Abstract
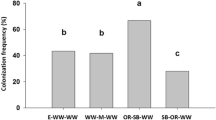
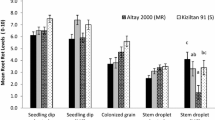
The effect of different crop rotation treatments and within-treatment crop sequences on crown rot and the incidence of Fusarium pseudograminearum in crowns of wheat from a long-term crop rotation experiment at Langgewens Experimental Farm, Moorreesburg, South Africa, were studied in 2000, 2001 and 2002. Crop rotation treatments included the following crops: canola (C), lupin (L), medic (M), medic-clover mixture (Mc) and wheat (W). Rotation treatments (RT) and within-treatment crop sequences were: RT 1=W-W-W-W, RT 2=C-W-W-W, W-C-W-W,W-W-C-W, RT 3=C-W-L-W, L-W-C-W, RT 4=W-L-C-W, L-C-W-W, RT 5=M-W-M-W, RT 6=Mc-W-Mc-W and RT 7=M-C-M-W. Crop rotation significantly affected the incidence of F. pseudograminearum, crown rot incidence and severity, dry mass and grain yield. The incidence of F. Pseudograminearum was significantly higher on wheat for the rotation treatment that included 3 years of wheat and 1 year of canola compared with the other treatments, and the highest severities and incidences of crown rot and the lowest yields were also recorded for this treatment and the monoculture wheat. The lowest incidences of the fungus, as well as crown rot incidences and severities, and the highest yields were recorded for the rotation treatment that alternated wheat with a medic-clover mixture and the treatment that included wheat after 3 years of rotation with broadleaf crops. Crop rotation should, therefore, be an important component of management strategies against crown rot of wheat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki T, O’Donnell K (1999) Morphological and molecular characterization of Fusarium graminearum sp. nov. formerly recognized as the Group 1 population of F. graminearum. Mycologia 91, 597–609.
Backhouse D, Abubakar AA, Burgess LW, Dennis JI, Hollaway GJ, et al. (2004) Survey of Fusarium species associated with crown rot of wheat and barley in eastern Australia. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 255–261. doi: 10.1071/AP04010
Balmas V (1994) Root rot of wheat in Italy caused by Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Plant Disease 78, 317.
Burgess LW, Backhouse D, Swan LJ, Esdaile RJ (1996) Control of Fusarium crown rot of wheat by late stubble burning and rotation with sorghum. Australasian Plant Pathology 25, 229–233. doi: 10.1071/AP96042
Burgess LW, Backhouse D, Summerell BA, Swan LJ (2001) Crown rot of wheat. In ‘Fusarium — Paul E. Nelson Memorial Symposium’. (Eds BA Summerell, JF Leslie, D Backhouse, WL Bryden, LW Burgess) pp. 271–294. (American Phytopathological Society: St Paul)
Cook RJ (1968) Fusarium root and foot rot of cereals in the Pacific north west. Phytopathology 58, 127–131.
Dodman RL, Wildermuth GB (1987) Inoculation methods for assessing resistance in wheat to crown rot caused by Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 38, 473–486.
Dodman RL, Wildermuth GB, Klein TA, Ellison FW (1985) Field resistance of wheat cultivars to crown rot (Fusarium graminearum Group 1). In ‘Ecology and management of soil borne plant pathogens’. (Eds CA Parker, AD Rovira, KJ Moore, PTW Wong, JF Kollmorgen) pp. 167–168. (American Phytopathological Society: St Paul)
Felton WL, Marcellos H, Alston C, Martin RJ, Backhouse D, Burgess LW, Herridge DF (1998) Chickpea in wheat-based cropping systems of northern New South Wales. II. Influence on biomass, grain yield and crown rot in the following wheat crop. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 49, 401–407. doi: 10.1071/A97067
Fisher NL, Burgess LW, Toussoun TA, Nelson PE (1982) Carnation leaves as a substrate and for preserving cultures of Fusarium species. Phytopathology 72, 151–153.
Francis RG, Burgess LW (1977) Characteristics of two populations of Fusarium roseum ‘Graminearum’ in eastern Australia. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 68, 421–427.
Kirkegaard JA, Simpfendorfer S, Holland J, Bambach R, Moore KJ, Rebetzke GJ (2004) Effects of previous crops on crown rot and yield of durum and bread wheat in northern NSW. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 55, 321–334. doi: 10.1071/AR03178
Klaasen JA, Matthee FN, Marasas WFO, Van Schalkwyk DJ (1991) Comparative isolation of Fusarium species from plant debris in soil, and wheat stubble and crowns at different locations in the southern and western Cape. Phytophylactica 23, 299–307.
Klaasen JA, Matthee FN, Marasas WFO, Van Schalkwyk DJ (1992) Survey of Fusarium species associated with crowns of healthy-head and white-head wheat plants in the southern and western Cape province. Phytophylactica 24, 85–94.
