . | Number of regulated genes . | LH2/LH7 regulated genes FC>2.0 . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up 894 | Down 505 | Not regulated | ||||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Up 281 | 9 | 115 | 157 | ||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Down 277 | 227 | 0 | 50 | ||
| Comparison . | Number of regulated genes . | LH2/LH7 regulated genes FC>2.0 . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up 894 | Down 505 | Not regulated | ||||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Up 281 | 9 | 115 | 157 | ||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Down 277 | 227 | 0 | 50 | ||
Number of genes up- and down-regulated in the different comparison performed
| Comparison . | Number of regulated genes . | LH2/LH7 regulated genes FC>2.0 . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up 894 | Down 505 | Not regulated | ||||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Up 281 | 9 | 115 | 157 | ||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Down 277 | 227 | 0 | 50 | ||
| Comparison . | Number of regulated genes . | LH2/LH7 regulated genes FC>2.0 . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up 894 | Down 505 | Not regulated | ||||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Up 281 | 9 | 115 | 157 | ||
| hCG+7/LH+7 | Down 277 | 227 | 0 | 50 | ||
The authors would like to thank Andre van Staalduinen for performing the Q-PCR experiments. We also thank IVI Foundation professionals for processing of biopsies.
References
Akerstrom B, Flower DR and Salier JP (
American Society for Reproductive Medicine (
Bennett M (
Borthwick J, Charnock-Jones S, Tom B et al. (
Carson D, Lagow E, Thathiah A et al. (
Chen DB, Hilsenrath R, Yang ZM et al. (
Develioglu OH, Hsiu JG, Nikas G et al. (
Esworthy RS, Chu F-F, Paxton RJ et al. (
Fauser BC and Devroey P (
Gearing DP, Gough NM, King JA et al. (
Giudice LC (
Gorodzanskaya EG, Larionova VB, Zubrikhina GN et al. (
Hough CD, Cho KR, Zonderman AB et al. (
Imai K, Maeda M, Fujiwara H et al. (
Julkunen M, Koistinen R, Sjöberg J et al. (
Kao LC, Tulac S, Lobo S et al. (
Kao LC, Germeyer A, Tulac S et al. (
Koistinen H, Easton RL, Chiu PC et al. (
Kolb BA and Paulson RJ (
Kolibianakis EM, Bourgain C, Platteau P et al. (
Lass A, Weiser W, Munafo A and Loumaye E (
Liu WJ and Hansen PJ (
Liu G, Loraine AE, Shigeta R et al. (
Ma WG, Song H, Das SK et al. (
Moestrup SK, Birn H, Fischer PB et al. (
Nikas G (
Nikas G, Develioglu OH, Toner JP et al. (
Paulson RJ, Sauer MV and Lobo RA (
Pellicer A, Valbuena D, Cano F et al. (
Psychoyos A (
Riesewijk A, Martín J, van Os R et al. (
Sato Y, Fujiwara H, Higuchi T, Yoshioka S, Tatsumi K, Maeda M and Fujii S (
Seif MW, Pearson JM, Ibrahim ZH et al. (
Simón C, Cano F, Valbuena D et al. (
Simón C, Mercader A, Francés A et al. (
Simón C, García-Velasco J, Valbuena D et al. (
Simón C, Domínguez F, Valbuena D et al. (
Stewart CL, Kaspar P, Brunet LJ et al. (
Vogiagis D, Marsh MM, Fry RC et al. (
Author notes
1Instituto Valenciano de Infertilidad Foundation (FIVI)-Valencia University, Spain, 2NV Organon, Department of Pharmacology, Oss, The Netherlands