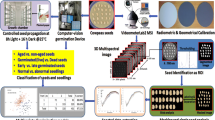
Abstract
The application of digital imaging information technology to seed germination testing is discussed. This technology is reviewed in light of recent interest on the development and adoption of sustainable agrosystems joined with a modern strategy of “precision agriculture”, which provides new complex information tools for better crop production. Basic concepts on the patterns of image analysis descriptors of imbibing seed performance are described with the objective of demonstrating the potential of this technique to be adequate for overcoming problems encountered with a standard seed germination test. The application of different image analysis system prototypes in monitoring seed germination of Brassica, as well as several other crop species, has provided encouraging results, highlighting the reliability of this technique to quickly acquire digital images and to extract numeric descriptors of germination and radicle growth events. Another aspect of digital imaging is the possibility to determine the colour space of a two-dimensional seed surface. Experiments carried out on lentil seed germination have shown that quantitative changes in Red-Green-Blue (RGB) colour component density may be considered as markers of the start of germination. In addition, the extracted RGB data may be used to trace a virtual three-dimensional surface plot allowing a better analysis of colour distribution on the lentil’s surface. RGB colour density can also be used to determine any variation in colour due to the ‘browning effect’ as a result of advancing seed deterioration. The potential of RGB markers in classifying sub-samples and maintaining high germination quality in aged seed samples represents a non-destructive method in seed testing and sorting. As a conclusion, the information flow deriving from digital image processing should be integrated with other bio-morphological, taxonomic and ‘omic-system’ databases. The final target should be an interrelated and complex database for a deeper functional and structural knowledge of plant species, which can respond to the needs of farmers, seed industries, biodiversity conservation and seed basic research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altieri M.A., Letourneau D.K., Davis J.R. (1983) Developing sustainable agroecosystems, Bioscience 33, 45–49.
Anquar F., Mannino M.R., Casals M.L., Fougereux J.A., Demilly D. (2001) Carrot seeds grading using a vision system, Seed Sci. Technol. 29, 215–225.
AOSA (2000) Rules for testing seeds, in: Association of Official Seed Analysts (Eds.).
Bewley J.D. (1997) Seed germination and dormancy, Plant Cell 9, 1055–1066.
Braga R., Dal Fabbro I.M., Borem F.M., Rabelao G., Arizaga R., Rabal H., Trivi M. (2003) Assessment of seed viability by laser speckle techniques, Biosyst. Eng. 86, 297–294.
Braga R., Rabelo G.F., Granato L.R., Santos E.F., Machado J.C., Arizaga R., Rabal H.J., Trivi M. (2005) Detection of fungi in beans by the laser biospeckle technique, Biosyst. Eng. 91, 465–469.
Chen P., Sun Z. (1991) A review of non-destructive methods for quality evaluation and sorting of agricultural products J. Agric. Eng. Res. 49, 85–98.
Clergue B., Amiaud B., Pervanchoon F., Laserre-Joulin F., Plantureux S. (2005) Biodiversity: function and assessment in agricultural areas. A review, Agron. Sustain. Dev. 25, 1–15.
Coen E., Rolland-lagan A.-G., Matthews M., Bangham J.A., Prusinkiewicz P. (2004) The genetics of geometry, PNAS 101, 4728–4735.
Cox S. (2002) Information technology: the global key to precision agriculture and sustainability, Comp. Electron. Agricult. 36, 93–111.
Daoust T., Fujimura K., McDonald M.B., Bennett M.A. (2005) A computer-based system for seed identification, Seed Technol. 27, 190–202.
Dell’Aquila A. (2003) Image analysis as a tool to study deteriorated cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) seed imbibition under salt stress conditions, Seed Sci. Technol. 31, 619–628.
Dell’Aquila A. (2004a) Cabbage, lentil, pepper and tomato seed germination monitored by an image analysis system, Seed Sci. Technol. 32, 225–229.
Dell’Aquila A. (2004b) Application of a computer-aided image analysis system to evaluate seed germination under different environmental conditions, It. J. Agron. 8, 51–62.
Dell’Aquila A. (2005) The use of image analysis to monitor the germination of seeds of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) and radish (Raphanus sativus L.), Ann. Appl. Biol. 146, 545–550.
Dell’Aquila A. (2006) Red-Green-Blue (RGB) colour density as a nondestructive marker in sorting deteriorated lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) seeds, Seed Sci. Technol. 34, 609–619.
Dell’Aquila A. (2007) Towards new computer imaging techniques applied to seed quality testing and sorting, Seed Sci. Technol. 38, 519–538.
Dell’Aquila A., van Eck J.W., van der Heijden G.W.A.M. (2000) The application of image analysis in monitoring the imbibition process of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) seeds, Seed Sci. Res. 10, 163–169.
Dell’Aquila A., van der Shoor R., Jalink H. (2002) Application of chlorophyll fluorescence in sorting controlled deteriorated white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) seeds, Seed Sci. Technol. 30, 689–695.
Ducournau S., Feutry A., Plainchault P., Revollon P., Vigouroux B., Wagner M.H. (2004) An image acquisition system for automated monitoring of the germination rate of sunflower seeds, Comp. Electron. Agric. 44, 189–202.