Klein TA, Burgess LW, Ellison FW (1991) Incidence and spatial patterns of wheat plants infected by Fusarium graminearum Group 1 and the effect of crown rot on yield. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 42, 399–407. doi: 10.1071/AR9910399
Lamprecht SC, Knox-Davies PS, Marasas WFO (1984) Fusarium species associated with diseased root and crown tissue of annual Medicago species. Phytophylactica 16, 195–200.
Lamprecht SC, Knox-Davies PS, Marasas WFO (1988) Fungi associated with root rot of annual Medicago spp. Phytophylactica 20, 281–286.
Lamprecht SC, Marasas WFO, Van Wyk PS, Knox-Davies PS (1990) Cross-pathogenicity of Fusarium avenaceum and Fusarium graminearum Gr. 1 to Medicago truncatula and wheat. Phytophylactica 22, 209–211.
McKnight T, Hart J (1966) Some field observations on crown rot disease of wheat caused by Fusarium graminearum. Queensland Journal of Agriculture and Animal Sciences 23, 373–378.
MacVicar CN, Loxton RF, Lambrechts JJN, le Roux J, de Villiers JM, Verster E, Merrywheather FR, van Rooyen TH, Von M, Harmse HJ (1977) Soil classification: a binomial system for South Africa. (Department of Agricultural Technical Services: Pretoria)
Oswald JW (1950) Cultural variation, taxonomy and pathogenicity of Fusarium species associated with cereal root rots. Phytopathology 39, 359–376.
Purss GS (1966) Studies of varietal resistance to crown rot of wheat caused by Fusarium graminearum Schw. Queensland Journal of Agriculture and Animal Sciences 23, 257–264.
SAS (1999) ‘SAS/STAT user’s guide. Version 8, Vol. 2.’ (SAS Institute Inc.: Cary)
Scott DB (1990) Wheat diseases in South Africa. Technical Communication No. 220. Department of Agricultural Development, Republic of South Africa.
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52, 591–611. doi: 10.2307/2333709
Smiley RW, Patterson LM (1996) Pathogenic fungi associated with Fusarium foot rot of winter wheat in the semiarid Pacific Northwest. Plant Disease 80, 944–949.
Summerell BA, Burgess LW (1988) The influence of stubble management practices on the survival of Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Australasian Plant Pathology 17, 88–93. doi: 10.1071/APP9880088
Summerell BA, Burgess LW, Klein TA (1988) The impact of stubble management practices on crown rot of wheat. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 29, 91–98. doi: 10.1071/ EA9890091
Swan LJ, Backhouse D, Burgess LW (2000) Surface soil moisture and stubble management practice effects on the progress of infection of wheat by Fusarium pseudograminearum. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 40, 693–698. doi: 10.1071/EA99106
Tio M, Burgess LW, Nelson PE, Toussoun TA (1977) Techniques for the isolation, culture and preservation of the Fusaria. Australasian Plant Pathological Society Newsletter 6, 11–13. doi: 10.1071/APP9770011
Van Wyk PS, Los O, Pauer GD, Marasas WFO (1987) Geographic distribution and pathogenicity of Fusarium species associated with crown rot of wheat in the Orange Free State, South Africa. Phytophylactica 19, 271–274.
Van Wyk PS, Pauer GDC, Rheeder JP, Los O, Marasas WFO (1988) Reaction of different wheat cultivars to crown rot caused by Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Phytophylactica 20, 69–72.
Wallwork H, Butt M, Cheong JPE, Williams KJ (2004) Resistance to crown rot in wheat identified through an improved method for screening adult plants. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 1–7. doi: 10.1071/AP03073
Wearing AH, Burgess LW (1977) Distribution of Fusarium roseum ‘Graminearum’ Group 1 in eastern Australian wheat belt soils and its mode of survival. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 69, 429–442.
Wildermuth GB, McNamara RB (1994) Testing wheat seedlings for resistance to crown rot caused by Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Plant Disease 78, 949–953.
Wildermuth GB, Morgan JM (2004) Genotypic differences in partial resistance to crown rot caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum in relation to an osmoregulation gene in wheat. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 121–123. doi: 10.1071/AP03078
Wildermuth GB, Purss GS (1971) Further sources of field resistance to crown rot (Gibberella zeae) of cereals in Queensland. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture and Animal Husbandry 11, 455–459. doi: 10.1071/EA9710455
Wildermuth GB, McNamara RB, Sparks T (1999) Different expressions of resistance to crown rot in wheat. In ‘Proceedings of the First Australasian Soilborne Disease Symposium’. (Ed. RC Magarey) p. 79. (Bureau of Sugar Experiment Stations: Brisbane)
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research 14, 415–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamprecht, S.C., Marasas, W.F.O., Hardy, M.B. et al. Effect of crop rotation on crown rot and the incidence of Fusarium pseudograminearum in wheat in the Western Cape, South Africa. Australasian Plant Pathology 35, 419–426 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP06040
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP06040