Abstract
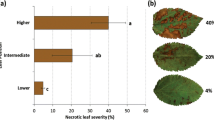
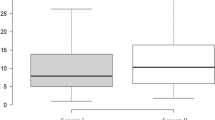
Chitinase enzymes are induced in many plants in response to pathogen challenge and other stress stimuli. Chitinase induction in flax leaves in response to inoculation with flax rust, caused by Melampsora lini (Pers.) Lev., was investigated in a line of flax (Forge) that has four resistance genes, viz. L6, M, N and P2. Four avirulent rust strains, each of which interacts with just one of the resistance genes in Forge, as well as a strain that is virulent on Forge, were used. Thus chitinase levels associated with resistance reactions triggered by the L6, M, N or P2 genes, and by a susceptible reaction, have been compared in the same host genotype. A marked increase in chitinase activity in inoculated leaves was observed with all four resistance reactions, with the increase occurring earlier with the P2 resistance reaction compared with the L6, M, and N reactions. A moderate increase in chitinase activity was also observed in systemic (new-growth) leaves of flax plants inoculated with strains interacting with the M, N or P2 genes. Leaves inoculated with a virulent strain of rust also had increased chitinase activity but the increase was much less than that found in leaves inoculated with the avirulent strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles FB, Bosshart RP, Forrence LE, Habig WH (1970) Preparation and purification of glucanase and chitinase from bean leaves. Plant Physiology 47, 129–134.
Coffey MD, Allen FHE (1983) A quantitative histological and ultrastructural analysis of interactions between the flax rust and near-isogenic host lines varying in their degree of incompatibility. Canadian Journal of Botany 61, 1831–1850.
Coffey MD, Cassidy DSM (1984) Peroxidase activity and induced lignification in rusted flax interactions varying in their degree of incompatibility. Canadian Journal of Botany 62, 134–141.
Ellis J, Lawrence G, Ayliffe M, Anderson P, Collins N, Finnegan J, Frost D, Luck J, Pryor T (1997) Advances in the molecular genetic analysis of the flax-flax rust interaction. Annual Review of Phytopathology 35, 271–291.
Flor HH (1956) The complementary genic systems in flax and flax rust. Advances in Genetics 8, 29–54.
Flor HH, Comstock VE (1971) Flax cultivars with multiple rustconditioning genes. Crop Science 11, 64–66.
Heath MC (1984) Relationship between heat-induced fungal death and plant necrosis in compatible and incompatible interactions involving the bean and cowpea rust fungi. Phytopathology 74, 1370–1376.
Keen NT, Littlefield LJ (1979) The possible association of phytoalexins with resistance gene expression in flax to Melampsora lini. Physiological Plant Pathology 14, 265–280.
Kobayashi I, Kobayashi Y, Hardham AR (1994) Dynamic reorganization of microtubules and microfilaments in flax cells during the resistance response to flax rust infection. Planta 195, 237–247.
Melchers LS, Stuiver MH (2000) Novel genes for disease-resistance breeding. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 3, 147–152.
Münch-Garthoff S, Neuhaus J-M, Boller T, Kemmerling B, Kogel K-H. (1997) Expression of β-1,3-glucanse and chitinase in healthy, stemrust-affected and elicitor-treated near-isogenic wheat lines showing Sr5- or Sr24-specified race-specific rust resistance. Planta 201, 235–244.
Sayler RJ, Ewing JD, McClean PE (1995) Monogenic and epistatic resistance to bean rust infection in common bean. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 47, 173–184.
Sutton BC, Shaw M (1986) Protein synthesis in flax following inoculation with flax rust. Canadian Journal of Botany 64, 13–18.
Wirth SJ, Wolf GA (1990) Dye-labelled substrates for the assay and detection of chitinase and lysozyme activity. Journal of Microbiological Methods 12, 197–205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McFadden, H.G., Lawrence, G.J. & Dennis, E.S. Differential induction of chitinase activity in flax (Linum usitatissimum) in response to inoculation with virulent or avirulent strains of Melampsora lini, the cause of flax rust. Australasian Plant Pathology 30, 27–30 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP00058
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP00058