Abstract
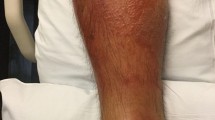
The rise of multiply antibiotic resistant bacteria has led to searches for novel antimicrobial therapies to treat infections. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a potential candidate; it uses the combination of a photosensitizer with visible light to produce reactive oxygen species that lead to cell death. We used PDT mediated by meso-mono-phenyl-tri(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)-porphyrin (PTMPP) to treat burn wounds in mice with established Staphylococcus aureus infections The third degree burn wounds were infected with bioluminescent S. aureus. PDT was applied after one day of bacterial growth by adding a 25% DMSO/500 µM PTMPP solution to the wound followed by illumination with red light and periodic imaging of the mice using a sensitive camera to detect the bioluminescence. More than 98% of the bacteria were eradicated after a light dose of 210 J cm−2 in the presence of PTMPP. However, bacterial re-growth was observed. Light alone or PDT both delayed the wound healing. These data suggest that PDT has the potential to rapidly reduce the bacterial load in infected burns. The treatment needs to be optimized to reduce wound damage and prevent recurrence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Coates, C. A. Adams, W. J. Cunliffe, K. T. McGinley, E. A. Eady, J. J. Leyden, J. Ravenscroft, S. Vyakrnam, B. Vowels, Does oral isotretinoin prevent Propionibacterium acnes resistance?, Dermatology, 1997, 195Suppl. 1, 4–9
P. Coates, C. A. Adams, W. J. Cunliffe, K. T. McGinley, E. A. Eady, J. J. Leyden, J. Ravenscroft, S. Vyakrnam, B. Vowels, Discussion of ‘Does oral isotretinoin prevent Propionibacterium acnes resistance?’, Dermatology, 1997, 195Suppl. 1, 38–40.
J. I. Ross, A. M. Snelling, E. Carnegie, P. Coates, W. J. Cunliffe, V. Bettoli, G. Tosti, A. Katsambas, J. I. Galvan Perez Del Pulgar, O. Rollman, L. Torok, E. A. Eady, J. H. Cove, Antibiotic-resistant acne: lessons from Europe, Br. J. Dermatol., 2003, 148, 467–478.
T. D. Wyatt, W. P. Ferguson, T. S. Wilson, E. McCormick, Gentamicin resistant Staphylococcus aureus associated with the use of topical gentamicin, J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 1977, 3, 213–217.
A. P. Castano, T. N. Demidova, M. R. Hamblin, Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: part one-photosensitizers, photochemistry and cellular localization, Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther., 2004, 1, 279–293.
T. N. Demidova, M. R. Hamblin, Photodynamic therapy targeted to pathogens, Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol., 2004, 17, 245–254.
M. R. Hamblin, T. Hasan, Photodynamic therapy: a new antimicrobial approach to infectious disease?, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2004, 3, 436–450.
H. Ashkenazi, Y. Nitzan, D. Gal, Photodynamic effects of antioxidant substituted porphyrin photosensitizers on gram-positive and -negative bacterial, Photochem. Photobiol., 2003, 77, 186–191.
Z. Malik, J. Hanania, Y. Nitzan, Bactericidal effects of photoactivated porphyrins—an alternative approach to antimicrobial drugs, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 1990, 5, 281–293.
M. Soncin, C. Fabris, A. Busetti, D. Dei, D. Nistri, G. Roncucci, G. Jori, Approaches to selectivity in the Zn(ii)-phthalocyanine-photosensitized inactivation of wild-type and antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2002, 1, 815–819.
M. Wainwright, D. A. Phoenix, S. L. Laycock, D. R. Wareing, P. A. Wright, Photobactericidal activity of phenothiazinium dyes against methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1998, 160, 177–81.
F. M. Lauro, P. Pretto, L. Covolo, G. Jori, G. Bertoloni, Photoinactivation of bacterial strains involved in periodontal diseases sensitized by porphycene–polylysine conjugates, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2002, 1, 468–470.
V. Edwards-Jones, J. E. Greenwood, M. B. R. Group, What’s new in burn microbiology? James Laing Memorial Prize Essay 2000, Burns, 2003, 29, 15–24.
