Abstract
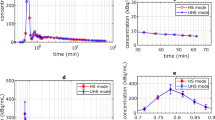
Dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) combined with the constant infusion of 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose (FDG) as a tracer permits real-time monitoring of systemic transient metabolic changes resulting from photodynamic therapy (PDT) in tumour bearing animals. The effect of PDT on tumour FDG uptake rates was evaluated using four different sulfonated phthalocyanine analogs as photosensitizers (PS) in combination with either continuous or fractionated illumination protocols. Mice bearing two EMT-6 tumours were infused with FDG to start PDT 30 min later. Dynamic images were acquired to produce FDG uptake over time for the treated and reference tumours. Practically all PDT protocols induced a reduction in the FDG uptake rates in the treated tumour during PDT, except for the zinc tetrasulfophthalocyanine, when using fractionated light, reflecting the low photodynamic efficacy of this PS. In general, the response to PDT was characterized by a rebound in the FDG uptake rate after illumination. A strong drop in FDG tumour uptake rates during PDT, followed by a strong rebound, together with short delay-to-response times, corresponded to optimal long-term tumour response outcomes. This dynamic FDG-PET protocol provides real-time observations to predict long-term PDT efficacy, while using fewer animals than conventional methods, thus making possible the rapid optimization of treatment parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Refernces
T. J. Dougherty, C. J. Gomer, B. W. Henderson, G. Jori, D. Kessel, M. Korbelik, J. Moan, Q. Peng, Photodynamic therapy, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 1988, 90, 889–905
E. J. Dennis, G. J. Dolmans, D. Fukumura, R. K. Jain, Photodynamic therapy for cancer, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2003, 3, 380–387
S. B. Brown, E. A. Brown, I. Walker, The present and future role of photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment, Lancet Oncol., 2004, 5, 497–508.
W. M. Sharman, C. M. Allen, J. E. van Lier, Photodynamic therapeutics: Basic principles and clinical applications, Drug Discovery Today, 1999, 4, 507–517.
W. M. Sharman, C. M. Allen, J. E. van Lier, Role of activated oxygen species in photodynamic therapy, Methods Enzymol., 2000, 319, 376–400
J. H. Woodhams, A. J. MacRobert, S. G. Bown, The role of oxygen monitoring during photodynamic therapy and its potential for treatment dosimetry, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2007, 6, 1246–1256.
E. Buytaert, M. Dewaele, P. Agostinis, Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Rev. Cancer, 2007, 1776, 86–107.
C. J. Gomer, A. Ferrario, M. Luna, N. Rucker, S. Wong, O. Bozkulak and F. Xu, Photodynamic therapy and the tumor micro-environment, in Handbook of Porphyrin Science: phototherapy, radioimmuno-therapy and imaging, ed. K. M. Kadish, K. M. Smith and R. Guilard, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2010, 4, pp. 425–441.
D. Preise, R. Oren, I. Glinert, V. Kalchenko, S. Jung, A. Scherz, Y. Salomon, Systemic antitumor protection by vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy involves cellular and humoral immunity, Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 2009, 58, 71–84
M. Firczuk, D. Nowis, J. Gołąb, PDT-induced inflammatory and host responses, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2011, 10, 653–663.
C. A. Robertson, D. H. Evans, H. Abrahamse, Photodynamic therapy (PDT): a short review on cellular mechanisms and cancer research applications for PDT, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2009, 96, 1–8.
B. W. Henderson, T. M. Busch, J. Snyder, Fluence rate as a modulator of PDT mechanisms, Lasers Surg. Med., 2006, 38, 489–493.
H. S. de Bruijn, E. R. de Haas, K. M. Hebeda, A. van der Ploeg-van den Heuvel, H. J. Sterenborg, H. A. Neumann, D. J. Robinson, Light fractionation does not enhance the efficacy of methyl 5-aminolevulinate mediated photodynamic therapy in normal mouse skin, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2007, 6, 1325–1331
M. Seshadri, D. A. Bellnier, L. A. Vaughan, J. A. Spernyak, R. Mazurchuk, T. H. Foster, B. W. Henderson, Light delivery over extended time periods enhances the effectiveness of photodynamic therapy, Clin. Cancer Res., 2008, 14, 2796–805
T. A. Middelburg, F. van Zaane, H. S. de Bruijn, A. van der Ploeg-van den Heuvel, H. J. Sterenborg, H. A. Neumann, E. R. de Haas, D. J. Robinson, Fractionated illumination at low fluence rate photo-dynamic therapy in mice, Photochem. Photobiol., 2010, 86, 1140–1146.
N. Cauchon, M. Nader, G. Bkaily, J. E. van Lier, D. Hunting, Photodynamic activity of substituted zinc trisulfo-phthalocyanines: role of plasma membrane damage, Photochem. Photobiol., 2006, 82, 1712–1720.
B. Krammer, Vascular effects of photodynamic therapy, Anticancer Res., 2001, 21, 4271–4277.
H. Ali, J. E. van Lier, Metal complexes as photo- and radiosensitizers, Chem. Rev., 1999, 99, 2379–2450
H. Ali and J. E. van Lier, Porphyrins and phthalocyanines as photo- and radiosensitizers, in Handbook of Porphyrin Science: phototherapy radioimmunotherapy and imaging, ed. K. M. Kadish, K. M. Smith and R. Guilard, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2010, 4, pp. 1–120.