Ducournau S., Feutry A., Plainchault P., Revollon P., Vigouroux B. (2005) Using computer vision to monitor germination time course of sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) seeds, Seed Sci. Technol. 33, 329–340.
Ellis R.H., Roberts E.H. (1981) The quantification of ageing and survival in orthodox seeds, Seed Sci. Technol. 9, 373–409.
Fairchild M.D. (1998) Color appearance Models, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
Geneve R.L., Kester S.T. (2001) Evaluation of seedling size following germination using computer-aided analysis of digital images from a flat-bed scanner, Hort. Sci. 36, 1117–1120.
Granitto P.M., Navone H.D., Verdes P.F., Ceccato H.A. (2002) Weed seeds identification by machine vision, Comp. Electr. Agr. 33, 91–103.
Gupta M.L., George D.L., Basnet B.B. (2005) Seed identification using a computerised database, Seed Sci. Technol. 33, 647–654.
Hampton J.C. (1995) Methods of viability and vigour testing: a critical appraisal, in: Basra A.S. (Ed.), Seed Quality. Basic Mechanism and Agricultural Implications, Food Products Press, The Haworth Press, Inc. New York, pp. 81–118.
Howarth M.S., Stanwood P.C. (1993) Imaging techniques to enhance the preservation and utilization of seed germplasm J. Seed Technol. 17, 54–64.
ISTA (2005) International rules for seed testing, in: International Seed Testing association (Eds.).
Keefe P.D., Draper S.R. (1986) The measurement of new characters for cultivar identification in wheat using machine vision, Seed Sci. Technol. 14, 715–724.
Keys R.D. (1982) CASAS (computerized automated seed analysis system): an approach to the analysis and testing of seed J. Seed Technol. 7, 23–35.
Kruse M. (2000) The effect of moisture content on linear dimensions in cereal seeds measured by image analysis, Seed Sci. Technol. 28, 779–791.
Kurugollu F., Sankur B., Harmanci A.E. (2001) Color image segmentation using histogram multithresholding and fusion, Image Vision Comput. 19, 915–928.
Lew M., Sebe N., Huang T.S. (2007) The Age of human computer interaction, Image Vision Comput. 25, 1833–1835.
Loomis J.J., Fujimura K., McDonald M., James D., Bennett M. (1999) Using computer graphics for three-dimensional seed cataloguing, Seed Sci. Technol. 27, 439–446.
McCormac A.C., Keefe P.D. (1990) Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) seed vigour: imbibition effects J. Exp. Bot. 41, 893–899.
McDonald M.B., Evans A.F., Bennet M.A. (2001) Using scanner to improve seed and seedling evaluations, Seed Sci. Technol. 29, 683–689.
Oakley K., Kester S.T., Geneve R.L. (2004) Computer-aided digital image analysis of seedling size and growth rate assessing seed vigour in Impatiens, Seed Sci. Technol. 32, 837–845.
Peña-Barragán J.M., López-Granados F., García-Torres L., Jurado-Expósito M., de la Orden M.S., García-Ferrer A. (2008) Discriminatin cropping systems and agro-environmental measures by remote sensing, Agron. Sustain. Dev. 28, 355–362.
Pérez A.J., López F., Benlloch J.V., Christensen S. (1997) Colour and shape analysis techniques for weed detection in cereal fields, First European Conference for information Technology in Agriculture, Copenhagen, 15–18 June, pp. 45–50.
Priestley D.A. (1986) Morphological, structural, and biochemical changes associated with seed ageing, in: Priestley D.A. (Ed.), Seed Aging, Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London, pp. 125–195.
Prusinkiewicz P. (2004) Modelling plant growth and development, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7, 79–83.
Sako Y., McDonald M.B., Fujimura K., Evans A.F., Bennett M.A. (2001) A system for automated seed vigour assessment, Seed Sci. Technol. 29, 625–636.
Silk W.K. (1984) Quantitative descriptions of development, Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35, 479–418.
Sun W.Q., Leopold A.C. (1995) The Maillard reaction and oxidative stress during aging of soybean seeds, Physiol. Plant. 94, 94–104.
Sundblad L.-G., Geladi P., Dunberg A., Sundberg B. (1998) The use of image analysis and automation for measuring mitotic index in apical conifer meristems J. Exp. Bot. 49, 1749–1756.
Ureña R., Rodriguez F., Berenguel M. (2001) A machine vision system for seeds germination quality evaluation using fuzzy logic, Comp. Electron. Agric. 32, 1–20.
van der Heijden G.W.A.M, Polder, G., van Eck J.W., Jalink H., van der Shoor R. (1999) Automatic determination of germination of seeds, 1999 Word Seed Conference, 6–8 September 1999, Cambridge, UK, Programme & Abstract, p. 14
Wettlauer S.H., Leopold, A.C. (1991) Relevance of Amadori and Maillard products to seed deterioration, Plant Physiol. 97, 165–169.
Xu L., Fujimura K., McDonald M.B. (2007) Automatic separation of overlapping seedlings by network optimization, Seed Sci. Technol. 35, 337–350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
(former Senior Scientist of the Institute of Plant Genetics — CNR, Bari, Italy).
About this article
Cite this article
Dell’ Aquila, A. Digital imaging information technology applied to seed germination testing. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 29, 213–221 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2008039
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2008039