B. A. Pruitt, Jr., A. T. McManus, S. H. Kim, C. W. Goodwin, Burn wound infections: current status, World J. Surg., 1998, 22, 135–145.
A. J. Singer, S. A. McClain, Persistent wound infection delays epidermal maturation and increases scarring in thermal burns, Wound Repair Regen., 2002, 10, 372–377.
N. Cook, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusversus the burn patient, Burns, 1998, 24, 91–98.
N. Komerik, H. Nakanishi, A. J. MacRobert, B. Henderson, P. Speight, M. Wilson, In vivo killing of Porphyromonas gingivalis by toluidine blue-mediated photosensitization in an animal model, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2003, 47, 932–940.
A. Orenstein, D. Klein, J. Kopolovic, E. Winkler, Z. Malik, N. Keller, Y. Nitzan, The use of porphyrins for eradication of Staphylococcus aureus in burn wound infections, FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol., 1997, 19, 307–14.
M. R. Hamblin, T. Zahra, C. H. Contag, A. T. McManus, T. Hasan, Optical monitoring and treatment of potentially lethal wound infections in vivo, J. Infect. Dis., 2003, 187, 1717–1726.
K. P. Francis, D. Joh, C. Bellinger-Kawahara, M. J. Hawkinson, T. F. Purchio, P. R. Contag, Monitoring bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus infections in living mice using a novel luxABCDE construct, Infect. Immun., 2000, 68, 3594–600.
T. C. Doyle, S. M. Burns, C. H. Contag, In vivo bioluminescence imaging for integrated studies of infection, Cell. Microbiol., 2004, 6, 303–317.
K. P. Francis, J. Yu, C. Bellinger-Kawahara, D. Joh, M. J. Hawkinson, G. Xiao, T. F. Purchio, M. G. Caparon, M. Lipsitch, P. R. Contag, Visualizing pneumococcal infections in the lungs of live mice using bioluminescent Streptococcus pneumoniae transformed with a novel gram-positive lux transposon, Infect. Immun., 2001, 69, 3350–8.
N. A. Kuklin, G. D. Pancari, T. W. Tobery, L. Cope, J. Jackson, C. Gill, K. Overbye, K. P. Francis, J. Yu, D. Montgomery, A. S. Anderson, W. McClements, K. U. Jansen, Real-time monitoring of bacterial infection in vivo: development of bioluminescent staphylococcal foreign-body and deep-thigh-wound mouse infection models, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2003, 47, 2740–2748.
J. L. Kadurugamuwa, L. V. Sin, J. Yu, K. P. Francis, T. F. Purchio, P. R. Contag, Noninvasive optical imaging method to evaluate postantibiotic effects on biofilm infection in vivo, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2004, 48, 2283–2287.
J. L. Kadurugamuwa, L. Sin, E. Albert, J. Yu, K. Francis, M. DeBoer, M. Rubin, C. Bellinger-Kawahara, T. R. Parr, Jr., P. R. Contag, Direct continuous method for monitoring biofilm infection in a mouse model, Infect. Immun., 2003, 71, 882–890.
T. G. Smijs, H. J. Schuitmaker, Photodynamic inactivation of the dermatophyte Trichophyton rubrum, Photochem. Photobiol., 2003, 77, 556–560.
S. A. Lambrechts, M. C. Aalders, D. H. Langeveld-Klerks, Y. Khayali, J. W. Lagerberg, Effect of monovalent and divalent cations on the photoinactivation of bacteria with meso-substituted cationic porphyrins, Photochem. Photobiol., 2004, 79, 297–302.
M. Merchat, J. D. Spikes, G. Bertoloni, G. Jori, Studies on the mechanism of bacteria photosensitization by meso-substituted cationic porphyrins, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 1996, 35, 149–57.
L. L. Trannoy, J. W. Lagerberg, T. M. Dubbelman, H. J. Schuitmaker, A. Brand, Positively charged porphyrins: a new series of photosensitizers for sterilization of RBCs, Transfusion, 2004, 44, 1186–1196.
C. P. Sawhney, R. K. Sharma, K. R. Rao, R. Kaushish, Long-term experience with 1 per cent topical silver sulfadiazine cream in the management of burn wounds, Burns, 1989, 15, 403–6.