Y. N. Konan, R. Gurny, E. Allémann, State of the art in the delivery of photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2002, 66, 89–106.
W. S. Chan, C. M. L. West, J. V. Moore, I. R. Hart, Phototoxic efficacy of sulphonated species of aluminium phthalocyanine against cell monolayers, multicellular spheroids and in vivo tumours, Br. J. Cancer, 1991, 64, 827–832
W. S. Chan, N. Brasseur, C. La Madeleine, J. E. van Lier, Evidence for different mechanisms of EMT-6 tumor necrosis by photodynamic therapy with disulfonated aluminum phthalocyanine or photofrin: tumor cell survival and blood flow, Anticancer Res., 1996, 16, 1887–1892
W. S. Chan, N. Brasseur, C. La Madeleine, R. Ouellet, J. E. van Lier, Efficacy and mechanism of aluminium phthalocyanine and its sulfonated derivatives mediated photodynamic therapy on murine tumours, Eur. J. Cancer, 1997, 33, 1855–1859.
V. H. Fingar, T. J. Wieman, P. S. Karavolos, K. W. Doak, R. Ouellet, J. E. van Lier, The effects of photodynamic therapy using differently substituted zinc phthalocyanines on vessel constriction, vessel leakage and tumor response, Photochem. Photobiol., 1993, 58, 251–258
H. L. L. M. van Leengoed, N. von der Veen, A. A. C. Versteeg, R. Ouellet, J. E. van Lier, W. M. Star, In vivo photodynamic effects of phthalocyanines in a skin-fold observation chamber model: Role of central metal ion and degree of sulfonation, Photochem. Photobiol., 1993, 58, 575–580.
N. Cauchon, H. Tian, R. Langlois, C. La Madeleine, S. Martin, H. Ali, D. Hunting, J. E. van Lier, Structure–photodynamic activity relationships of substituted zinc trisulfophthalocyanines, Bioconjugate Chem., 2005, 16, 80–89
N. Cauchon, H. Ali, H. M. Hasséssian, J. E. van Lier, Structure–activity relationships of mono-substituted trisulfonated porphyrazines for the photodynamic therapy (PDT) of cancer, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, 9, 331–341.
D. Lapointe, N. Brasseur, J. Cadorette, S. Rodrigue, J. E. van Lier, R. Lecomte, High-resolution PET imaging for in vivo monitoring of tumor response after photodynamic therapy in mice, J. Nucl. Med., 1999, 40, 876–882.
V. Bérard, J. A. Rousseau, J. Cadorette, L. Hubert, M. Bentourkia, J. E. van Lier, R. Lecomte, Dynamic imaging of transient metabolic processes by small-animal PET for the evaluation of photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy of cancer, J. Nucl. Med., 2006, 47, 1119–1126.
N. L. Oleinick, R. L. Morris, I. Belichenko, The role of apoptosis in response to photodynamic therapy: what, where, why, and how, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2002, 1, 1–21
N. Cauchon, R. Langlois, J. A. Rousseau, G. Tessier, J. Cadorette, R. Lecomte, D. J. Hunting, R. A. Pavan, S. K. Zeisler, J. E. van Lier, PET imaging of apoptosis with (64)Cu-labeled streptavidin following pretargeting of phosphatidylserine with biotinylated annexin-V, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging, 2006, 34, 247–258.
R. Kubota, S. Yamamda, K. Kubota, K. Ishiwata, N. Tamahashi, T. Ido, Intratumoral distribution of fluorin-18-fluorodeosyglucose in vivo; high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissues studied by microauto-radiography, J. Nucl. Med., 1992, 33, 1972–1980.
H. Ali, R. Langlois, R. Wagner, N. Brasseur, B. Paquette, J. E. van Lier, Biological activities of phthalocyanines-X: syntheses and analyses of sulfonated phthalocyanines, Photochem. Photobiol., 1988, 47, 713–717
E. R. Ranyuk, N. Cauchon, H. Ali, R. Lecomte, B. Guérin, J. E. van Lier, PET imaging using 64Cu-labeled sulfophthalocyanines: Synthesis and biodistribution, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 7470–7473.
H. Tian, H. Ali, J. E. van Lier, Synthesis of water soluble trisulfonated phthalocyanines via palladium catalysed cross coupling reactions, Tetrahedron Lett., 2000, 41, 8435–8438.
M. S. O’Reilly, L. Holmgren, C. Chen, J. Folkman, Angio-statin induces and sustains dormancy of human primary tumors in mice, Nat. Med., 1996, 2, 689–692.
K. Hamacher, H. H. Coenen, G. Stocklin, Efficient stereo-specific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution, J. Nucl. Med., 1986, 27, 235–238.
M. Bergeron, J. Cadorette, J. F. Beaudoin, M. D. Lepage, G. Robert, V. Selivanov, M. A. Tétrault, N. Viscogliosi, J. P. Noremberg, R. Fontaine, R. Lecomte, Performance evaluation of the LabPET (APD-based digital PET) scanner, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2009, 56, 10–16.
V. Selivanov, Y. Picard, J. Cadorette, S. Rodrigue, R. Lecomte, Detector response models for statistical iterative image reconstruction in high resolution PET, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2000, 47, 1168–1175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cauchon, N., Turcotte, E., Lecomte, R. et al. Predicting efficacy of photodynamic therapy by real-time FDG-PET in a mouse tumour model. Photochem Photobiol Sci 11, 364–370 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1pp05294b
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c1pp05294b