Abstract
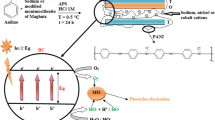
Optically responsive, luminescent Ni/Co/Ti layered double hydroxide (LDH), synthesized by a single step hydrothermal route, exhibits highly efficient photodegradation of cationic and anionic dyes, Rhodamine B (∼99.8%) and Acid Red G (∼99.6%) respectively, better than that of commercial catalysts like NiO, CoO and TiO2. The LDH has been characterized by using XRD, XPS, PL, TRES, EIS, TEM, SEM-EDX, AFM, UV-visible DRS, N2-sorption desorption, ξ-potential, FT-IR and TG techniques. The characterized results indicate that the LDH possesses hexagonal morphology, a high surface area, a narrow band gap, defect states and oxygen vacancies within its layered framework. The degradations follow the e−–h+ hopping pattern and dye-photosensitized mechanistic pathways. The active species generated during photocatalysis have been evaluated using ESR, terephthalic acid fluorescence probe and indirect radical–hole trapping experiments. The colourless end products were investigated by GC-MS and reaction mechanisms have been established for the degradation of the dyes to less toxic and more eco-friendly molecules than their parent analogues. Dye mineralization studies (performed using a TOC analyser) and closure of carbon mass balance experiments quantified the amount of carbon entering and leaving the reaction systems. Reaction mechanisms have been proposed on the basis of the asymmetric cleavage of the dyes. The LDH demonstrated its remarkable efficiency in the field of waste water treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 October 2020
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1039/d0pp90010a
References
N. Zhang, M. Q. Yang, S. Liu, Y. Sun and Y. J. Xu, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10307.
P. Roy Chowdhury and K. G. Bhattacharyya, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 112016.
B. Liu, K. Nakata, M. Sakai, H. Saito, T. Ochiai, T. Murakami, K. Takagi and A. Fujishima, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2, 1933.
G. Chen, S. Qian, X. Tu, X. Wei, J. Zou, L. Leng and S. Luo, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 293, 345.
S. Kim, J. Fahel, P. Durand, E. André and C. Carteret, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2017, 669.
Q. Wang and D. O’Hare, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 4124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Characterization, photoassisted degradations, mechanistic pathways and reaction mechanisms of degradations of the dyes with Ni/Co/Ti LDH. See DOI: 10.1039/c7pp00030h
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, P.R., Bhattacharyya, K.G. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Ni/Co/Ti layered double hydroxide for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B and Acid Red G: a comparative study. Photochem Photobiol Sci 16, 835–839 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00030h
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00030h