Q. L. Feng, J. Wu, G. Q. Chen, F. Z. Cui, T. N. Kim, J. O. Kim, A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2000, 52, 662–668.
A. B. Lansdown, Silver. I: Its antibacterial properties and mechanism of action, J. Wound Care, 2002, 11, 125–130.
B. D. Jett, K. L. Hatter, M. M. Huycke, M. S. Gilmore, Simplified agar plate method for quantifying viable bacteria, Biotechniques, 1997, 23, 648–50.
N. A. Busch, E. M. Zanzot, P. M. Loiselle, E. A. Carter, J. E. Allaire, M. L. Yarmush, H. S. Warren, A model of infected burn wounds using Escherichia coli O18:K1:H7 for the study of gram-negative bacteremia and sepsis, Infect. Immun., 2000, 68, 3349–51.
D. A. Gilpin, Calculation of a new Meeh constant and experimental determination of burn size, Burns, 1996, 22, 607–611.
M. R. Hamblin, D. A. O’Donnell, N. Murthy, C. H. Contag, T. Hasan, Rapid control of wound infections by targeted photodynamic therapy monitored by in vivo bioluminescence imaging, Photochem. Photobiol., 2002, 75, 51–7.
A. C. Williams, B. W. Barry, Penetration enhancers, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2004, 56, 603–618.
Z. Malik, G. Kostenich, L. Roitman, B. Ehrenberg, A. Orenstein, Topical application of 5-aminolevulinic acid, DMSO and EDTA: protoporphyrin IX accumulation in skin and tumours of mice, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 1995, 28, 213–218.
F. S. De Rosa, J. M. Marchetti, J. A. Thomazini, A. C. Tedesco, M. V. Bentley, A vehicle for photodynamic therapy of skin cancer: influence of dimethylsulfoxide on 5-aminolevulinic acid in vitro cutaneous permeation and in vivo protoporphyrin IX accumulation determined by confocal microscopy, J. Control. Release, 2000, 65, 359–366.
C. Lucas, L. J. Criens-Poublon, C. T. Cockrell, R. J. de Haan, Wound healing in cell studies and animal model experiments by Low Level Laser Therapy; were clinical studies justified? A systematic review, Lasers Med. Sci., 2002, 17, 110–134.
A. Kubler, R. K. Finley, 3rd, I. A. Born, T. S. Mang, Effect of photodynamic therapy on the healing of a rat skin flap and its implication for head and neck reconstructive surgery, Lasers Surg. Med., 1996, 18, 397–405.
R. S. Jayasree, A. K. Gupta, K. Rathinam, P. V. Mohanan, M. Mohanty, The influence of photodynamic therapy on the wound healing process in rats, J. Biomater. Appl., 2001, 15, 176–186.
F. Gad, T. Zahra, K. P. Francis, T. Hasan, M. R. Hamblin, Targeted photodynamic therapy of established soft-tissue infections in mice, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2004, 3, 451–458.
K. Kassab, C. Fabris, M. P. Defilippis, D. Dei, L. Fantetti, G. Roncucci, E. Reddi, G. Jori, Skin-photosensitizing properties of Zn(ii)-2(3),9(10),16(17),23(24)-tetrakis-(4-oxy-N-methylpiperidinyl) phthalocyanine topically administered to mice, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2000, 55, 128–37.
B. W. Henderson, T. J. Dougherty, How does photodynamic therapy work?, Photochem. Photobiol., 1992, 55, 145–57.
M. R. Thissen, M. W. de Blois, D. J. Robinson, H. S. de Bruijn, R. P. Dutrieux, W. M. Star, H. A. Neumann, PpIX fluorescence kinetics and increased skin damage after intracutaneous injection of 5-aminolevulinic acid and repeated illumination, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2002, 118, 239–245.
C. G. Mayhall, The epidemiology of burn wound infections: then and now, Clin. Infect. Dis., 2003, 37, 543–550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambrechts, S.A.G., Demidova, T.N., Aalders, M.C.G. et al. Photodynamic therapy for Staphylococcus aureus infected burn wounds in mice. Photochem Photobiol Sci 4, 503–509 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1039/b502125a
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b502125a