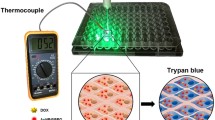
Abstract
Gold colloidal nanoparticles were prepared by the liquid laser ablation of a gold metal plate in water and also by the citratereduction of HAuCl4·4H2O. The gold colloidal nanoparticles with the plasmonic band strongly absorb light, which is converted to the photothermal energy. This photothermal energy gives a cytotoxic effect on epithelial carcinoma cells. Interestingly, we found that the size and shape of the nanoparticles are changed by light during the photothermal process in vitro. The cervical carcinoma cell line (HeLa cell) was incubated with the colloidal gold nanoparticles and then exposed to continuous visible light at 400–600 nm with UV- and heat-cutoff filters. The distinct cell-killing effect was observed by this procedure. In the absence of the gold colloidal nanoparticles, only a small amount of cells were photothermally destroyed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. E. McNeil, Nanotechnology for the biologist, J. Leukocyte Biol., 2005, 78, 585–594.
B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts and P. Walter, in Molecular biology of the cell, ed. S. Gibbs, Garland Science, Taylor & Francis Group, New York, 4th edn, 2002, pp. 616–619.
I. Brigger, C. Dubernet, P. Couvreur, Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2002, 54, 631–651.
Y. Matsumura, H. Maeda, A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs, Cancer Res., 1986, 46, 6387–6392.
D. R. Siwak, A. M. Tari, G. Lopez- Berestein, The potential of drug-carrying immunoliposomes as anticancer agents, Clin. Cancer Res., 2002, 8, 955–956.
N. Kohler, C. Sun, J. Wang, M. Zhan, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 8858–8864.
B. D. Chithrani, A. A. Ghazani, W. C. W. Chan, Nano Lett., 2006, 64, 662–668.
W. P. McConnell, J. P. Novak, L. C. Brousseau, R. R. Fuierer, R. C. Tenent, D. L. Feldheim, Electronic and optical properties of chemically modified metal nanoparticles and molecularly bridged nanoparticle arrays, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 8925–8930.
U. Kreibig and M. Vollmer, in Optical Properties of Metal Clusters, Springer Series in Materials Science 25, ed. H. K. V. Lotsch, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1995, pp. 14–21.
M. A. EI-Sayed, Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes, Acc. Chem. Res., 2001, 34, 257–264.
S. Link, M. A. El-Sayed, Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2003, 54, 331–366.
S. Link, M. A. El-Sayed, Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals, Int. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2000, 19, 409–453.
X. Huang, I. H. El-Sayed, W. Qian, M. A. El-Sayed;, Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 2115–2120.
D. O. Lapotko, E. Lukianova, A. A. Oraevsky, Selective laser nano-thermolysis of human leukemia cells with microbubbles generated around clusters of gold nanoparticles, Lasers Surg. Med., 2006, 38, 631–642.
H. Takahashi, T. Niidome, A. Nariai, Y. Niidome, S. Yamada, Gold nanorod-sensitized cell death: microscopic observation of single living cells irradiated by pulsed near-infrared laser light in the presence of gold nanorods, Chem. Lett., 2006, 35, 500–501.
G. Frens, Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions, Nature Phys. Sci., 1973, 241, 20–22.
C. F. Bohern and D. R. Huffman, Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. John Wiley, New York, 1983.
M. Kerker, in The Scattering of light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation, ed. Ernest M. Loebl, Academic Press, New York, 1969, pp. 27–93.
S. Link, M. B. Mohamed, M. A. El-Sayed, Simulation of the optical absorption spectra of gold nanorods as a function of their aspect ratio and the effect of the medium dielectric constant, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103, 3073–3077.
C. D. Wagner, W. M. Riggs, L. E. Davis, S. F. Moulder and G. E. Mullenberg, in Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, ed. G. E. Mullenberg, Perkin-Elmer Corporation Physical Electronics Division, New York, 1979, p. 154.
Z. P. Xu, Q. H. Zeng, G. Q. Lu, A. B. Yu, Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers for efficient cellular delivery, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2006, 61, 1027–1040.
I. H. El-Sayed, X. Huang, M. A. El-Sayed, Selective laser photo-thermal therapy of epithelial carcinoma using anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles, Cancer Lett., 2006, 239, 129–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulla-Al-Mamun, M., Kusumoto, Y., Mihata, A. et al. Plasmon-induced photothermal cell-killing effect of gold colloidal nanoparticles on epithelial carcinoma cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 8, 1125–1129 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b907524k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b907524k